|
Regions Of Djibouti
The regions of Djibouti are the primary geographical divisions through which Djibouti is administered. History The first administrative division of the territory, in 1914, defined two zones besides the city of Djibouti: the Sub-prefectures of Djibouti, sub-prefecture "Dankali" and "Issa". With the occupation of the territory at the end of the 1920s, the circles of Tadjourah Region, Tadjourah and "Dikhil Region, Gobad-Dikkil" are created. In 1939, the circle of Ali Sabieh Region, Ali Sabieh is extracted from the last. In 1963, Obock's circle was created by division of that of Tadjourah region. In 1967, the circle of Djibouti is transformed into sub-prefecture, then divided into three sub-prefectures. After independence in 1977, the circles become regions. The last important modification of the administrative map of the territory is the creation of the region of Arta in 2003. Regions See also * ISO 3166-2:DJ {{Articles on first-level administrative divisions of African co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
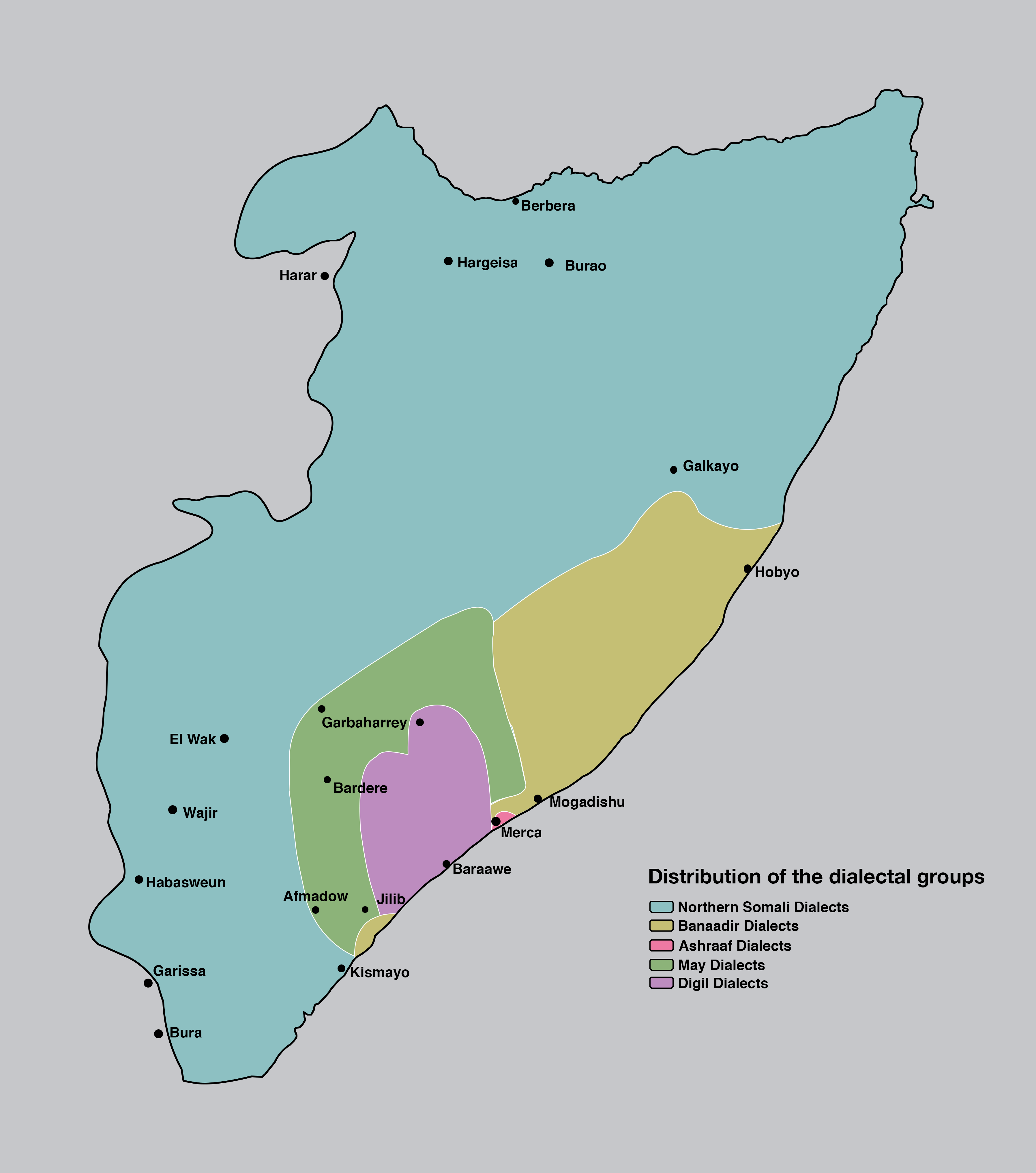
Somali Language
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djibouti City
Djibouti (also called Djibouti City and Jibuti in early Western texts) is the capital city of the Djibouti, Republic of Djibouti. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura. Djibouti has a population of around 780,000 inhabitants, which counts for 73% of the country's population. The settlement was founded in 1888 by the French, on land leased from the ruling Somali and Afar Sultans. During the ensuing period, it served as the capital of French Somaliland and its successor the French Territory of the Afars and Issas. History There is evidence of human settlement on the eastern coastline of Djibouti dating back to the Bronze Age. From 1862 until 1894, the land to the north of the Gulf of Tadjoura was called ''Obock'' and was ruled by Issa clan, Issa and Afar people, Afar Sultans, local authorities with whom France signed various treaties between 1883 and 1887 to first gain a foothold in the region.Raph Uwechue, ''Africa year book and who's who'', (Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obock
Obock (also Obok, , ) is a small port town in Djibouti. It is located on the Northern shore of the Gulf of Tadjoura, where it opens out into the Gulf of Aden. The town is home to an airstrip and has ferries to Djibouti City. The French form Obock derives from Arabic "Oboh", which is a deformation of Oboki, a name given to a local wadi. History The fishing village was originally built on the plateau of Dala-h Húgub near the Dar'i Wadi, with some houses constructed of mud and stone and Daboyta. Most of the inhabitants made their living through animal husbandry, fishing, commerce and used a well for drinking water. During the Middle Ages, Obock was ruled by the Ifat Sultanate and then the Adal Sultanate. The Sultans of Raheita emerged from the Adal Sultanate. Although nominally part of the Ottoman Empire since 1554, between 1821 and 1841, Muhammad Ali, Pasha of Egypt, came to control Yemen and modern-day Eritrea, and claims on Ethiopia as far as Harar. In 1884, the commander of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obock Region
The Obock Region (, , ) is a Regions of Djibouti, region in northern Djibouti. Covering an area of 4,700 square kilometres (1,800 sq mi), it had an estimated population of 37,856 as of 2009.The region borders the Red Sea, Bab-el-Mandeb, Gulf of Aden, Gulf of Tadjoura, and includes the Seven Brothers Islands, Seven Brothers, Doumeira Islands, Doumeira Islands, and the coastal city of Obock. It also shares a section of Djibouti’s northern border with Eritrea. Geographically, Oblock is larger than Cape Verde but smaller than Trinidad and Tobago, featuring a mix of highland and coastal plains. History In the mid-19th century and earlier, the area now known as the Obock Region was governed by Afar people, Afar sultans, local rulers with whom France signed a series of treaties between 1862 and 1887 to establish a colonial presence.Raph Uwechue, ''Africa year book and who's who'', (Africa Journal Ltd.: 1977), p.209.''A Political Chronology of Africa'', (Taylor & Francis), p.132. On Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tadjoura
Tadjoura (; ; ) is one of the oldest towns in Djibouti and the capital of the Tadjourah Region. The town rose to prominence in the early 19th century as an alternative port to nearby Zeila. Lying on the Gulf of Tadjoura, it is home to a population of around 19,000 inhabitants. It is the third-largest city in the country after Djibouti and Ali Sabieh. Tadjoura has an airstrip and is linked by ferry with Djibouti City. It is also known for its whitewashed buildings and nearby beaches, along with its mosques. Etymology The Afar name ''Tagórri'' derives from the noun ''tágor'' or ''tógor'', (pl. ''tágar'' meaning "outre à puiser" ("goatskin flask for drawing water"). The name ''Tagórri'' is specifically derived from *''tagór-li'', which means "qui a des outre à puiser" ("that which has goatskin flasks to draw water"), in effect meaning "abondante en eau" ("abundant with water"). History The emergence of Tadjoura occurred following the rise of the Adoimara or "white h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dikhil
Dikhil () is a town in the western Dikhil Region of Djibouti. Lying east of Lake Abbe, It is situated about southwest of Djibouti City and north of the border with Ethiopia. It serves as the administrative centre of the Dikhil Region, and is home to the Afar and Somali ethnic groups. The town develops gardens and fruit trees. History Prehistory In 1986, the survey work sites were performed by R. Joussaume and researchers ISERST. The engravings oldest discovered to date are from the fourth or third millennium BC, the most famous is the site of Handoga near Dikhil where the ruins of a village squares sub circular dry stone delivered different objects. Including ceramic shards matching vases used brazier, or containers that can hold water, several choppers and microliths, blades, drills, trenchers basalt, rhyolite or obsidian. Also a pearl orange coralline, three glass paste, etc.. There were no trace of metal object. French Somaliland The village was originally built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arta, Djibouti
Arta (, ) is a town in southeastern Djibouti. The center of the Arta Region, it is the country's sixth-largest city. , the population was 11,221. Arta is situated on the Mountains of Arta and is famous for its mild climate. It is located some west of the national capital, Djibouti City. History Arta was a small village when the French created their French Somaliland. During the Middle Ages, it was ruled by the Ifat and Adal Sultanates subsequently came under Ottoman and French protection in the 18th century. Arta later formed a part of the French Somaliland protectorate in the first half of the 20th century. In the December 1942 British invasion of French Somaliland, about 700 British troops and Free French troops occupied the town. Under French colonial rule in 1946, a new housing estate and hill station was built. Arta's climate lent itself to becoming the prime sanctuary of the French civil servants in Djibouti. The region of Arta is inhabited of the popular ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arta Region
Arta Region (, ) is one of the six regions of Djibouti. It was officially created in 2003 by the regrouping of sub-prefectures of the regions of Dikhil and Djibouti. It is situated in the south-central of the country, bordering the Tadjoura Region to the north, and the Djibouti (city)#Djibouti Region, Djibouti Region to the north-east, and Dikhil Region the Ali Sabieh Region to the south, the country of Somaliland lies to the east. The capital of Arta Region is Arta, Djibouti, Arta. Other towns include We`a, Damerjog and Loyada. The Hemed (mountain), Hemed mountain is the highest point in the region of Arta. Climate The climate of Arta Region is generally semi-arid to arid, and its territory is mostly covered by mountains, high plains, and desert. The climate of the coastal strip is influenced by warm ocean waters, keeping the region free from extremes of temperature and providing moisture for rainfall. However, most of the Arta Region populace experience two weather seasons: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Sabieh
Ali Sabieh (, ) is the second largest city in Djibouti. It is situated about Southwest of Djibouti City and north of the border with Ethiopia. It sprawls on a wide basin surrounded by granitic mountains on all sides. Ali Sabieh's mild climate makes it a popular tourist destination for Djiboutians. The famous landmark of Ali Sabieh Mountain, Ali Sabieh mountain is located near the city. History Ali Sabieh was a small village when the French created their French Somaliland. According to an old legend, the present-day territory of Ali Sabieh was covered by some trees, wadis, and a well. nomadic, Nomads used to stop at the well for water on their way to the towns of Zeila or Harar, after signing the treaties in 1894 with the then ruling Ugaas of Issa (clan), Issa Somali, to establish a protectorate in the region referred to as French Somaliland. Ali Sabieh became an administrative and commercial centre in the 19th century after the construction of the Ethio-Djibouti Railways, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djibouti Region
Djibouti Region, also known formerly as Djibouti District, is the capital of the Republic of Djibouti and one of the six regional administrative divisions of the country. With 777,000 residents across a total area of about 80 square miles (200 km2), Djibouti Region is the most populous in Djibouti. It is the smallest region in Djibouti, and contains the national capital, Djibouti. History Ambouli in the Djibouti Region is identifies the city with Canbala by O.G.S. Crawford. Canbala appears in Muhammad al-Idrisi's map of 1192 on the coast of the Horn of Africa, southeast of the straits of Bab-el-Mandeb, and with Cambaleh, a town where the Venetian traveler Bragadino, a thirteenth-century European visitor to Ethiopia, resided for eight years. In the mid-19th century and earlier, Djibouti Region was ruled by local authorities with whom France signed various treaties between 1883 and 1887 to first gain a foothold in the region. Demographics About 70% of Djibouti's population lives in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afar Language
Afar is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Afar people, native to parts of Djibouti, Eritrea and Ethiopia. It is an official language in Ethiopia; and a national language in Djibouti and Eritrea. Afar is officially written in the Latin script and has over 2.6 million speakers. Classification Afar is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family. It is further categorized in the Lowland East Cushitic sub-group, along with Saho and Somali. Its closest relative is the Saho language. Geographic distribution The Afar language is spoken as a mother tongue by the Afar people in Djibouti, Eritrea, and the Afar Region of Ethiopia. According to '' Ethnologue'', there are total Afar speakers. Of these, 1,280,000 were recorded in the 2007 Ethiopian census, with 906,000 monolinguals registered in the 1994 census. Official status In Djibouti, Afar is a recognized national language. It is also one of the broadcasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Sabieh Region
Ali Sabieh Region (, ) is a region in southern Djibouti. With a mainland area of 2,400 square kilometres (900 sq mi), it lies along the national border with Somalia and Ethiopia, bordering also the Dikhil Region to the west and the Arta Region to the north. Its capital is Ali Sabieh. The Arrei Mountains are the highest point in the region. History Nomadic life in the Ali Sabieh Region dates back at least 2,000 years. During the Middle Ages, the Ali Sabieh Region was ruled by the Ifat Sultanate and the Adal Sultanate. It later formed a part of the French Somaliland protectorate in the first half of the 20th century. Considered the border with Ethiopia, the area had few permanent settlements at the turn of the 20th century. In 1904, a report notes that "when the border post of Ali Sabieh, it has the appearance of a fortress. Attached to the circle of "Gobad-Dikkil" from its inception in 1931, Ali Sabieh became the chief town of a circle autonomously 1939. It was briefly attached ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |