|
Saqqara
Saqqara ( : saqqāra[t], ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in the markaz (county) of Badrashin in the Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis, Egypt, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Pyramid, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty of Egypt, Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire History of ancient Egypt, Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serapeum Of Saqqara
The Serapeum of Saqqara was the ancient Egyptian burial place for sacred bulls of the Apis cult at Memphis. It was believed that the bulls were incarnations of the god Ptah, which would become immortal after death as ''Osiris-Apis'', a name which evolved to ''Serapis ('') in the Hellenistic period, and ''Userhapi'' () in Coptic. It is one of the animal catacombs in the Saqqara necropolis, which also contains the burial vaults of the mother cows of the Apis, the Iseum. Over a timespan of approximately 1400 years, from the New Kingdom of Egypt to the end of the Ptolemaic Period, at least sixty Apis are attested to have been interred at the Serapeum. For the earliest burials, isolated tombs were constructed. As the cult gained importance, underground galleries were dug that connected subsequent burial chambers. Above ground, the main temple enclosure was supplemented by shrines, workshops, housing and administrative quarters. From the Late Period onward, most Apis were bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
Memphis (, ; Bohairic ; ), or Men-nefer, was the ancient capital of Inebu-hedj, the first Nome (Egypt), nome of Lower Egypt that was known as ''mḥw'' ("North"). Its ruins are located in the vicinity of the present-day village of Mit Rahina (), in markaz (county) Badrashin, Giza, Egypt. Along with the Memphite Necropolis, pyramid fields that stretch on a desert plateau for more than on its west, including the famous Giza pyramid complex, Pyramids of Giza, Memphis and its necropolis have been listed as a World Heritage Site. The site is open to the public as an open-air museum. According to legends related in the early third century BC by Manetho, a priest and historian who lived in the Ptolemaic Kingdom during the Hellenistic period of ancient Egypt, the city was founded by Pharaoh, King Menes. It was the List of Egyptian capitals, capital of ancient Egypt (''Kemet'' or ''Kumat'') during both the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt, Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom and remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortuary Complex Of Pepi I
The pyramid of Pepi I (in Egyptian language, ancient Egyptian Men-nefer-Pepi meaning Pepi's splendour is enduring) is the pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Pepi I of the Sixth Dynasty of Egypt, Sixth Dynasty in the 24th century BC, 24th or 23rd century BC, 23rd century BC. The complex gave its name to the capital city of Egypt, Memphis, Egypt, Memphis. As in the pyramids of his predecessors, Pepi I's substructure was filled with vertical columns of hieroglyphic texts, Pyramid Texts. It was in Pepi I's pyramid that these texts were initially discovered in 1880 by Gaston Maspero, though they originated in the pyramid of Unas. The corpus of Pepi I's texts is also the largest from the Old Kingdom, comprising 2,263 columns and lines of hieroglyphs. Pepi I sited his pyramid complex in Saqqara, South Saqqara an approximate north of Pyramid of Djedkare Isesi, Djedkare Isesi's pyramid. It is unclear why Pepi I relocated to South Saqqara. Perhaps Pepi I had moved the royal pal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
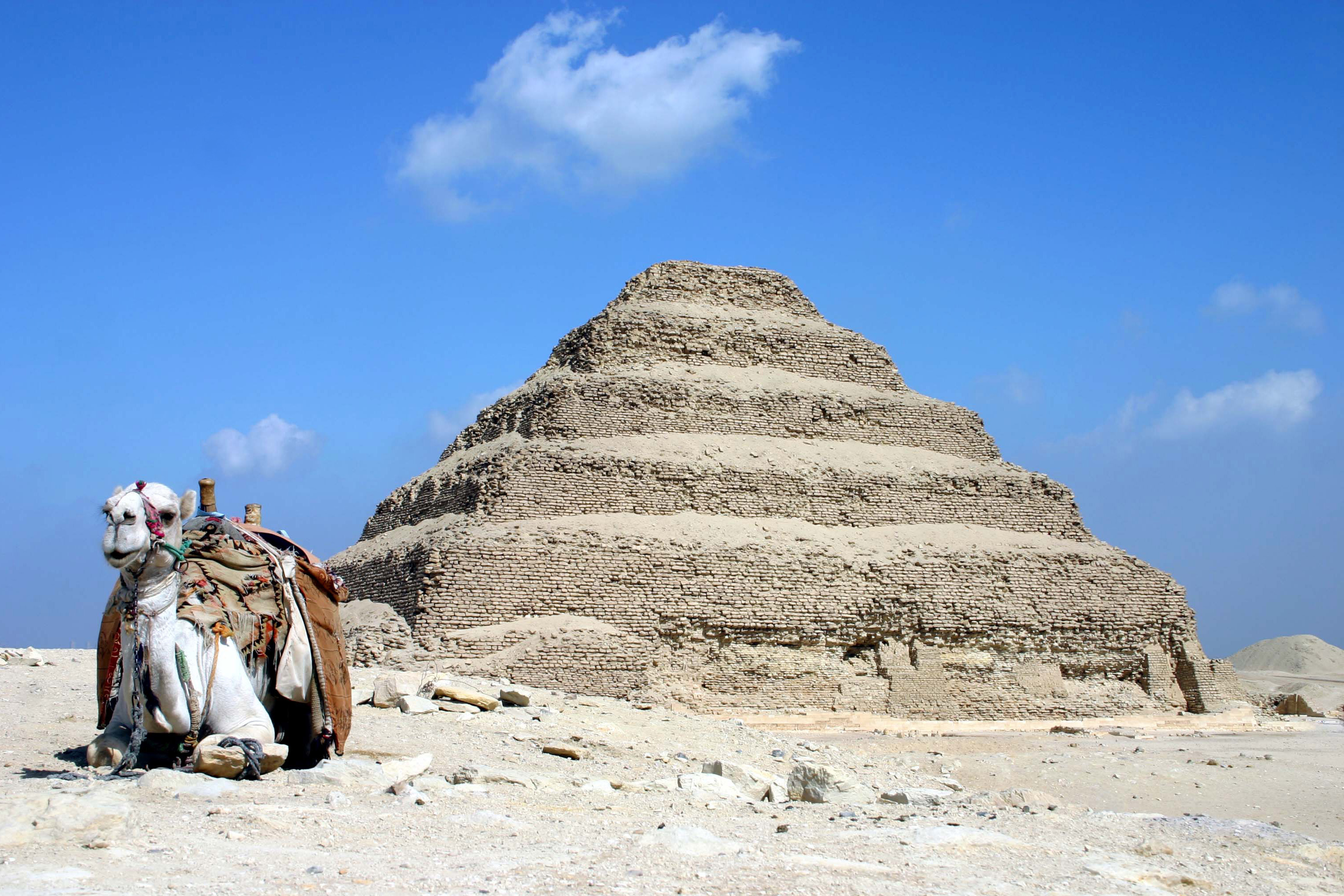
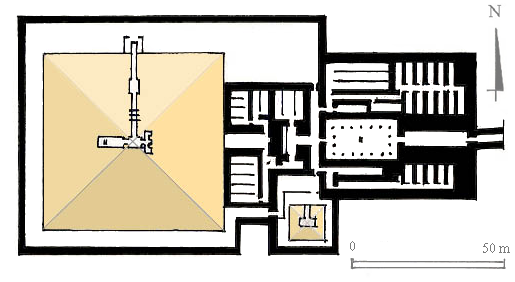
Pyramid Of Djoser
The pyramid of Djoser, sometimes called the Step Pyramid of Djoser or Step Pyramid of Horus Netjerikhet, is an archaeological site in the Saqqara necropolis, Egypt, northwest of the ruins of Memphis.Bard, Kathryn A., and Jean-Philipee Lauer, eds. 1999. "Saqqara, pyramids of the 3rd Dynasty" ''Encyclopedia of the Archaeology of Ancient Egypt''. London: Routledge. 859 It is the first Egyptian pyramid to be built. The 6-tier, 4-sided structure is the earliest colossal stone building in Egypt. It was built in the 27th century BC during the Third Dynasty for the burial of Pharaoh Djoser. The pyramid is the central feature of a vast mortuary complex in an enormous courtyard surrounded by ceremonial structures and decoration. The pyramid went through several revisions and redevelopments of the original plan. The pyramid originally stood tall, with a base of and was clad in polished white limestone. As of 1997 the step pyramid (or proto-pyramid) was considered to be the earliest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Unas
The pyramid of Unas (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''Nfr swt Wnjs'' "Beautiful are the places of Unas") is a smooth-sided pyramid built in the 24th century BC for the Egyptian pharaoh Unas, the ninth and final king of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, Fifth Dynasty. It is the smallest Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom pyramid, but significant due to the discovery of Pyramid Texts, spells for the king's afterlife incised into the walls of its subterranean chambers. Inscribed for the first time in Unas's pyramid, the tradition of Ancient Egyptian funerary texts, funerary texts carried on in the pyramids of subsequent rulers, through to the end of the Old Kingdom, and into the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom through the Coffin Texts that form the basis of the ''Book of the Dead''. Unas built his pyramid between the complexes of Buried Pyramid, Sekhemket and Step Pyramid of Djoser, Djoser, in North Saqqara. Anchored to the valley temple at a nearby lake, a long causeway was construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Djedkare Isesi
The pyramid of Djedkare Isesi (in ancient Egyptian ''Nfr Ḏd-kꜣ-rꜥ'' ("Beautiful is Djedkare")) is a late 25th to mid 24th century BC pyramid complex built for the Fifth Dynasty pharaoh Djedkare Isesi. The pyramid is referred to as ''Haram el-Shawaf'' () by locals. It was the first pyramid to be built in South Saqqara. Djedkare Isesi's monument complex encompasses: a main pyramid; a mortuary temple situated on the east face of the main pyramid; a valley temple buried under modern Saqqara; a causeway that has been only partially dug out; and a cult pyramid. The main pyramid had a six-stepped core built from roughly cut limestone bound together by clay mortar which was then encased in fine white Tura limestone reaching a peak height of . The casing has been plundered, and the top three steps of the core have been lost, leaving the pyramid a paltry tall. The basic dimensions of Djedkare's pyramid were adopted by succeeding kings in their own funerary monuments. Inside Djedka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Userkaf
The pyramid complex of Userkaf was built c. 2490 BC for the king Userkaf, founder of the Fifth Dynasty of Egypt, 5th Dynasty of Egypt (c. 2494–2345 BC). It is located in the Egyptian pyramids, pyramid field at Saqqara, on the north-east of the Pyramid of Djoser, step pyramid of Djoser. Constructed in dressed stone with a core of rubble, the pyramid is now ruined and resembles a conical hill in the sands of Saqqara.Mark Lehner, ''The Complete Pyramids'', Thames & Hudson, , p. 140 For this reason, it is known locally as ''El-Haram el-Maharbish'', the "Heap of Stone",Jean-Phillipe Lauer (in French): ''Saqqarah, Une vie, Entretiens avec Phillipe Flandrin'', Petite Bibliotheque Payot 107, 1988, and was recognized as a royal pyramid by western archaeologists in the 19th century. Userkaf's pyramid is part of a larger mortuary complex comprising a mortuary temple, an offering chapel and a cult pyramid as well as separate pyramid and mortuary temple for Userkaf's wife, queen N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Fields From Giza To Dahshur
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Most were built as tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. At least 138 identified pyramids have been discovered in Egypt. Approximately 80 pyramids were built within the Kingdom of Kush, now located in the modern country of Sudan. The earliest known Egyptian pyramids are at Saqqara, west of Memphis. Step-pyramid-like structures, like Mastaba 3808 attributed to pharaoh Anedjib, may predate the Pyramid of Djoser built during the Third Dynasty. This pyramid and its surrounding complex are generally considered to be the world's oldest monumental structures constructed of dressed masonry. The most famous Egyptian pyramids are those found at Giza, on the outskirts of Cairo. Several of the Giza pyramids are counted among the largest structures ever built. The Pyramid of Khufu is the largest Egyptian pyramid and the last of the Seven Wonders of the Ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Teti
The pyramid of Teti is a smooth-sided pyramid situated in the pyramid field at Saqqara in Egypt which belonged to Teti, founder of the sixth dynasty of Egypt. It is the second known pyramid containing pyramid texts. Excavations have revealed a satellite pyramid, two pyramids of queens accompanied by cult structures, and a funerary temple. The pyramid was opened by Gaston Maspero in 1882 and the complex explored during several campaigns ranging from 1907 to 1965. It was originally called ''Teti's Places Are Enduring''. The preservation above ground is very poor, and it now resembles a small hill. Below ground the chambers and corridors are very well preserved. The funerary complex The pyramid complex of Teti follows a model established during the reign of Djedkare Isesi, the arrangement of which is inherited from the funerary complexes of Abusir. A valley temple, now lost, was probably destroyed in antiquity due to the place of an Old Kingdom temple dedicated to Anubis construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gisr El-Mudir
Gisr el-Mudir (Arabic:جسر المدير, "bridge of the chief"), also known as the Great Enclosure, is one of the oldest known stone structures in Egypt, located at Saqqara only a few hundred metres west of the Step Pyramid and the Buried Pyramid. The function of the space is not yet clear. Description The structure consists of a rectangular wall oriented north-south and measuring about 650 by 350 metres. The walls consist of two outer walls made of roughly hewn limestone about 15 metres apart; the space between them is filled with crushed stone, gravel and sand. In the northwestern corner, the walls survive to a height of 4.5 to 5 metres (over 15 courses of stone). The style of construction suggests an original height of around 10 metres. In the south the state of preservation is clearly worse than in the north. Since the west wall of the structure is 30 metres shorter than the east, the south wall probably consisted of two parallel walls forming an entranceway. This pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Dynasty Of Egypt
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis. Overview After the turbulent last years of the Second Dynasty, which might have included civil war, Egypt came under the rule of Djoser, marking the beginning of the Third Dynasty.Dodson, Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', 2004 Both the Turin King List and the Abydos King List record five kings,Toby A.H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge, 2001 while the Saqqara Tablet only records four, and Manetho records nine,Aidan Dodson: ''The Layer Pyramid of Zawiyet el-Aryan: Its Layout and Context.'' In: ''Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt (JARCE)'', No. 37 (2000). American Research Center (Hg.), Eisenbrauns, Winona Lake/Bristol 2000, , pp. 81–90. many of whom did not exist or are simply the same king und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Akhethetep
The Tomb of Akhethetep, also known as Mastaba of Akhethetep (), is a tomb complex in Saqqara, Egypt. It was built for Akhethetep, a royal official, near the western part of the Pyramid of Djoser. Akhethetep was an official with several, mainly religious titles, including ''priest of Heka'', ''priest of Khnum'' and ''priest of Horus''. The tomb's decorated chapel was removed in 1903 and reassembled at the Louvre in Paris, where it is also known as the "Mastaba of Akhethetep" or simply "". History The tomb was discovered in 1903 by a team of Georges Aaron Bénédite, Curator of the Louvre's Egyptian Department, Hilda Petrie, and Margaret Murray. In line with Egypt's policy at the time, the Louvre was allowed to buy the entire chapel, and relocate and reassemble it to Paris. The chapel was initially displayed in 1905 in the ground floor of the in the Denon (South) Wing of the Louvre Palace, which the museum had recently taken over from non-museum users. It was then moved in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |