|
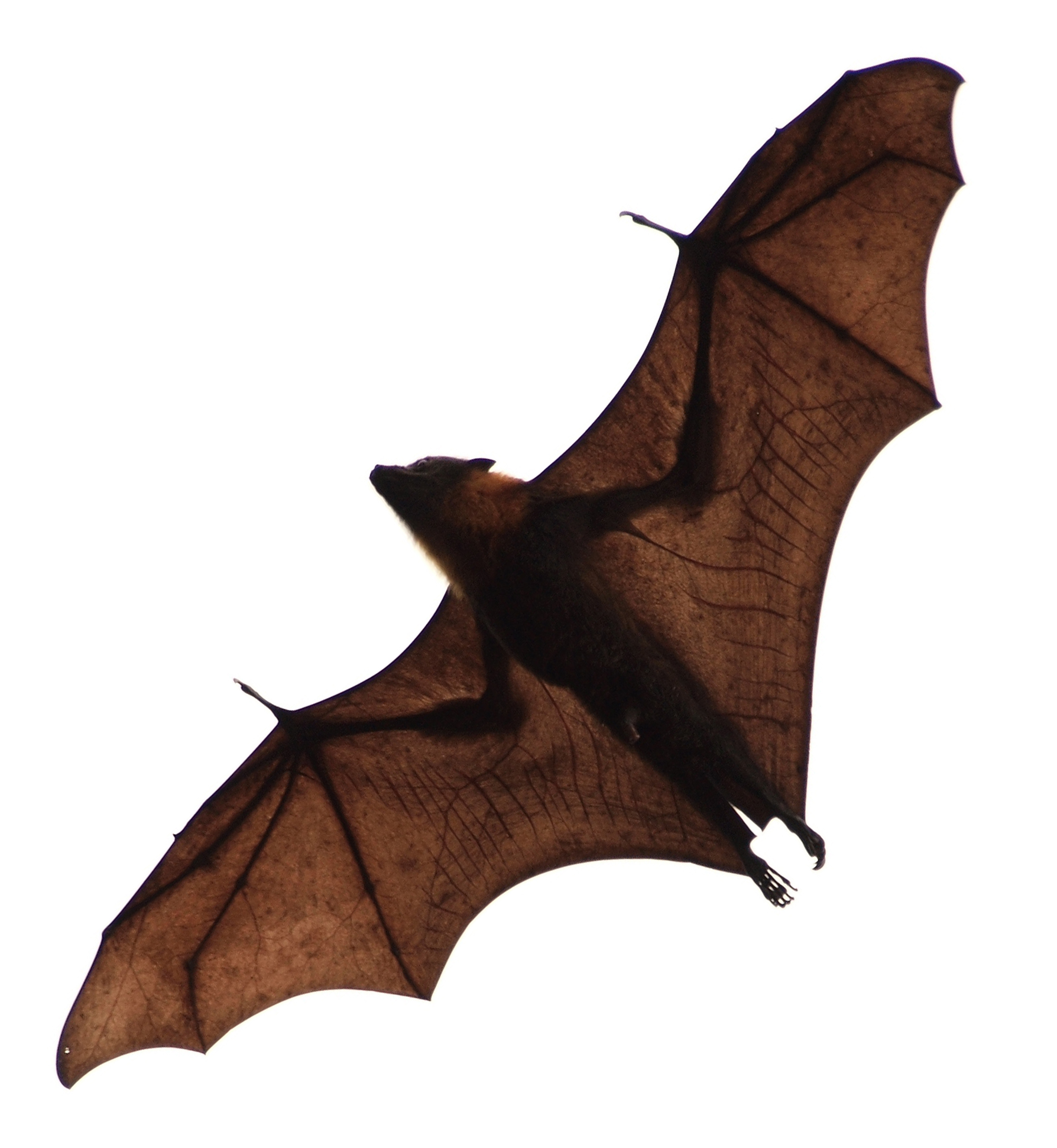
Pteropus
''Pteropus'' (suborder Yinpterochiroptera) is a genus of megabats which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names. They live in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia, East Africa, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. There are at least 60 extant species in the genus. Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell. Most, but not all, are nocturnal. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot echolocate. They have long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as overhunting, culling, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been made extinct in modern times by overhunting. Flying foxes are often persecuted for their real or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteropus Niger
''Pteropus'' (suborder Yinpterochiroptera) is a genus of megabats which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names. They live in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia, East Africa, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. There are at least 60 Extant taxon, extant species in the genus. Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell. Most, but not all, are nocturnality, nocturnal. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot Animal echolocation, echolocate. They have R/K selection theory#K-selection, long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as Overexploitation, overhunting, culling, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabat
Megabats constitute the Family (biology), family Pteropodidae of the Order (biology), order Chiroptera. They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genus, genera ''Acerodon'' and ''Pteropus''—Pteropus, flying foxes. They are the only member of the Superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since Subfamily, subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various Tribe (biology), tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described. The leading theory of the evolution of megabats has been determined primarily by genetic data, as the fossil record for this family is the most fragmented of all bats. They likely evolved in Australasia, with the common ancestor of all living pteropodids existing approximately 31 million years ago. Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteropus Tonganus
The insular flying fox or Pacific flying fox (''Pteropus tonganus'') is a species of flying fox in the family Pteropodidae. It is geographically widespread, the most widespread flying fox in the Pacific: it is found in American Samoa, the Cook Islands, Fiji, New Caledonia, Niue, Papua New Guinea, Samoa (where it is called ''pe'a fanua, pe'a fai'' and ''taulaga''), the Solomon Islands, Tonga, and Vanuatu. History Archaeologists on an excavation site at Rurutu announced in 2006 some important fossil finds: Description The range of coloration in this bat species varies somewhat. Its back is described as black or seal brown; its mantle has been called orange, yellow, cream Buff (colour), buff, and Tawny (color), tawny. This bat lacks an interfemoral membrane; its forearms and tibia are bare, and the fur of the males is described as "stiff, short, oily hairs". In flight, their outstretched wings appear a translucent dark brown when viewed from below. Distribution and habitat The i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipah Virus
Nipah virus (''Henipavirus nipahense'') is a bat-borne, Zoonosis, zoonotic virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a very high mortality rate (40-75%). Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus have occurred in South East Africa and Southeast Asia. Nipah virus belongs to the genus ''Henipavirus'' along with the Hendra virus, which has also caused disease outbreaks. Virology Like other henipaviruses, the Nipah virus genome is a single (non-segmented) negative-sense, single-stranded RNA of over 18 kb, which is substantially longer than that of other Paramyxoviridae, paramyxoviruses. The viral envelope, enveloped virus particles are variable in shape, and can be filamentous or spherical; they contain a helical nucleocapsid. Six structural proteins are generated: N (nucleocapsid), P (phosphoprotein), M (matrix), F (fusion), G (glycoprotein) and L (RNA polymerase). The ''P'' open reading frame also encodes three nonstructural pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Bat Lyssavirus
Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV) is a enzootic virus closely related to the rabies virus. It was first identified in a 5-month-old juvenile black flying fox (''Pteropus alecto'') collected near Ballina, New South Wales, Ballina in northern New South Wales, Australia, in January 1995 during a national surveillance program for the recently identified Hendra virus. ABLV is the seventh member of the genus ''Lyssavirus'' (which includes Rabies virus) and the only ''Lyssavirus'' member present in Australia. ABLV has been categorized to the Phylogroup I of the Lyssaviruses. Virology Molecular structure The Australian bat lyssavirus (ABLV) shares many structural characteristics with the other Lyssaviruses, despite being genetically and serologically distinct from the others. Visually, ABLV is a bullet shaped virus. Molecularly, ABLV is an enveloped, negative-sense, single-stranded RNA virus. The (-)ssRNA genome is relatively small, containing 12kilobases of genetic material and encod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yinpterochiroptera
The Yinpterochiroptera (or Pteropodiformes) is a suborder of the Chiroptera, which includes taxa formerly known as megabats and five of the microbat families: Rhinopomatidae, Rhinolophidae, Hipposideridae, Craseonycteridae, and Megadermatidae. This suborder is primarily based on molecular genetics data. This proposal challenged the traditional view that megabats and microbats form monophyletic groups of bats. Further studies are being conducted, using both molecular and morphological cladistic methodology, to assess its merit. The term Yinpterochiroptera is constructed from the words Pteropodidae (the family of megabats) and Yinochiroptera (a term proposed in 1984 by Karl F. Koopman to refer to certain families of microbats). Recent studies using transcriptome data have found strong support for the Yinpterochiroptera-Yangochiroptera classification system. Researchers have created a relaxed molecular clock that estimates the divergence between Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiropter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henipavirus
''Henipavirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Paramyxoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales'' containing five established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably Pteropus, pteropid fruit bats (flying foxes), microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonosis, zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern. In 2009, RNA sequences of three novel viruses in phylogenetic relationship to known henipaviruses were detected in African straw-colored fruit bats (''Eidolon helvum'') in Ghana. The finding of these novel henipaviruses outside Australia and Asia indicates that the region of potential endemicity of henipaviruses may be worldwide. These African henipaviruses are slowly being characterised. Nipah virus and He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains. Insects are the major pollinators of most plants, and insect pollinators include all families of bees and most families of Aculeata, aculeate wasps; ants; many families of flies; many lepidopterans (both butterflies and moths); and many families of beetles. Vertebrates, mainly bats and birds, but also some non-bat mammals (monkeys, lemurs, Phalangeriformes, possums, rodents) and some lizards pollinate certain plants. Among the pollinating birds are hummingbirds, honeyeaters and sunbirds with long beaks; they pollinate a number of deep-throated flowers. Humans may also carry out artificial pollination. A pollinator is different from a pollenizer, a plant that is a source of pollen for the pollination process. Background Plants fall into pollination s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Reservoir
In Infection, infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir is usually a living Host (biology), host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside of which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease for the reservoir itself. By some definitions a reservoir may also be an environment external to an organism, such as a volume of contaminated air or water. Because of the enormous variety of infectious microorganisms capable of causing disease, precise definitions for what constitutes a natural reservoir are numerous, various, and often conflicting. The reservoir concept applies only for pathogens capable of infecting more than one host population and only with respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes encephalitis in humans and other mammals. It was historically referred to as hydrophobia ("fear of water") because its victims panic when offered liquids to drink. Early symptoms can include fever and abnormal sensations at the site of exposure. These symptoms are followed by one or more of the following symptoms: nausea, vomiting, violent movements, uncontrolled excitement, fear of water, an inability to move parts of the body, confusion, and loss of consciousness. Once symptoms appear, the result is virtually always death. The time period between contracting the disease and the start of symptoms is usually one to three months but can vary from less than one week to more than one year. The time depends on the distance the virus must travel along Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nerves to reach the central nervous system. Rabies is caused by lyssaviruses, including the rabies virus and Australian bat lyssavirus. It is spread when an i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben
Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben (; 22 June 1744 – 19 August 1777) was a German naturalist from Quedlinburg. Erxleben was professor of physics and veterinary medicine at the University of Göttingen The University of Göttingen, officially the Georg August University of Göttingen (, commonly referred to as Georgia Augusta), is a Public university, public research university in the city of Göttingen, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1734 .... He wrote ''Anfangsgründe der Naturlehre'' (1772) and ''Systema regni animalis'' (1777). He was founder of the first and oldest academic veterinary school in Germany, the Institute of Veterinary Medicine, in 1771. He was the son of Dorothea Christiane Erxleben, the first woman in Germany to earn a medical degree. Works * 1767 ''Einige Anmerkungen über das Insektensystem des Hr. Geoffroy und die Schäfferschen Verbesserungen desselben''. Hannoverisches Magazin, Hannover (Stück 20). 305–316. * 1772 ''Anfangsgründe der Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |