|
Quinoxalines
A quinoxaline, also called a benzopyrazine, in organic chemistry, is a heterocyclic compound containing a ring complex made up of a benzene ring and a pyrazine ring. It is isomeric with other naphthyridines including quinazoline, phthalazine and cinnoline. It is a colorless oil that melts just above room temperature. Although quinoxaline itself is mainly of academic interest, quinoxaline derivatives are used as dyes, pharmaceuticals (such as varenicline), and antibiotics such as olaquindox, carbadox, echinomycin, levomycin and actinoleutin. Synthesis They can be formed by condensing ''ortho''-diamines with 1,2-diketones. The parent substance of the group, quinoxaline, results when glyoxal is condensed with 1,2-diaminobenzene. Substituted derivatives arise when α-ketonic acids, α-chlorketones, α-aldehyde alcohols and α-ketone alcohols are used in place of diketones. Quinoxaline and its analogues may also be formed by reduction of amino acids substituted 1,5-difluoro-2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varenicline
Varenicline, sold under the brand names Chantix and Champix among others, is a medication used for smoking cessation and for the treatment of dry eye syndrome. It is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist. When activated, this receptor leads to the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, the brain's reward center, thereby reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms with smoking cessation, although less pronounced than a full agonist (e.g. nicotine). Common side effects include nausea, insomnia, abnormal dreams, headache, and nasopharyngitis ( inflammation of the nose and throat). Despite these potential adverse effects, varenicline has proven efficacy in helping individuals quit smoking. It is estimated that approximately one in eleven smokers who use varenicline successfully remain abstinent from tobacco at six months. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The medication is available as a generic medication. In the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbadox
Carbadox is a veterinary drug that combats infection in swine, particularly swine dysentery. Indications Carbadox is indicated for control of swine dysentery (vibrionic dysentery, bloody scours, or hemorrhagic dysentery); control of bacterial swine enteritis (salmonellosis or necrotic enteritis caused by ''Salmonella enterica''); aid in the prevention of migration and establishment of large roundworm (''Ascaris suum'') infections; aid in the prevention of establishment of nodular worm ('' Oesophagostomum'') infections. Safety In animal models, carbadox has been shown to be carcinogenic and to induce birth defects. The Food and Drug Administration's Center for Veterinary Medicine has questioned the safety in light of its possible carcinogenicity. Regulation Carbadox is approved in the United States only for use in swine and may not be used within 42 days of slaughter or used in pregnant animals. In 2016, the United States Food and Drug Administration moved to ban its use in por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinomycin
Echinomycin is a peptide antibiotic. It is a dimer of two peptides creating a cyclic structure. It contains a bicyclic aromatic chromophore that is attached to the dimerized cyclic peptide core and a thioacetal bridge. It intercalates into DNA at two specific sites, thereby blocking the binding of hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1alpha). Biosynthesis Echinomycin is a bis-intercalator peptide and is biosynthesized by a unique nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS). Echinomycin is isolated from various bacteria such as ''Streptomyces'' ''lasalienis''. It belongs to a family of quinoxaline antibiotics. There is great interest in this group of compounds because they have very potent antibacterial, anticancer, and antiviral activities. The biosynthesis of echinomycin starts with molecule QC. L-tryptophan is the precursor for QC and its biosynthesis parallels the first stage of nikkomycin biosynthesis. After QC is biosynthesized, the adenylation domain-containing Ecm1 acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzil
Benzil (i.e. Bz2, systematically known as 1,2-diphenylethane-1,2-dione) is the organic compound with the formula ( C6H5 CO)2, generally abbreviated ( PhCO)2. This yellow solid is one of the most common diketones. Its main use is as a photoinitiator in polymer chemistry.Hardo Siegel, Manfred Eggersdorfer "Ketones" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, 2002 by Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Structure The compound's most noteworthy structural feature is the long carbon-carbon bond of 1.54 Å, which indicates the absence of pi-bonding between the two carbonyl centers. The PhCO centers are planar, but the pair of benzoyl groups are twisted with respect to the other with a dihedral angle of 117°. In less hindered analogues (glyoxal, biacetyl, oxalic acid derivatives), the (RCO)2 group adopts a planar, anti-conformation. Applications Most benzil can be used as a photoinitiator in the free-radical curing of polymer networks. It absorbs ultraviolet radiation at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
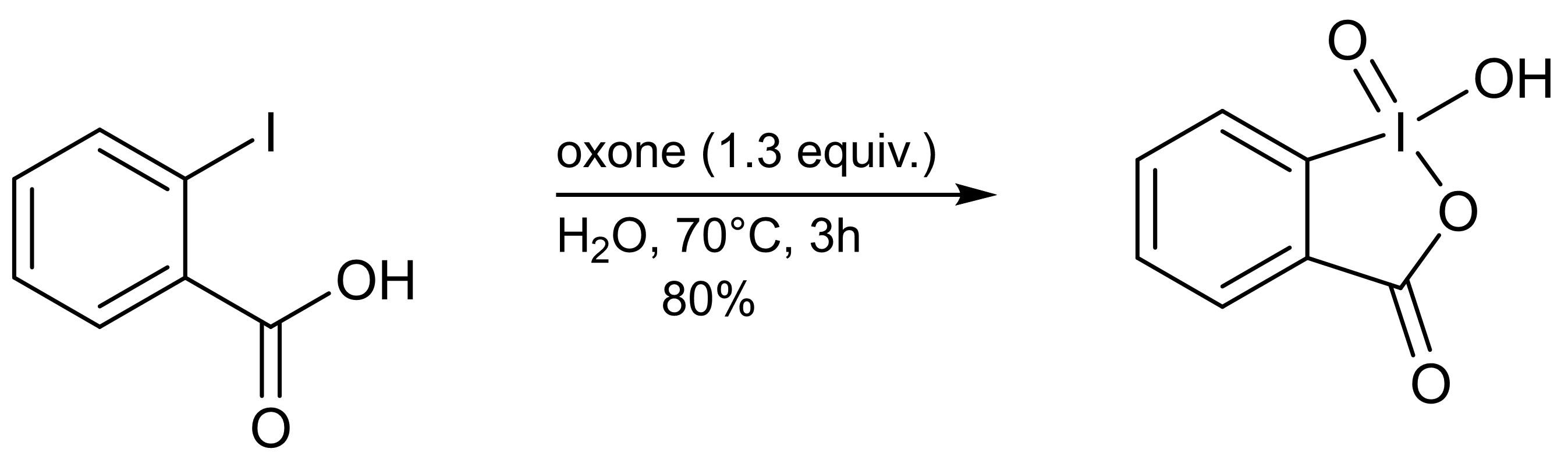
2-Iodoxybenzoic Acid
2-Iodoxybenzoic acid (IBX) is an organic compound used in organic synthesis as an oxidizing agent. This periodinane is especially suited to oxidize alcohols to aldehydes. IBX is most often prepared from 2-iodobenzoic acid and a strong oxidant such as potassium bromate and sulfuric acid, or more commonly, oxone. One of the main drawbacks of IBX is its limited solubility; IBX is insoluble in many common organic solvents. IBX is an impact- and heat-sensitive explosive (>200°C). Commercial IBX is stabilized by carboxylic acids such as benzoic acid and isophthalic acid. Preparation IBX can be prepared in a single step by adding an excess of oxone to an aqueous solution of 2-iodobenzoic acid. After warming the solution to 70°C for three hours, the precipitated IBX is collected as a white crystalline solid (80% yield, ≥95% purity). Decomposition of IBX to 2-iodosobenzoic acid and 2-iodobenzoic acid occurs at elevated temperatures, and therefore purification by recrystallization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde
In organic chemistry, an aldehyde () (lat. ''al''cohol ''dehyd''rogenatum, dehydrogenated alcohol) is an organic compound containing a functional group with the structure . The functional group itself (without the "R" side chain) can be referred to as an aldehyde but can also be classified as a formyl group. Aldehydes are a common motif in many chemicals important in technology and biology. Structure and bonding Aldehyde molecules have a central carbon atom that is connected by a double bond to oxygen, a single bond to hydrogen and another single bond to a third substituent, which is carbon or, in the case of formaldehyde, hydrogen. The central carbon is often described as being sp2- hybridized. The aldehyde group is somewhat polar. The bond length is about 120–122 picometers. Physical properties and characterization Aldehydes have properties that are diverse and that depend on the remainder of the molecule. Smaller aldehydes such as formaldehyde and acetaldehyde are solubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |