|
Query Languages
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve information. A well known example is the Structured Query Language (SQL). Types Broadly, query languages can be classified according to whether they are ''database'' query languages or ''information retrieval'' query languages. The difference is that a database query language attempts to give factual answers to factual questions, while an information retrieval query language attempts to find documents containing information that is relevant to an area of inquiry. Other types of query languages include: * Full-text. The simplest query language is treating all terms as bag of words that are to be matched with the postings in the inverted index and where subsequently ranking models are applied to retrieve the most relevant documents. Only tokens ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Computer Language
A computer language is a formal language used to communicate with a computer. Types of computer languages include: * Software construction#Construction languages, Construction language – all forms of communication by which a human can Computer programming, specify an executable problem solution to a computer ** Command language – a language used to control the tasks of the computer itself, such as starting programs ** Configuration file#Configuration languages, Configuration language – a language used to write configuration files ** Programming language – a formal language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer ***Scripting language – a type of programming language which typically is interpreted at runtime rather than being compiled ** Query language – a language used to make Information retrieval, queries in databases and information systems ** Transformation language – designed to transform some input te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cypher Query Language
Cypher is a declarative graph query language that allows for expressive and efficient data querying in a property graph. Cypher was largely an invention of Andrés Taylor while working for Neo4j, Inc. (formerly Neo Technology) in 2011. Cypher was originally intended to be used with the graph database Neo4j, but was opened up through the openCypher project in October 2015. The language was designed with the power and capability of SQL (standard query language for the relational database model) in mind, but Cypher was based on the components and needs of a database built upon the concepts of graph theory. In a graph model, data is structured as nodes ( vertices in math and network science) and relationships (edges in math and network science) to focus on how entities in the data are connected and related to one another. Graph model Cypher is based on the Property Graph Model, which organizes data into nodes and edges (called “relationships” in Cypher). In addition to tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Apache Software Foundation
The Apache Software Foundation ( ; ASF) is an American nonprofit corporation (classified as a 501(c)(3) organization in the United States) to support a number of open-source software projects. The ASF was formed from a group of developers of the Apache HTTP Server, and incorporated on March 25, 1999. it includes approximately 1000 members. The Apache Software Foundation is a decentralized open source community of developers. The software they produce is distributed under the terms of the Apache License, a permissive open-source license for free and open-source software (FOSS). The Apache projects are characterized by a collaborative, consensus-based development process and an open and pragmatic software license, which is to say that it allows developers, who receive the software freely, to redistribute it under non-free terms. Each project is managed by a self-selected team of technical experts who are active contributors to the project. The ASF is a meritocracy, implying tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Gremlin (programming Language)
Gremlin is a graph traversal language and virtual machine developed by Apache TinkerPop of the Apache Software Foundation. Gremlin works for both OLTP-based graph databases as well as OLAP-based graph processors. Gremlin's automata and functional language foundation enable Gremlin to naturally support: imperative and declarative querying; host language agnosticism; user-defined domain specific languages; an extensible compiler/optimizer, single- and multi-machine execution models; hybrid depth- and breadth-first evaluation with Turing completeness. As an explanatory analogy, Apache TinkerPop and Gremlin are to graph databases what the JDBC and SQL are to relational databases. Likewise, the Gremlin traversal machine is to graph computing as what the Java virtual machine is to general purpose computing. History * 2009-10-30 the project is born, and immediately named "TinkerPop" * 2009-12-25 v0.1 is the first release * 2011-05-21 v1.0 is released * 2012-05-24 v2.0 is rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Knowledge Modeling
Knowledge modeling is a process of creating a computer interpretable model of knowledge or standard specifications about a kind of process and/or about a kind of facility or product. The resulting knowledge model can only be computer interpretable when it is expressed in some knowledge representation language or data structure that enables the knowledge to be interpreted by software and to be stored in a database or data exchange file. Knowledge-based engineering or knowledge-aided design is a process of computer-aided usage of such knowledge models for the design of products, facilities or processes. The design of products or facilities then uses the knowledge model to guide the creation of the facility or product that need to be designed. In other words, it used knowledge about a kind of object to create a product model of an (imaginary) individual object. Similarly, the design of a particular process implies the creation of a process model, which design activity can be guided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Gellish English
Gellish is an ontology language for data storage and communication, designed and developed by Andries van Renssen since mid-1990s. It started out as an engineering modeling language ("Generic Engineering Language", giving it the name, "Gellish") but evolved into a universal and extendable conceptual data modeling language with general applications. Because it includes domain-specific terminology and definitions, it is also a semantic data modelling language and the Gellish modeling methodology is a member of the family of semantic modeling methodologies. Although its concepts have 'names' and definitions in various natural languages, Gellish is a natural-language-independent formal language. Any natural language variant, such as Gellish Formal English is a controlled natural language. Information and knowledge can be expressed in such a way that it is computer-interpretable, as well as system-independent and natural language independent. Each natural language variant is a struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
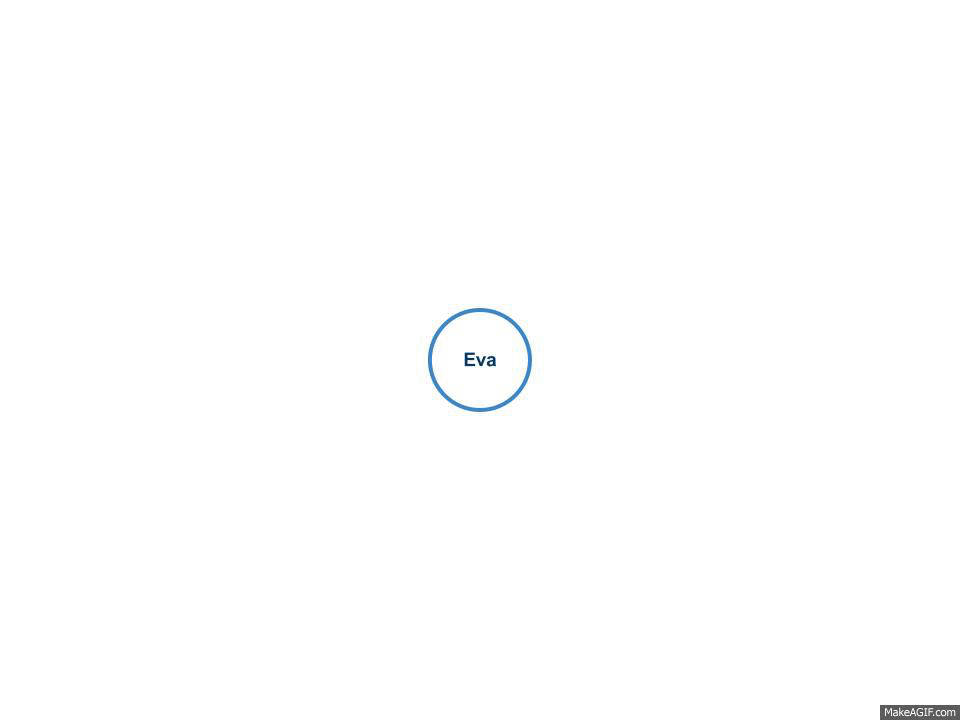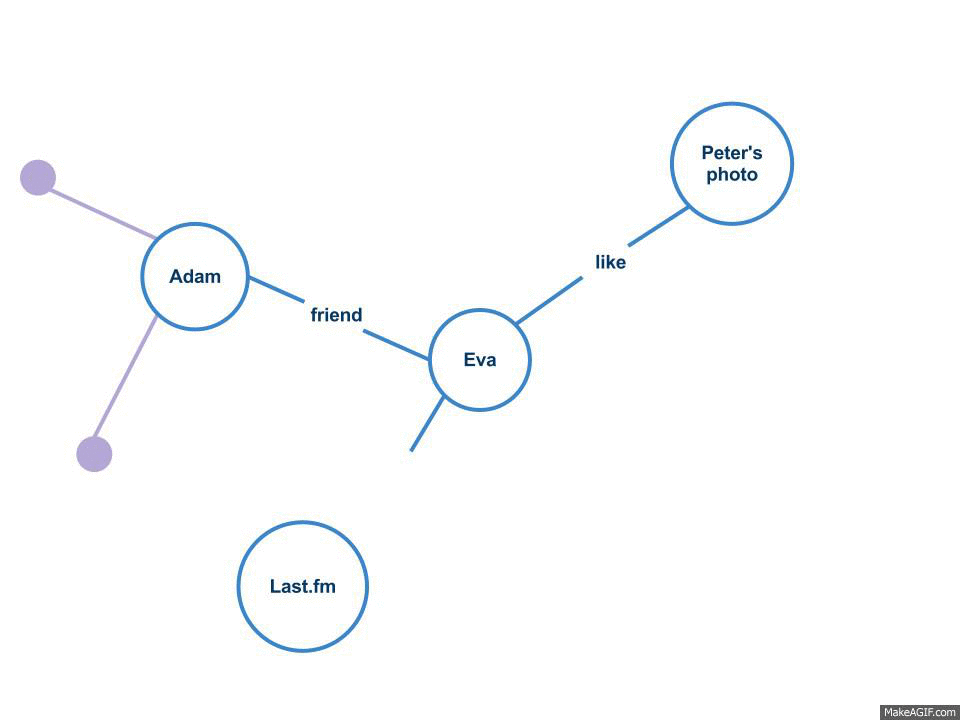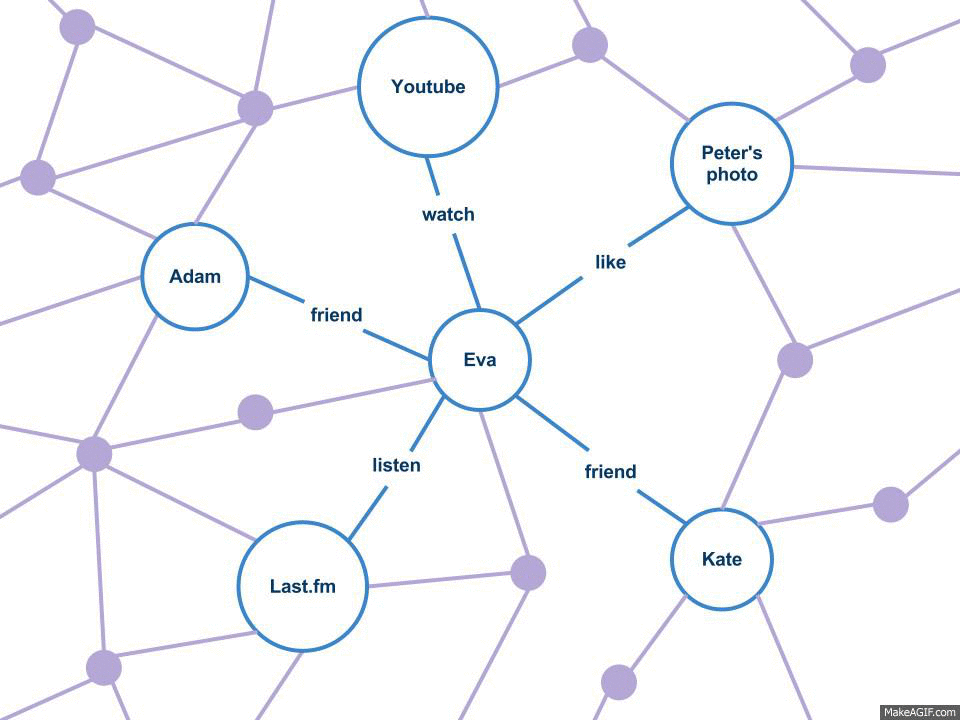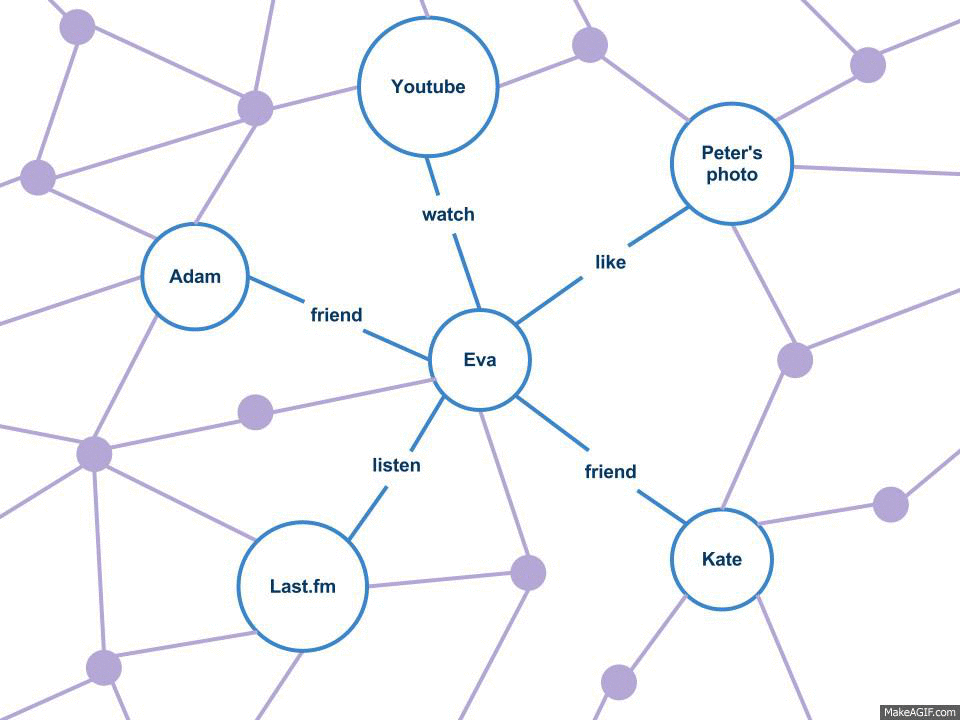 |
Graph API
A social graph is a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph that represents social relations between entities. It is a model or representation of a social network. The social graph has been referred to as "the global mapping of everybody and how they're related". The term was used as early as 1964, albeit in the context of isoglosses. Leo Apostel uses the term in the context here in 1978. The concept was originally called sociogram. The term was popularized at the Facebook F8 conference on May 24, 2007, when it was used to explain how the newly introduced Facebook Platform would take advantage of the relationships between individuals to offer a richer online experience. The definition has been expanded to refer to a social graph of all Internet users. Since explaining the concept of the social graph, Mark Zuckerberg, one of the founders of Facebook, has often touted Facebook's goal of offering the website's social graph to other websites so that a user's relationships can be put ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Facebook Query Language
__NOTOC__ Facebook Query Language (FQL) is a query language that allows querying Facebook user data by using a SQL-style interface, avoiding the need to use the Facebook Platform Graph API. Data returned from an FQL query is in JSON JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced or ) is an open standard file format and electronic data interchange, data interchange format that uses Human-readable medium and data, human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consi ... format by default. History FQL was first made publicly available in February 2007. FQL was no longer available as of August 7, 2016, when Facebook API 2.0 was no longer available. Facebook API versions newer than API 2.0 do not support FQL. Example In the following query, four different types of data are retrieved from a single table (status) and for a single user ("me"): SELECT status_id,message,time,source FROM `status` WHERE uid = me() This query can run by querying the Facebook graph endpoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Knowledge Representation
Knowledge representation (KR) aims to model information in a structured manner to formally represent it as knowledge in knowledge-based systems whereas knowledge representation and reasoning (KRR, KR&R, or KR²) also aims to understand, reason, and interpret knowledge. KRR is widely used in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) with the goal to represent information about the world in a form that a computer system can use to solve complex tasks, such as diagnosing a medical condition or having a natural-language dialog. KR incorporates findings from psychology about how humans solve problems and represent knowledge, in order to design formalisms that make complex systems easier to design and build. KRR also incorporates findings from logic to automate various kinds of ''reasoning''. Traditional KRR focuses more on the declarative representation of knowledge. Related knowledge representation formalisms mainly include vocabularies, thesaurus, semantic networks, axiom system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
F-logic
F-logic (Frame logic) is a knowledge representation and ontology language. It combines the advantages of conceptual modeling with Object-oriented programming, object-oriented, Frame (artificial intelligence), frame-based languages, and offers a Declarative programming, declarative, compact and simple Syntax (programming languages), syntax, and the well-defined semantics of a logic programming language. Features include, among others, object identity, complex objects, Inheritance (object-oriented programming), inheritance, Polymorphism (computer science), polymorphism, query methods, Encapsulation (computer programming), encapsulation. F-logic stands in the same relationship to object-oriented programming as classical relational calculus stands to relational database programming. Overview F-logic was developed by Michael Kifer at Stony Brook University and Georg Lausen at the University of Mannheim. F-logic was originally developed for deductive databases, but is now used most often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Deductive Database
A deductive database is a database system that can make deductions (i.e. conclude additional facts) based on rules and facts stored in its database. Datalog is the language typically used to specify facts, rules and queries in deductive databases. Deductive databases have grown out of the desire to combine logic programming with relational databases to construct systems that support a powerful formalism and are still fast and able to deal with very large datasets. Deductive databases are more expressive than relational databases but less expressive than logic programming systems such as Prolog. In recent years, deductive databases have found new application in data integration, information extraction, networking, program analysis, security, and cloud computing. Deductive databases reuse many concepts from logic programming; rules and facts specified in Datalog look very similar to those written in Prolog, but there are some important differences: * Order sensitivity and proced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Datalog
Datalog is a declarative logic programming language. While it is syntactically a subset of Prolog, Datalog generally uses a bottom-up rather than top-down evaluation model. This difference yields significantly different behavior and properties from Prolog. It is often used as a query language for deductive databases. Datalog has been applied to problems in data integration, networking, program analysis, and more. Example A Datalog program consists of ''facts'', which are statements that are held to be true, and ''rules'', which say how to deduce new facts from known facts. For example, here are two facts that mean ''xerces is a parent of brooke'' and ''brooke is a parent of damocles'': parent(xerces, brooke). parent(brooke, damocles). The names are written in lowercase because strings beginning with an uppercase letter stand for variables. Here are two rules: ancestor(X, Y) :- parent(X, Y). ancestor(X, Y) :- parent(X, Z), ancestor(Z, Y). The :- symbol is read as "if", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |