|
Pteraspidomorphi
Pteraspidomorpha is an extinct class of early jawless fish. They have long been regarded as closely related or even ancestral to jawed vertebrates, but the few characteristics they share with the latter are now considered as basal traits for all vertebrates. Characteristics Pteraspidomorphs are characterized by their massive dermal head armour having large, median, ventral and dorsal plates or shields. Janvier, Philippe (1997Pteraspidomorphi''The Tree of Life Web Project''. The fossils show extensive shielding of the head. Many had hypocercal tails in order to generate lift to increase ease of movement through the water for their armoured bodies, which were covered in dermal bone. They also had sucking mouth parts and some species may have lived in fresh water. Most pteraspidomorphs were marine, but lived very near to the shore, in lagoons and deltas. Some groups are thought to have been fresh water-dwelling. They were certainly bottom-dwellers, as shown by traces of abrasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
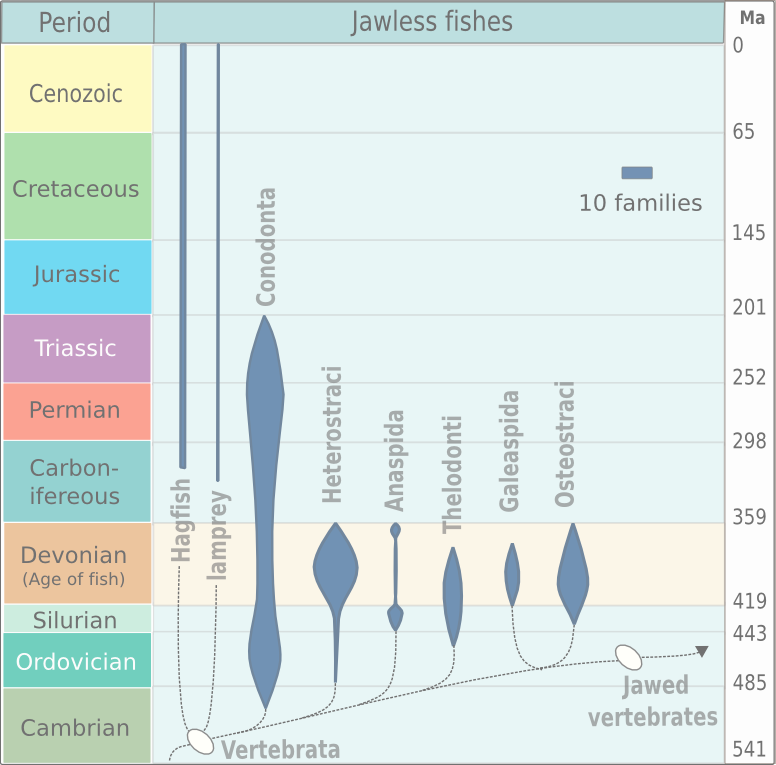
Jawless Fish
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arandaspidiformes
Arandaspida is a taxon of very early, jawless prehistoric fish which lived during the Ordovician period. Arandaspids represent some of the oldest known vertebrates. The group represents a subclass within the class Pteraspidomorphi, and contains only one order, the Arandaspidiformes. The oldest known genus of this group is '' Sacabambaspis'' found in South America. Characteristics The head armor of arandaspids is elongated, fusiform, with a rather flat dorsal shield, and a bulging ventral shield. In the anterior part of the dorsal shield are two closely set holes, which have been thought to be a paired pineal opening, but which are more likely the external openings of the endolymphatic ducts. The eyes, surrounded by a sclerotic ring, are housed in a notch at the anterior end of the dorsal shield. The nostrils are not clearly located, but may have been situated between the eyes. Ventrally, the ventral lip of the mouth is armed with long series of small oral plates which recall t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eriptychiida
Eriptychiida is an extinct marine taxon of vertebrate in the group Pteraspidomorphi. The order contains the genus, '' Eriptychius'', and fossilized specimens from this genus have been found in the Gull River Formation of Ontario, the Harding Formation of Colorado, and the Bighorn Dolomite of Wyoming. The group contains two documented species: ''Eriptychius americanus'' and ''Eriptychius orvigi''. Characteristics The structure of the dentine of eriptychiids is in many respects closer to that of heterostracans than to that of astraspids. This is the only argument to place them, as the closest relatives to heterostracans, among the Ordovician vertebrates. A 450 million years old fossil of eriptychius shows it had a skull consisting of separate cartilage plates, with the frontal plates being mineralized, and that a thin body armor covered the head. It appears to be the first step towards a more solid braincase in vertebrates. Taxonomy * Order † Eriptychiiformes Ørvig 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astraspida
Astraspida, or astraspids, are a small group of extinct armored jawless vertebrates, which lived in the Late Ordovician (about 450 million years ago) in North America. They are placed among the Pteraspidomorphi because of the large dorsal and ventral shield of their head armor. They are represented by a single genus, Astraspis, including possibly two species, ''A. desiderata'' and ''A. splendens'' but their remains are fairly abundant in Ordovician sandstones of the USA (Colorado, Arizona, Oklahoma, Wyoming) and Canada (Quebec Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...). The head armor of Astraspis is rather massive, with a series of ten gill openings lining the margin of the dorsal shield, and laterally placed eyes. The dorsal shield is ribbed by strong longitudinal crests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterostraci
Heterostraci (Ancient Greek, ἕτερος+ὄστρακον "those [with] a different shell" [-i is pl. of -us]) is an extinct subclass (biology), subclass of Pteraspidomorphi, pteraspidomorph, ostracoderm, jawless vertebrate that lived primarily in Marine (ocean), marine and estuary environments. Heterostraci existed from the mid-Ordovician to the conclusion of the Devonian. Description and anatomy The heterostracans differed from other Paleozoic agnathan taxa both in the arrangement and histology of their scales. Most heterostracans had two plates which form a large dorsal shield and a large ventral shield, and had series of scales arranged in various patterns on the sides of their bodies, the exact pattern differing from one group to another. In a few primitive forms, such as ''Lepidaspis'', the dorsal and ventral shields are composed of a mosaic of tiny scales. In most other known forms, though, these tiny scales have fused together to form the shield-plates. The scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostracoderm
Ostracodermi () or ostracoderms is an informal group of vertebrate animals that include all armored jawless fish of the Paleozoic Era. The term does not often appear in classifications today because it is paraphyletic (excluding jawed fishes and possibly the cyclostomes if anaspids are closer to them) and thus does not correspond to one evolutionary lineage. However, the term is still used as an informal way of loosely grouping together the armored jawless fishes. An innovation of ostracoderms was the use of gills not for feeding, but exclusively for respiration. Earlier chordates with gill precursors used them for both respiration and feeding. Ostracoderms had separate pharyngeal gill pouches along the side of the head, which were permanently open with no protective operculum. Unlike invertebrates that use ciliated motion to move food, ostracoderms used their muscular pharynx to create a suction that pulled small and slow-moving prey into their mouths. Swiss anatomist L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate (anatomy)
A plate in animal anatomy may refer to several things: Flat bones (examples: bony plates, dermal plates) of vertebrates * an appendage of the Stegosauria group of dinosaurs * articulated armoured plates covering the head of thorax of Placodermi (literally "plate-skinned"), an extinct class of prehistoric fish (including skull, thoracic and tooth plates) * bony shields of the Ostracoderms (armored jawless fishes) such as the dermal head armour of members of the class Pteraspidomorphi that include dorsal, ventral, rostral and pineal plates * plates of a carapace, such as the dermal plates of the shell of a turtle * dermal plates partly or completely covering the body of the fish in the order Gasterosteiformes that includes the sticklebacks and relatives * plates of dermal bones of the armadillo * Zygomatic plate, a bony plate derived from the flattened front part of the zygomatic arch (cheekbone) in rodent anatomy Other flat structures * hairy plate-like keratin scales of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteraspidiformes
Pteraspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan agnathan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Early Devonian strata of Europe and North America, and from Upper Silurian Canada. Anatomy A pteraspidiform heterostracan has the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, rostral, pineal plates, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Many genera were benthic, others were apparently active swimming nekton.Botella, Hector, and Richard A. Farina. "Flow pattern around the rigid cephalic shield of the Devonian agnathan Errivaspis waynensis (Pteraspidiformes: Heterostraci)." Palaeontology 51.5 (2008): 1141-1150/ref> Delicate, finger-like components of the anterior end of the ventral plate forming the edges of the mouth suggest that pteraspidiform heterostracans were filter-feeding, filter-feeders that selectively filtered specific sized plankton from the water column.Purnell, Mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathaspidiformes
Cyathaspidiformes is an extinct order of heterostracan vertebrates known from extensive fossil remains primarily from Silurian to Early Devonian strata of Europe, and North America, and from Early Devonian marine strata of Siberia. Anatomy Like their descendants, the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiform heterostracans had the cephalothorax enclosed in armor, formed from several plates, including dorsal, ventral, a dorsal spine derived from a scale, and a large, scale-covered tail. Thus, the living animals would have resembled tadpoles encased in massive armor. The majority of taxa have the rostral and pineal plates fused or merged with the dorsal plate, and in the amphiaspidids, all the plates of the cephalothorax were fused together into a single "muff-like" unit. Unlike the pteraspidids, all cyathaspidiforms are thought to be almost uniformly benthic in lifestyle, though only the amphiaspids and the ctenaspids are thought to be burrowers. Taxonomy The taxonomy of Cyathaspidif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |