|
Roman Fortifications
Roman military borders and fortifications were part of a grand strategy of territorial defense in the Roman Empire, although this is a matter of debate. By the early 2nd century, the Roman Empire had reached the peak of its territorial expansion and rather than constantly expanding their borders as earlier in the Empire and Republic, the Romans solidified their position by fortifying their strategic position with a series of fortifications and established lines of defense. Historian Adrian Goldsworthy argues that the Romans had reached the natural limits which their military traditions afforded them conquest over and that beyond the borders of the early-to-mid Empire lay peoples whose military traditions made them militarily unconquerable, despite many Roman battle victories. In particular, Goldsworthy argues that the cavalry-based warfare of the Parthian Empire, Parthians, Sarmatians and Sassanian Empire, Persians presented a major challenge to the expansion of Rome's infantr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes And Borders
Limes may refer to: *Limes (Roman Empire), ''Limes'' (Roman Empire), a border marker and defense system of the Roman Empire *Limes (Italian magazine), ''Limes'' (Italian magazine), an Italian geopolitical magazine *Limes (Romanian magazine), ''Limes'' (Romanian magazine), a Romanian literary and political quarterly magazine See also * Lime (other) * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Running from Wallsend on the River Tyne in the east to Bowness-on-Solway in the west of what is now northern England, it was a stone wall with large ditches in front and behind, stretching across the whole width of the island. Soldiers were garrisoned along the line of the wall in large Castra, forts, smaller milecastles, and intervening Turret (Hadrian's Wall), turrets. In addition to the wall's defensive military role, its gates may have been customs posts. Hadrian's Wall Path generally runs close along the wall. Almost all the standing masonry of the wall was removed in early modern times and used for local roads and farmhouses. None of it stands to its original height, but modern work has exposed much of the footings, and some segments d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vexillation
A ''vexillatio'' (: ''vexillationes'') was a detachment of a Roman legion formed as a temporary task force created by the Roman army of the Principate. It was named from the standard carried by legionary detachments, the ''vexillum'' (: ''vexilla''), which bore the emblem and name of the parent legion. Although commonly associated with legions, it is likely that ''vexillationes'' included auxiliaries. The term is found in the singular, referring to a single detachment, but is usually used in the plural to refer to an army made up of picked detachments. ''Vexillationes'' were assembled ''ad hoc'' to meet a crisis on Rome's extensive frontiers, to fight in a civil war, or to undertake an offensive against Rome's neighbours. They varied in size and composition, but usually consisted of about 1000 infantry and/or 500 cavalry. Purpose Most of the Roman Army (around 400,000 strong at the beginning of the 3rd century) was stationed along the frontiers from the time of Hadrian, if not e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 infantry and 300 cavalry. After the Marian reforms in 107 BC, the legions were formed of 5,200 men and were restructured around 10 cohorts, the first cohort being double strength. This structure persisted throughout the Principate and Roman Empire, middle Empire, before further changes in the fourth century resulted in new formations of around 1,000 men. Size The size of a typical legion varied throughout the history of ancient Rome, with complements ranging from 4,200 legionaries and 300 ''equites'' (drawn from the wealthier classes – in early Rome all troops provided their own equipment) in the Republic, to 5,500 in the Imperial period, when most legions were led by a Roman Imperial Legate. A legion had 4,800 Legionary, legionaries ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonine Wall
The Antonine Wall () was a turf fortification on stone foundations, built by the Romans across what is now the Central Belt of Scotland, between the Firth of Clyde and the Firth of Forth. Built some twenty years after Hadrian's Wall to the south, and intended to supersede it, while it was garrisoned it was the northernmost frontier barrier of the Roman Empire. It spanned approximately and was about high and wide. Lidar scans have been carried out to establish the length of the wall and the Roman distance units used. Security was bolstered by a deep ditch on the northern side. It is thought that there was a wooden palisade on top of the turf. The barrier was the second of two "great walls" created by the Romans in Great Britain in the second century AD. Its ruins are less evident than those of the better-known and longer Hadrian's Wall to the south, primarily because the turf and wood wall has largely weathered away, unlike its stone-built southern predecessor. Construction be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
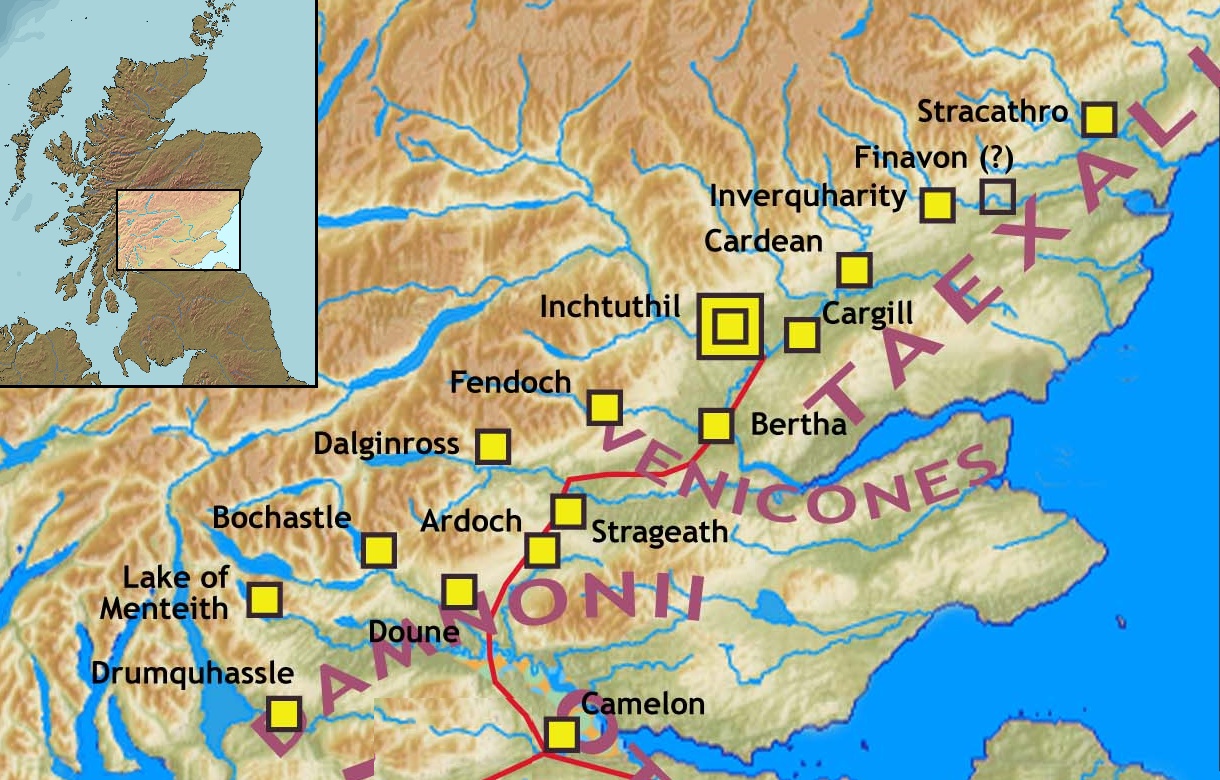
Gask Ridge
The Gask Ridge is the modern name given to an early series of Castra, fortifications, built by the Roman Empire, Romans in Scotland, close to the Highland Boundary Fault, Highland Line. Modern excavation and interpretation has been pioneered by the Roman Gask Project, with Birgitta Hoffmann and David Woolliscroft. The ridge fortifications: forts, fortlets and watchtowers were only in operation for a few years, probably fewer than ten. Name The name "Gask Ridge" refers to the ridge of land to the north of the River Earn in Perthshire. In Scottish Gaelic, a ''gasg'' is a projecting tail or strip of land. In the early 20th century, a line of Roman signal-towers (or watch-towers) was discovered along this ridge between the Roman forts of Strageath and Bertha (Perth), Bertha. History The Gask Ridge system was constructed sometime between 70 and 80 AD. Construction on Hadrian's Wall was started 42 years after completion of the Gask Ridge (from 122 to 130 AD), and the Antonine Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples in what is now Scotland north of the Firth of Forth, in the Scotland in the early Middle Ages, Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and details of their culture can be gleaned from early medieval texts and Pictish stones. The name appears in written records as an Exonym and endonym, exonym from the late third century AD. They are assumed to have been descendants of the Caledonians, Caledonii and other northern British Iron Age, Iron Age tribes. Their territory is referred to as "Pictland" by modern historians. Initially made up of several chiefdoms, it came to be dominated by the Pictish kingdom of Fortriu from the seventh century. During this Fortriu#Verturian_hegemony, Verturian hegemony, ''Picti'' was adopted as an endonym. This lasted around 160 years until the Pictish kingdom merged with that of Dál Riata to form the Kingdom of Alba, ruled by the House of Alpin. The concept of "Pictish kingship" continued for a few decades until it was ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Belt
The Central Belt of Scotland is the Demographics of Scotland, area of highest population density within Scotland. Depending on the definition used, it has a population of between 2.4 and 4.2 million (the country's total was around 5.4 million in 2019), including multiple List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, major Scottish settlements such as Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, Glasgow, East Kilbride, Livingston, West Lothian, Livingston, and Edinburgh. Despite the name, it is not geographically central but is nevertheless at the "waist" of Scotland on a conventional map and the term "central" is used in many Subdivisions of Scotland, local government, police, and NGO designations. It was formerly known as the Midlands or Scottish Midlands, but this term has fallen out of fashion. The Central Belt lies between the Scottish Highlands, Highlands to the north and the Southern Uplands to the south. In the early 21st century, predictions were made that due to economic mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonia
Caledonia (; ) was the Latin name used by the Roman Empire to refer to the forested region in the central and western Scottish Highlands, particularly stretching through parts of what are now Lochaber, Badenoch, Strathspey, and possibly as far south as Rannoch Moor, known as Coed Celedon (Coed Celyddon using the modern alphabet) to the native Brython (Britons). Today, it is used as a romantic or poetic name for all of Scotland. During the Roman Empire's occupation of Britain, the area they called Caledonia was physically separated from the rest of the island by the Antonine Wall. It remained outside the administration of Roman Britain. Latin historians, including Tacitus and Cassius Dio, referred to the territory north of the River Forth as "Caledonia", and described it as inhabited by the Maeatae and the Caledonians (). The name is derived from the word Celyddon in Common Brittonic. History Etymology means 'the forested region’; it is derived from the Wels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defense In Depth
Defence in depth (also known as deep defence or elastic defence) is a military strategy that seeks to delay rather than prevent the advance of an attacker, buying time and causing additional casualties by yielding space. Rather than defeating an attacker with a single, strong defensive line, defence in depth relies on the tendency of an attack to lose momentum over time or as it covers a larger area. A defender can thus yield lightly defended territory in an effort to stress an attacker's logistics or spread out a numerically superior attacking force. Once an attacker has lost momentum or is forced to spread out to pacify a large area, defensive counter-attacks can be mounted on the attacker's weak points, with the goal being to cause attrition or drive the attacker back to its original starting position. Strategy A conventional defence strategy would concentrate all military resources at a front line, which, if breached by an attacker, would leave the remaining defenders in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I
Constantine I (27 February 27222 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was a Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337 and the first Roman emperor to convert to Christianity. He played a Constantine the Great and Christianity, pivotal role in elevating the status of Christianity in Rome, Edict of Milan, decriminalising Christian practice and ceasing Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, Christian persecution. This was a turning point in the Historiography of the Christianization of the Roman Empire, Christianisation of the Roman Empire. He founded the city of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and made it the capital of the Empire, which it remained for over a millennium. Born in Naissus, a city located in the Roman province, province of Moesia Superior (now Niš, Serbia), Constantine was the son of Flavius Constantius, a Roman army officer from Moesia Superior, who would become one of the four emperors of the Tetrarchy. His mother, Helena, mother of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |