|
Ranga Reddy District
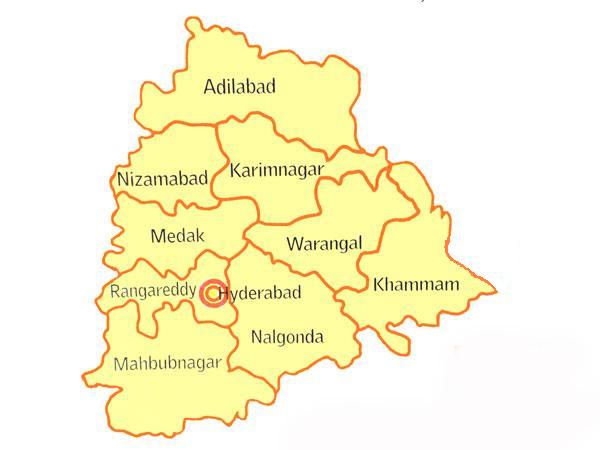
Ranga Reddy district is a district in the Indian state of Telangana. The district headquarters is located at Kongara Kalan Village, Ibrahimpatnam Mandal. The district was named after the former deputy chief minister of the United Andhra Pradesh, K. V. Ranga Reddy. The district shares boundaries with Nalgonda, Yadadri Bhuvanagiri, Hyderabad, Medchal–Malkajgiri, Nagarkurnool, Mahabubnagar, Sangareddy and Vikarabad districts. History Dynasties Chronological order of kingdoms who ruled Rangareddy and Hyderabad regions is as follows: 1. Nandas 2. Mauryas 3. Satavahanas 4. Ikshvakus 5. Vakatakas 6. Vishnukundinas 7. Badami Chalukyas 8. Rashtrakutas 9. Kalyani Chalukyas 10. Kakatiyas 11. Delhi Sultanate(Khilji & Tughlaq dynasties) 12. Musunuri Nayakas 13. Recherla Padmanayakas(Rachakonda & Devarakonda Velamas) 14. Bahamanis 15. Qutub Shahis 16. Mughals 17. Asaf Jahis Formation of District The di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts In Telangana
The Indian state of Telangana has 33 districts, each headed by a District collector. History Telangana region of Hyderabad State consisted of 8 Districts in 1948 when it was inducted in Dominion of India; they are Hyderabad, Mahbubnagar, Medak, Nalgonda, Nizamabad, Adilabad, Karimnagar and Warangal districts. Khammam district was created by bifurcation of Warangal district on 1 October 1953. Andhra Pradesh was formed by merging Telangana region of Hyderabad State and Andhra state on 1 November 1956. Bhadrachalam division and Aswaraopet taluka parts was merged in Khammam district from Godavari districts for better Administration. Hyderabad district was split into Hyderabad Urban District and Hyderabad Rural District on 15 August 1978. Hyderabad Urban District was made by 4 Talukas are Charminar, Golkonda, Mushirabad and Secunderabad Talukas which consist of only MCH area, Secunderabad cantonment and Osmania University. Hyderabad rural district was later renamed as Ranga R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian State
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 districts and smaller administrative divisions by the respective subnational government. The states of India are self-governing administrative divisions, each having a state government. The governing powers of the states are shared between the state government and the union government. On the other hand, the union territories are directly governed by the union government. History 1876–1919 The British Raj was a very complex political entity consisting of various imperial divisions and states and territories of varying autonomy. At the time of its establishment in 1876, it was made up of 584 constituent states and the directly ruled territories of the Crown. The entire empire was divided into provinces and agencies. A province consisted of territory under the direct rule of the Empe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andhra Ikshvaku
The Ikshvaku dynasty (IAST: Ikṣvāku) ruled in the eastern Krishna River valley of India, from their capital at Vijayapuri (modern Nagarjunakonda in Andhra Pradesh) for over a century during 3rd and 4th centuries CE. The Ikshvakus are also known as the Andhra Ikshvakus or the Ikshvakus of Vijayapuri to distinguish them from their legendary namesakes: the Ikshvakus of Kosala. The Ikshvaku kings were Shaivites and performed Vedic rites, but Buddhism also flourished during their reign. Several Ikshvaku queens and princes contributed to the construction of the Buddhist monuments at present-day Nagarjunakonda. Political history Ancient Sanskrit texts, such as ''Rigveda'', ''Atharvaveda'', and ''Jaiminiya Upanishad Brahmana'', mention a legendary king named Ikshvaku (literally, "gourd"). The Atharvaveda and Brahmanas associate the Ikshvakus with non-Aryan people, distinct from the Aryans who composed the hymns of the four Vedas. F. E. Pargiter has equated the ancient Ikshvak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satavahana Dynasty
The Satavahanas (; ''Sādavāhana'' or ''Sātavāhana'', IAST: ), also referred to as the Andhras (also ''Andhra-bhṛtyas'' or ''Andhra-jatiyas'') in the Puranas, were an ancient Indian dynasty. Most modern scholars believe that the Satavahana rule began in the late 2nd century BCE and lasted until the early 3rd century CE, although some assign the beginning of their rule to as early as the 3rd century BCE based on the Puranas, but uncorroborated by archaeological evidence. The Satavahana kingdom mainly comprised the present-day Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, and Maharashtra. At different times, their rule extended to parts of modern Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka. The dynasty had different capital cities at different times, including Pratishthana (Paithan) and Amaravati (Dharanikota). The origin of the dynasty is uncertain, but according to the Puranas, their first king overthrew the Kanva dynasty. In the post-Maurya era, the Satavahanas established peace in the Deccan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary sources for the written records of the Mauryan times are partial records of the lost history of Megasthenes in Roman texts of several centuries later; the Edicts of Ashoka, which were first read in the modern era by James Prinsep after he had deciphered the Brahmi and Kharoshthi scripts in 1838; and the ''Arthashastra'', a work first discovered in the early 20th century,: "... another source that enjoyed high standing as a description of the early Mauryan state was the Arthashastra, a treatise on power discovered in the early twentieth century." and previously attributed to Chanakya, but now thought to be composed by multiple authors in the first centuries of the common era. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |