|
Saccade
In vision science, a saccade ( ; ; ) is a quick, simultaneous movement of both Eye movement (sensory), eyes between two or more phases of focal points in the same direction. In contrast, in Smooth pursuit, smooth-pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for focal points, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic reflex, optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Louis Émile Javal, Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements. Function Humans and many organisms do not look at a scene in steadiness; instead, the eyes move around, locating interesting parts of the scene and building up a three-dimensional 'map' corresponding to the scen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsaccade
Microsaccades are a kind of fixational eye movement. They are small, jerk-like, involuntary eye movements, similar to miniature versions of voluntary saccades. They typically occur during prolonged visual fixation (of at least several seconds), not only in humans, but also in animals with foveal vision (primates, cats, dogs etc.). Microsaccade amplitudes vary from 2 to 120 arcminutes. The first empirical evidence for their existence was provided by Robert Darwin, the father of Charles Darwin. Function The role of microsaccades in visual perception has been a highly debated topic that is still largely unresolved. It has been proposed that microsaccades correct displacements in eye position produced by drifts, although non-corrective microsaccades also occur. Some work has suggested that microsaccades are directly correlated with the perception of illusory motion. Although microsaccades can enhance vision of fine spatial detail, they can also impair visual perception in that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
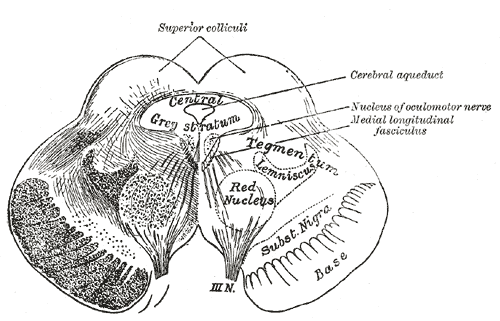
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the tectum, roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the Homology (biology), homologous structure is known as the optic tectum or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectum, tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar in all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers (retinal nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research on the visual system, in psychology, in psycholinguistics, marketing, as an input device for human-computer interaction, and in product design. In addition, eye trackers are increasingly being used for assistive and rehabilitative applications such as controlling wheelchairs, robotic arms, and prostheses. Recently, eye tracking has been examined as a tool for the early detection of autism spectrum disorder. There are several methods for measuring eye movement, with the most popular variant using video images to extract eye position. Other methods use search coils or are based on the electrooculogram. History In the 1800s, studies of eye movement were made using direct observations. For example, Louis Émile Javal observed in 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
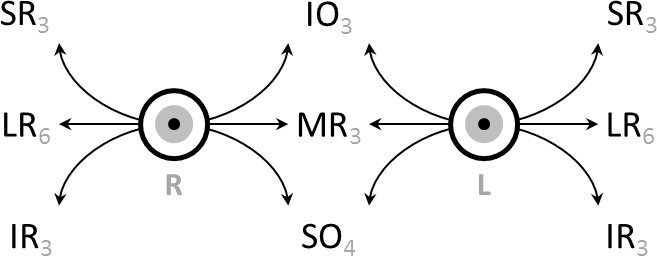
Eye Movement (sensory)
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep. The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex. Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit, vergence shifts and saccades. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe. This is corroborated by removal of the fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Movements
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms (e.g. primates, rodents, flies, birds, fish, cats, crabs, octopus) to fixate, inspect and track visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep. The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex. Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit, vergence shifts and saccades. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe. This is corroborated by removal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Pursuit
In the scientific study of vision, smooth pursuit describes a type of eye movement in which the eyes remain fixated on a moving object. It is one of two ways that visual animals can voluntarily shift gaze, the other being saccadic eye movements. Pursuit differs from the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which only occurs during movements of the head and serves to stabilize gaze on a stationary object. Most people are unable to initiate pursuit without a moving visual signal. The pursuit of targets moving with velocities of greater than 30°/s tends to require catch-up saccades. Smooth pursuit is asymmetric: most humans and primates tend to be better at horizontal than vertical smooth pursuit, as defined by their ability to pursue smoothly without making ''catch-up saccades''. Most humans are also better at downward than upward pursuit. Pursuit is modified by ongoing visual feedback. Measurement There are two basic methods for recording smooth pursuit eye movements, and eye movement in g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listing's Law
Listing's law, named after German mathematician Johann Benedict Listing (1808–1882), describes the three-dimensional orientation of the eye and its axes of rotation. Listing's law has been shown to hold when the head is stationary and upright and gaze is directed toward far targets, i.e., when the eyes are either fixating, making saccades, or pursuing moving visual targets. Listing's law (often abbreviated L1) has been generalized to yield the '' binocular extension of Listing's law'' (often abbreviated L2) which also covers vergence. It was proposed by Listing based on its geometric beauty, and never published it. It was first published by Ruete in a 1855 textbook. Helmholtz first found empirical justification based on measurements of afterimages. Listing's law has also been reported for the head, the arm, and the wrist, although for the head, the control is more nuanced. Definition Listing's law states that the eye does not achieve all possible 3D orientations and that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocular Tremor
Ocular tremor (ocular microtremor) is a constant, involuntary eye tremor of a low amplitude and high frequency. It is a type of fixational eye movement that occurs in all normal people, even when the eye appears still. The frequency of ocular microtremor has been found to range from 30 Hz to 103 Hz, and the amplitude is approximately four thousandths of a degree. Cause Human eyes are constantly moving, even if they appear to be focused on an object. These constant oscillations are called fixational eye movements, and they include ocular microtremor, microsaccades, and drift. Ocular tremor is the smallest of these movements, and it often overlaps with drift. This makes it the most difficult fixational eye movement to measure. Due to these difficulties in measurement, fewer studies have been performed on ocular microtremor, leading to the phenomenon of ocular tremor not being well-understood. Researchers are not entirely sure of the cause of ocular microtremor. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silent Reading
Silent reading is reading done silently, or without speaking the words being read. Before the reintroduction of separated text (spaces between words) in the Late Middle Ages, the ability to read silently may have been considered rather remarkable, though some scholars object to this idea. In contrast, reading aloud activates many more parts of the brain due to the dual-route of feedback when pronouncing and reading. History Scholars assume that reading aloud (Latin ''clare legere'') was the more common practice in antiquity, and that reading silently (''legere tacite'' or ''legere sibi'') was unusual.Carruthers, Mary. 2008. ''The Book of Memory: A Study of Memory in Medieval Culture''. 2nd. ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 212 ff. In his ''Confessions'', Saint Augustine remarks on Saint Ambrose's unusual habit of reading silently in the 4th century AD: "When Ambrose read, his eyes ran over the columns of writing and his heart searched out the meaning, but hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
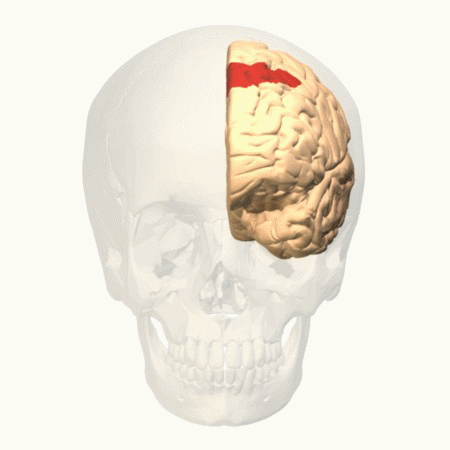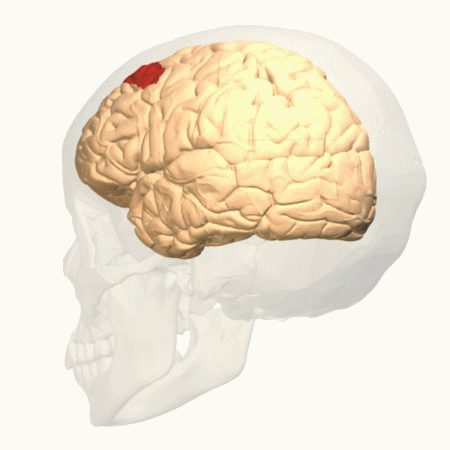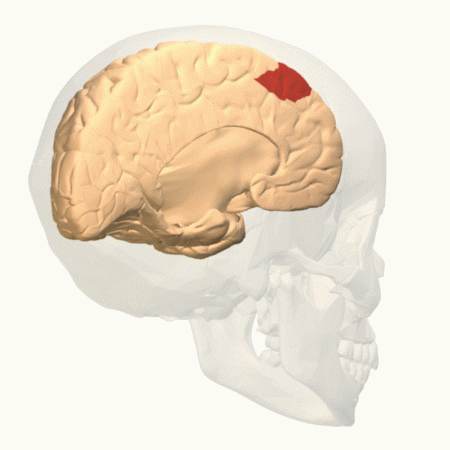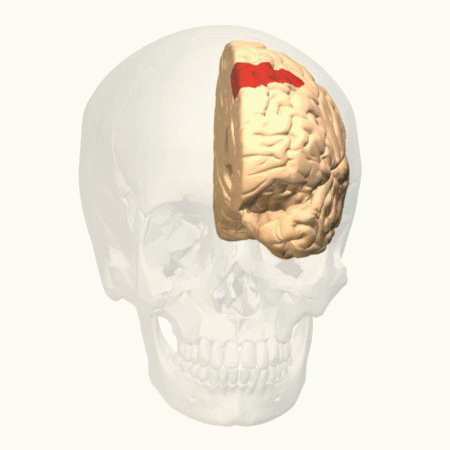
Frontal Eye Fields
The frontal eye fields (FEF) are a region located in the frontal cortex, more specifically in Brodmann area 8 or BA8, of the primate brain. In humans, it can be more accurately said to lie in a region around the intersection of the middle frontal gyrus with the precentral gyrus, consisting of a frontal and parietal portion. The FEF is responsible for Saccade, saccadic eye movements for the purpose of visual field perception and awareness, as well as for voluntary eye movement. The FEF communicates with extraocular muscles indirectly via the paramedian pontine reticular formation. Destruction of the FEF causes deviation of the eyes to the ipsilateral side. Function The cortical area called the frontal eye field (FEF) plays an important role in the control of visual attention and eye movements. Electrical stimulation in the FEF elicits saccadic eye movements. The FEF have a topographic structure and represents saccade targets in retinotopic coordinates. The frontal eye field is rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |