|
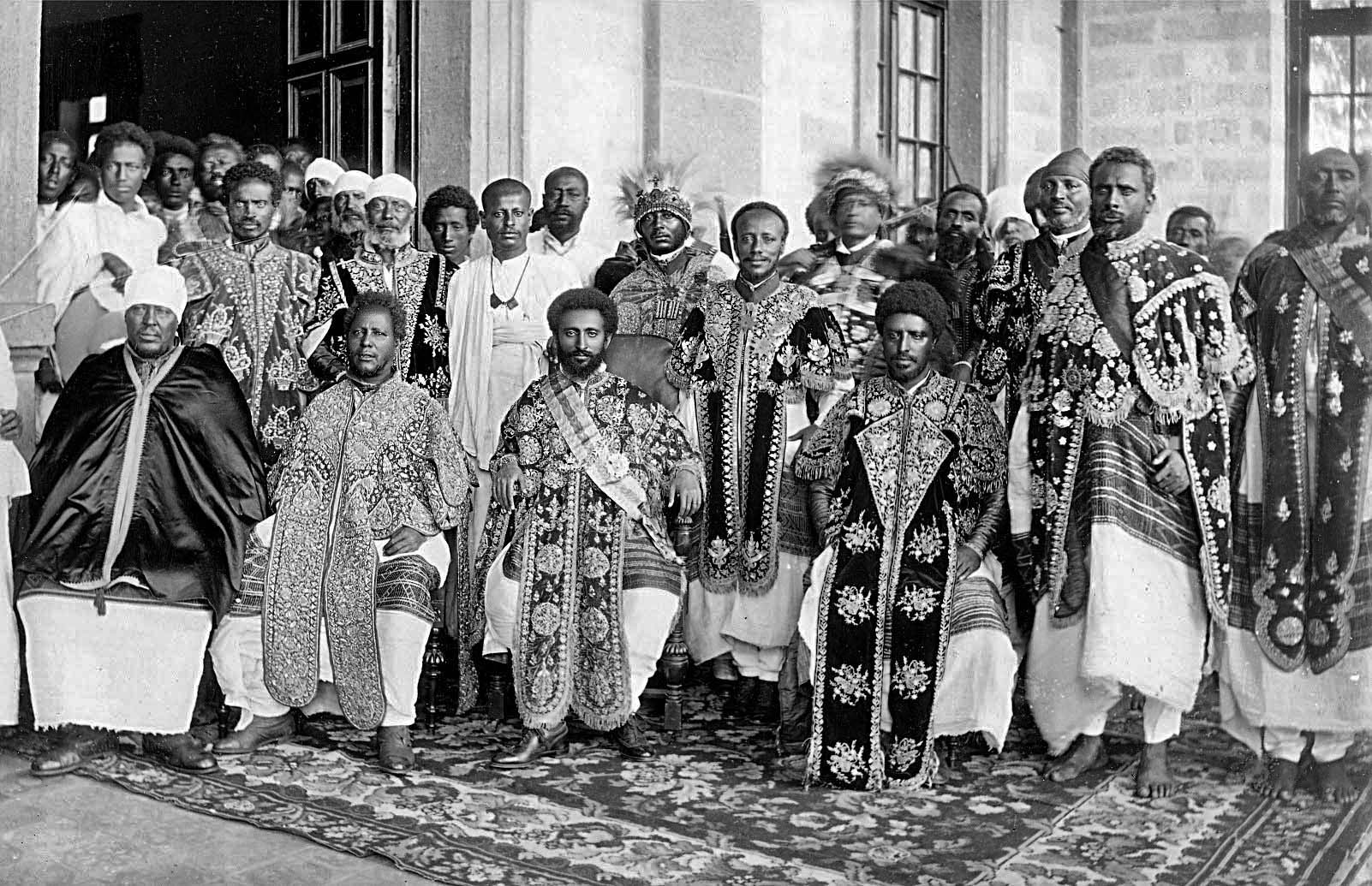
Rulers Of Shewa
This article lists the rulers of Shewa, a historical region of Ethiopia. c. 960–1270 According to tradition, the Solomonic dynasty (1270–1974) was descended from king Solomon and queen Makeda via the kings of Axum. After Axum was destroyed by Gudit in the 10th century, the royal family fled to Shewa and reigned there for 330 years before the accession of Yekuno Amlak. A line of kings ruled at Shewa during the time of the Zagwe dynasty and claimed descent from Dil Na'od, the last king of Axum. The 1922 regnal list of Ethiopia includes eight unnumbered kings described as "8 generations of an Israelitish dynasty" who "did not mount the throne". 1682–1889 Claiming Solomonic descent, Nagasi Krestos established Shewa as an autonomous region of the weakening Ethiopian Empire in the 17th century before requesting the title of ''Meridazmatch'', which would be adopted by his successors, and beginning a southern expansion of his realm that would culminate in the conquests o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Aristocratic And Court Titles
Until the end of the Ethiopian Empire, Ethiopian monarchy in 1974, there were two categories of nobility in Ethiopia and Eritrea. The Mesafint ( , modern transcription , singular መስፍን , modern , "prince"), the hereditary royal nobility, formed the upper echelon of the ruling class. The Mekwanint ( , modern , singular መኰንን , modern or , "officer") were the appointed nobles, often of humble birth, who formed the bulk of the aristocracy. Until the 20th century, the most powerful people at court were generally members of the ''Mekwanint'' appointed by the monarch, while regionally, the ''Mesafint'' enjoyed greater influence and power. Emperor Haile Selassie greatly curtailed the power of the ''Mesafint'' to the benefit of the ''Mekwanint'', who by then were essentially coterminous with the Ethiopian government. The ''Mekwanint'' were officials who had been granted specific offices in the Abyssinian government or court. Higher ranks from the title of ''Ras'' descendi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gudit
Gudit () is the Classical Ethiopic name for a personage also known as Yodit in Tigrinya, and Amharic, but also Isato in Amharic, and Ga'wa in Ţilţal. The person behind these various alternative names is portrayed as a powerful female ruler, probably identical to Māsobā Wārq, the daughter of the last Aksumite king, Dil Na'ad, mentioned in an early Arabic source. She is said to have been responsible for laying waste the Kingdom of Aksum and its countryside, and the destruction of its churches and monuments in the 10th century AD. If she is the same as the ''Tirda' Gābāz'' in other Ethiopian sources, she is also said to have attempted to exterminate the members of the ruling dynasty. The deeds attributed to her are recorded in oral tradition and in a variety of historical narratives. Name The name "Gudit" in the Geʽez narrative associates her positively with the Biblical Judith. It has been conjectured that the form Gudit is connected etymologically with the Amh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidane Kale
Kidane Kale (reigned c. 1718 - c. 1744; literal meaning: "Beginning, Word"), better known as Abuye or 'Abbiye, was a Meridazmach of Shewa, an important Amhara noble of Ethiopia. He was the son of Sebestyanos. Harold G. Marcus is less definite on this, calling him Sebestyanos' "brother or his son". Marcus, ''The Life and Times of Menelik II: Ethiopia 1844-1913'' (Lawrenceville: Red Sea Press, 1995), p. 8 Abir states that he ruled for 25 years, although noting that William Cornwallis Harris claims he ruled for 15 years, Coulbeaux for 25 (from 1725 to 1750), and Rochet d'Hericourt for 60. His wife was Woizero Tagunestiya, daughter of Mama Rufa'el, Governor of Mamameder. Abuye succeeded on the death of his father, and made his capital at Har Amba. Sebestyanos had died "by a curious accident", according to Levine. Abuye had been rebuilding some of the churches destroyed by Ahmad Gragn, one of which was in Doqaqit dedicated to St. Michael. Part of the ceremony required the tabot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebestyanos
Sebestyanos (reigned c. 1703 - c. 1718) was a ruler of Shewa, an important Amhara noble of Ethiopia. He was one of the sons of Negasi Krestos. Abir states that he ruled for 15 years, although noting that William Cornwallis claims states that he ruled for 25 years, and Rochet d'Hericourt 33. According to Donald Levine, Sebestyanos' father, Negasi Krestos, proclaimed in his will that his oldest son Akawa would inherit his "throne". Sebestyanos would receive his spear, silver cutlass, and gilded shield. Land and money would go to his other five sons. However, drought and famine afflicted Shewa: the nobility deposed Akawa in favor of his younger son Daña. Dreading the fighting that he knew would follow, Sebestyanos fled Menz to the safety of Merhabete, where he served the governor. Meanwhile, his relatives grew dissatisfied with his brother Daña, and successfully lured Sebestyanos back to Menz, where his victories over the neighboring Oromo inevitably led him to fight his brother. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menelik II's Conquests
Menelik II's conquests, also known as the Agar Maqnat (), were a series of late 19th-century military campaigns led by Emperor Menelik II of Shewa to expand the territory of the Ethiopian Empire. Emerging from a fragmented Abyssinian highland polity, Menelik—who had ascended to power in 1866—began, a decade later, to capitalize on growing centralization efforts, an increasing militarized state apparatus, and substantial arms imports from European powers to launch a wave of expansive and often violent annexations across the south, west, and east of the Horn of Africa beginning in the early 1880s. These campaigns, conducted largely by Amhara forces from Shewa, mirrored European colonial practices—such as indirect rule, settler militarism, and land dispossession—and were frequently justified by Menelik as part of a Christianizing civilizing mission. Central to the imperial structure in many southern regions was the ''neftenya-gabbar'' system, a settler-colonial arrangem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire, historically known as Abyssinia or simply Ethiopia, was a sovereign state that encompassed the present-day territories of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It existed from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak around 1270 until the 1974 Ethiopian coup d'état, 1974 coup d'état by the Derg, which ended the reign of the final Emperor, Haile Selassie. In the late 19th century, under Emperor Menelik II, the Menelik II's conquests, empire expanded significantly to the south, and in 1952, Federation of Ethiopia and Eritrea, Eritrea was federated under Selassie's rule. Despite being surrounded by hostile forces throughout much of its history, the empire maintained a kingdom centered on its Orthodox Tewahedo, ancient Christian heritage. Founded in 1270 by Yekuno Amlak, who claimed to descend from the last Kingdom of Aksum, Aksumite king and ultimately King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, it replaced the Agaw people, Agaw Zagwe Kingdom, kingdom of the Za ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of Ethiopia
The emperor of Ethiopia (, "King of Kings"), also known as the Atse (, "emperor"), was the hereditary monarchy, hereditary ruler of the Ethiopian Empire, from at least the 13th century until the abolition of the monarchy in 1975. The emperor was the head of state and head of government, with ultimate executive power, executive, judicial power, judicial and legislative power in that country. A ''National Geographic'' article from 1965 called Imperial Ethiopia "nominally a constitutional monarchy; in fact it was a benevolent dictatorship, benevolent autocracy". Title and style The title "King of Kings", often rendered imprecisely in English as "emperor", dates back to ancient Mesopotamia, but was used in Aksumite Empire, Axum by King Sembrouthes (). However, Yuri Kobishchanov dates this usage to the period following the Persian Empire, Persian victory over the Roman Empire, Romans in 296–297. The most notable pre-Solomonic usage of the title "Negusa Nagast" was by Ezana of Ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yekuno Amlak (cropped)
Yekuno Amlak (); throne name Tesfa Iyasus (; died 19 June 1285) was Emperor of Ethiopia, from 1270 to 1285, and the founder of the Solomonic dynasty, which lasted until 1974. He was a ruler from Bete Amhara (in parts of modern-day Wollo and northern Shewa) who became the Emperor of Ethiopia following the defeat of the last Zagwe king. Origins and rise to power Yekuno Amlak hailed from an ancient Amhara family. Later medieval texts, written in support of his dynasty, claimed that he was a direct male line descendant of the former royal house of the Kingdom of Aksum which was, itself, descended, it was claimed, from the biblical king Solomon. However, there is no credible historical evidence for such an ancestry or that the Aksumite kings ever claimed descent from Solomon. The claims, nevertheless, formed the basis of his dynasty's pretense that Yekuno Amlak "restored" the Solomonic dynasty to the Ethiopian throne when he overthrew the last of the Zagwe kings in 1270. The Zag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 Regnal List Of Ethiopia
The 1922 regnal list of Ethiopia is an official regnal list used by the Emperor of Ethiopia, Ethiopian monarchy which names over 300 monarchs across six Millennium, millennia. The list is partially inspired by older regnal lists of Ethiopia, Ethiopian regnal lists and chronicles, but is notable for additional monarchs who ruled Nubia, which was known as ''Aethiopia'' in ancient times. Also included are various figures from Greek mythology and the Biblical canon who were known to be "Aethiopian", as well as figures who originated from Egyptian sources (Ancient Egyptian, Coptic literature, Coptic and Arabic literature, Arabic). This list of monarchs was included in Charles Fernand Rey's book ''In the Country of the Blue Nile'' in 1927, and is the longest Ethiopian regnal list published in the Western world. It is the only known regnal list that attempts to provide a timeline of Ethiopian monarchs from the 5th millennium BC, 46th century BC up to modern times without any gaps. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dil Na'od
Dil Na'od was the last King of Aksum before the Zagwe dynasty. He lived in either the 9th or 10th century. Dil Na'od was the younger son of Ged'a Jan (or Degna Djan), and succeeded his older brother 'Anbasa Wedem as ''negus''. According to E. A. Wallis Budge, "The reign of Delna'ad was short, perhaps about ten years." However, James Bruce has recorded another tradition, that Dil Na'od was an infant when Gudit slaughtered the princes imprisoned at Debre Damo, his relatives, and forced some of his nobles to take him out of his kingdom to save his life. Dil Na'od is recorded as both campaigning in the Ethiopian Highlands south of Axum Axum, also spelled Aksum (), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015). It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire. Axum is located in the Central Zone of the Tigray Re ..., and sending missionaries into that region. With Abuna Salama I, he helped to build the chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagwe Dynasty
The Zagwe dynasty () was a medieval Agaw monarchy that ruled the northern parts of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It ruled large parts of the territory from approximately 1137 to 1270 AD, when the last Zagwe King Za-Ilmaknun was killed in battle by the forces of the Amhara King Yekuno Amlak. The Zagwe are most famous for their king Gebre Meskel Lalibela, who is credited with having ordered the construction of the rock-hewn monolithic churches of Lalibela. The name "Zagwe" is thought to derive from the ancient Ge'ez phrase ''Ze- Agaw'', meaning "of the Agaw", in reference to the Mara Tekle Haymanot, the founder of the dynasty. This term does not appear in contemporary sources, neither in indigenous documents nor in accounts of foreign observers. David Buxton has stated that the areas under the direct rule of the Zagwe kings apart from the centre of power in Lasta "probably embraced the highlands of modern Eritrea, Tigray, Wag and Bete Amhara and thence westwards towards Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Bulmer (printer)
William Bulmer (1757–1830) was an English printer and typographer. Biography William Bulmer was born in 1757 as one of the youngest children of Thomas Bulmer in Newcastle-upon-Tyne. He was apprenticed to the printer Mr. Thompson, at Burnt House Entry, St. Nicholas' Churchyard. During his apprenticeship he formed a friendship with Thomas Bewick, which lasted throughout his life When William Bulmer first came to London, he worked for the printer and publisher John Bell and was introduced to George Nicol, bookseller to King George III, who, with John Boydell had conceived a lavish edition of the works of Shakespeare with illustrations from the foremost artists of the day. For the project Nicol had already engaged the services of William Martin, a type-founder from Birmingham who had worked for John Baskerville, to design and cut the type. In the spring of 1790, William Bulmer established The Shakespeare Press at 3 Russell Court, off Cleveland Row, St. James's and the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |