|
Rukwa Languages
The Rukwa languages are a group of Bantu languages established by Nurse (1988) and Fourshey (2002). They constitute half of Guthrie classification of Bantu languages#Zone M, Guthrie's Zone M, plus Bungu. The languages, or clusters, along with their Guthrie identifications, are: *Rungwe (M30): Nyakyusa language, Nyakyusa–Ngonde language, Ngonde (Konde), Ndali language, Ndali *Mbozi **Mbeya ***Bungu language, Bungu (Wungu, F20) ***Safwa language, Safwa (M20) ***South Mbeya (M20): Malila language, Malila; Lambya language, Lambya–Sukwa, Nyiha language, Nyiha **Mwika ***Nyika language, Nyika (M20) ***North Mwika (M10): Pimbwe language, Pimbwe, Rungwa language, Rungwa ***Plateau Mwika: ****Fipa language, Fipa (M10) ****South: Wanda language, Wanda, Namwanga language, Namwanga–Iwa–Tambo (M20), Mambwe-Lungu language, Mambwe-Lungu (M10) Nurse (1988) had established a more limited Mbozi ("Corridor"), without Pimbwe or Bungu, and with the addition of Rungwe tentative. Maho (2009) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic–Congo Languages
The Atlantic–Congo languages make up the largest demonstrated family of languages in Africa. They have characteristic noun class systems and form the core of the Niger–Congo family hypothesis. They comprise all of Niger–Congo apart from Mande, Dogon, Ijoid, Siamou, Kru, the Katla and Rashad languages (previously classified as Kordofanian), and perhaps some or all of the Ubangian languages. Hans Gunther Mukanovsky's "Western Nigritic" corresponded roughly to modern Atlantic–Congo. In the infobox, the languages which appear to be the most divergent are placed at the top. The Atlantic branch is defined in the narrow sense (as Senegambian), while the former Atlantic branches Mel and the isolates Sua, Gola and Limba are split out as primary branches; they are mentioned next to each other because there is no published evidence to move them; Volta–Congo is intact apart from Senufo and Kru. ''Glottolog'', based primarily on Güldemann (2018), has a more limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyiha Language
Nyiha (Nyixa, Nyika) is a Bantu language The Bantu languages (English: , Proto-Bantu language, Proto-Bantu: *bantʊ̀), or Ntu languages are a language family of about 600 languages of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern, East Africa, Eastern and Southeast Africa, South ... primarily spoken in Tanzania and Zambia. The language of the 10,000 speakers in Malawi is different enough to sometimes be considered a distinct language. References External linksUniversity of Malawi Language Mapping Survey (2006)Contains comparative vocabulary and a short text in Malawian Nyika. *Krüger et al. (2009"A Sociolinguistic Survey of the Nyiha and Nyika language communities in Tanzania, Zambia and Malawi" {{Narrow Bantu languages (Zones J–M) Rukwa languages Languages of Tanzania Languages of Malawi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penja Language
Penja is a possibly extinct Bantu language of southern Tanzania, near the north end of Lake Malawi Lake Malawi, also known as Lake Nyasa in Tanzania and Lago Niassa in Mozambique, () is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake and the southernmost lake in the East African Rift system, located between Malawi, Mozambique and Tanzania. It is .... References Rukwa languages {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mambwe-Lungu Language
The Mambwe and Lungu peoples living at the southern end of Lake Tanganyika in Tanzania and Zambia Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ... speak a common language with minor dialectical differences. Perhaps half of the Fipa people to their north speak it as a native language. When spoken by the Fipa, it is called "Fipa-Mambwe"; this is also the term for the branch of Bantu languages which includes Fipa and Mambwe-Lungu. Mambwe-Lungu is spoken by the people of Rukwa region, southern Sumbawanga town in Tanzania. The language is also spoken in Mankato, Mpulungu and Senga district of Zambia. It has close affinities with languages spoken by other Tanganyikan people like Pimbwe, Rungwa and Namwanga. References Relevant literature * Bickmore, Lee. 2008. ''Cilungu Phon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namwanga Language
Mwanga, or Namwanga (Nyamwanga), is a Bantu language spoken by the Mwanga people in the Muchinga Province of Zambia (mainly in the districts of Isoka and Nakonde) and in Mbeya Region, Tanzania. The 2010 Zambian census found 140,000 speakers. The current number in Tanzania is unknown; ''Ethnologue'' cites a figure from 1987 of 87,000. There are also some speakers of Namwanga in the north-west part of Chitipa District in northern Malawi. p. 29. The Namwanga language is similar to the Mambwe language spoken by the |
Wanda Language
Wanda (also, known as Ichiwanda, Iciwanda, Kiwanda, Vanda, Wandia ) is a Bantu language of Tanzania. It is considered a vulnerable language with less than 43,000 native speakers worldwide. At least half of Wanda people speak limited Swahili, one of the official languages of Tanzania Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t .... Speakers are particularly concentrated in Kamsamba ward in Momba District Council and Kipeta ward in Sumbawanga District. References {{Narrow Bantu languages (Zones J–M) Rukwa languages Languages of Tanzania Languages of Zambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fipa Language
Fipa (Fipa: ''Ichifipa'') is a Bantu language of Tanzania. It is spoken by the Fipa people, who live on the Ufipa plateau in the Rukwa Region of South West Tanzania between Lake Tanganyika and Lake Rukwa. The ethnic group of the Fipa people is larger than the group of Fipa language speakers. On the Tanzanian side, people who speak Mambwe-Lungu language, Mambwe-Lungu may identify as Fipa and consider their language to be a dialect of Fipa. Lungu language, Lungu and Mambwe language, Mambwe are also spoken in Zambia where they are considered languages and their speakers are considered to be ethnic groups in their own right, although linguists consider Lungu and Mambwe to be dialects of a single language. There are three dialects: Milanzi (also referred to as IchiSukuuma), Kwa (Ichikwa) and Nkansi. Maho (2009) classifies M.131 Kulwe (Kuulwe, no ISO code) as closest to Fipa. Otherwise the dialects are Milanzi (Fipa-Sukuma, ''Icisukuuma''), South Fipa, Kandaasi (''Icikandaasi''), Siiwa ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rungwa Language
Rungwa is a Bantu language of the Rukwa Region of western Tanzania Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t .... References Rukwa languages {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pimbwe Language
The Pimbwe are an ethnic and linguistic group based in the Rukwa Region of western Tanzania, in the neighbourhood of Mpimbwe to the northwest of Lake Rukwa Lake Rukwa is an endorheic lake located in the Rukwa Valley of Rukwa Region, Songwe Region and Katavi Region in southwestern Tanzania. The lake is the third largest inland body of water in the country. Geography The alkaline Lake Rukwa lies ...Margaret Arminel Bryan, ''The Bantu Languages of Africa'' Oxford University Press 1959. References Ethnic groups in Tanzania Indigenous peoples of East Africa Rukwa languages {{Bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nyika Language
Nyika (Nyiha) is a Bantu language of Tanzania and Zambia Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor .... References Rukwa languages Languages of Tanzania {{bantu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambya Language
Lambya ( Rambia) is a Bantu language of Tanzania and Malawi. In Northern Malawi it is spoken particularly in the Chitipa District Chitipa District is the northernmost district in the Northern Region of Malawi. The capital is Chitipa (formerly known as Fort Hill). The district covers an area of 4,288 km2, and has a population of 234,927. The major and common language s ....University of Malawi Language Mapping Survey for Northern Malawi (2006) (see External links). Sukwa, once thought to be a dialect of Nyakyusa, is now considered to be a dialect of Lambya. The University of Malawi Language Mapping Survey for Northern Malawi (2006), agreeing with this, found that the three languages Cilambya, Cindali, and Cisukwa form a single dialect group, although there are differences between them, especially between Cilambya and the other two. The examples below come in the order Lambya, Ndali, Sukwa: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
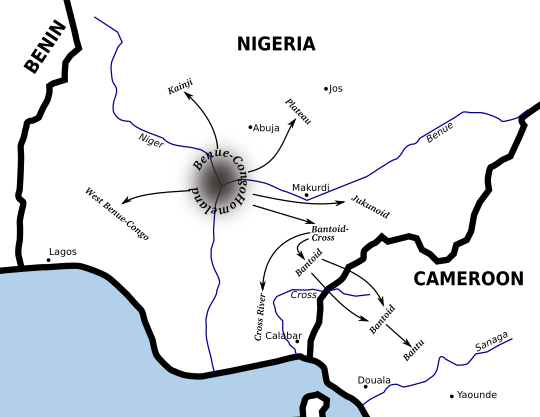
Benue–Congo Languages
Benue–Congo (sometimes called East Benue–Congo) is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Subdivisions Central Nigerian (or Platoid) contains the Plateau languages, Plateau, Jukunoid languages, Jukunoid and Kainji languages, Kainji families, and Bantoid–Cross combines the Bantoid languages, Bantoid and Cross River languages, Cross River groups. Bantoid is only a collective term for every subfamily of Bantoid–Cross except Cross River, and this is no longer seen as forming a valid branch, however one of the subfamilies, Southern Bantoid, is still considered valid. It is Southern Bantoid which contains the Bantu languages, which are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa. This makes Benue–Congo one of the largest subdivisions of the Niger–Congo language family, both in number of languages, of which ''Ethnologue'' counts 976 (2017), and in speakers, numbering perhaps 350 million. Benue–Congo also includes a few minor Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |