|
Professorship Of Mineralogy And Petrology (Cambridge)
The Professorship of Mineralogy and Petrology is a statutory professorship at the University of Cambridge. It was created in 1931 following the simultaneous retirements of Alfred Harker, from the post of Reader in Petrology in the Department of Geology, Cambridge; and of Arthur Hutchinson, Professor of Mineralogy. A committee of the Council of the Senate of the university proposed that these two posts be discontinued, and the remit of the Professorship of Mineralogy be expanded to include the disciplines of petrology and crystallography. The Professorship was established in the newly created Department of Mineralogy and Petrology. The first incumbent was Prof Cecil Edgar Tilley, who was appointed in 1931. Tilley was succeeded in 1961 by William Alexander Deer. Since 1980, and following the appointment of Ron Oxburgh, the Professorship has been associated with the Department of Earth Sciences, Cambridge. The other statutory professorships in this department are the Woodwardian P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, world's third-oldest university in continuous operation. The university's founding followed the arrival of scholars who left the University of Oxford for Cambridge after a dispute with local townspeople. The two ancient university, ancient English universities, although sometimes described as rivals, share many common features and are often jointly referred to as Oxbridge. In 1231, 22 years after its founding, the university was recognised with a royal charter, granted by Henry III of England, King Henry III. The University of Cambridge includes colleges of the University of Cambridge, 31 semi-autonomous constituent colleges and List of institutions of the University of Cambridge#Schools, Faculties, and Departments, over 150 academic departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
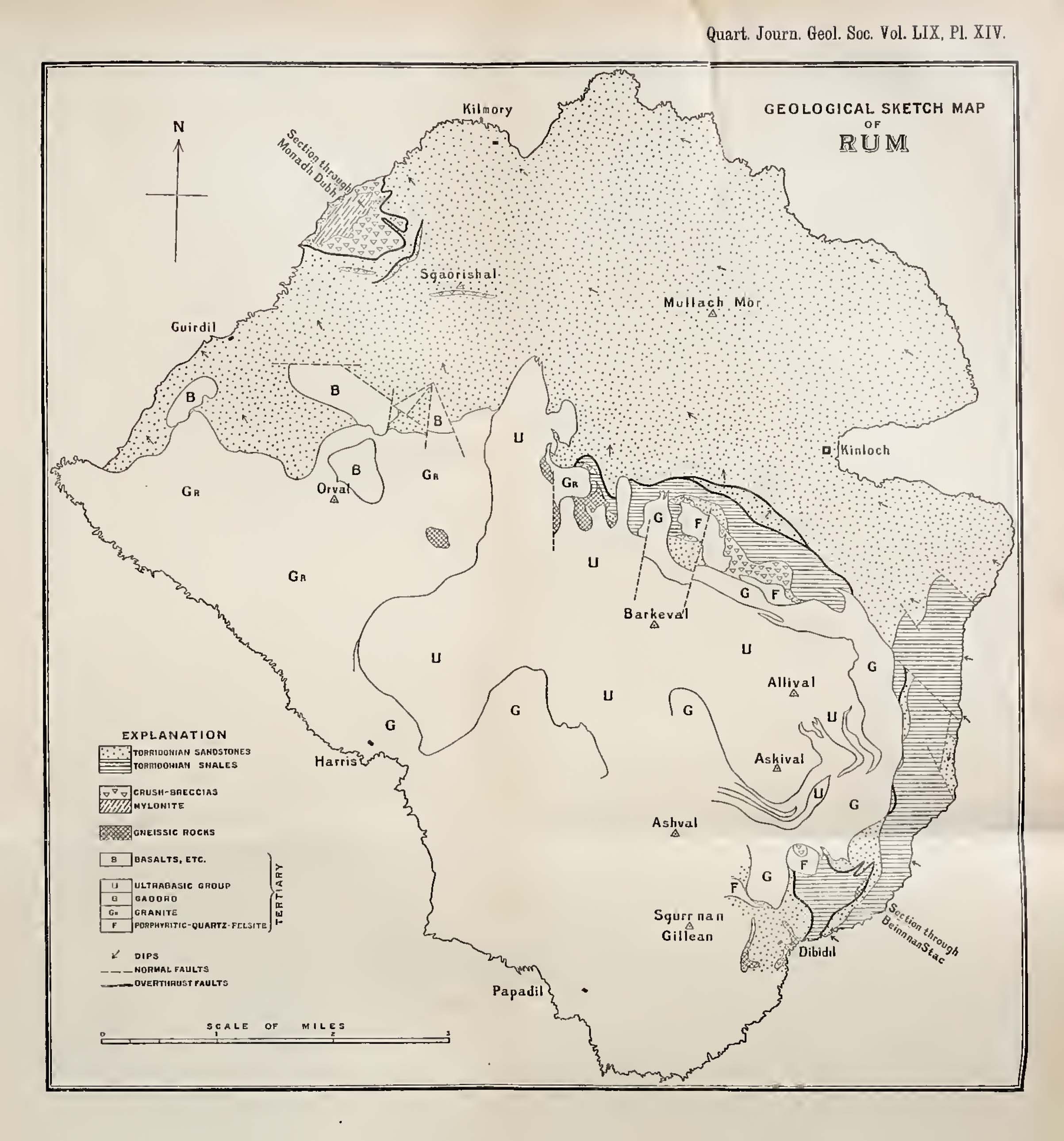
Alfred Harker
Alfred Harker Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS (19 February 1859 – 28 July 1939) was an English geologist who specialised in petrology and interpretive petrography. He was lecturer in petrology at the University of Cambridge for many years, and carried out field mapping for the Geological Survey of Scotland and geological studies of western Scotland and the Isle of Skye. He and other British geologists pioneered the use of thin sections and the petrographic microscope in interpretive petrology. Education and career Harker's father was the Yorkshire corn merchant Portas Hewart Harker, his mother Ellen Mary Harker. He attended Hull College, Hull and East Riding College, and the private Clewer House School (Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor) before enrolling as an undergraduate at St John's College, Cambridge, St. John's College (Cambridge) from where he graduated with an Master's degree, M.A. on 18 January 1882. Whilst at Cambridge he was an early member of the Sedgwick Club. In 1884 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Earth Sciences, University Of Cambridge
The Department of Earth Sciences at Cambridge is the University of Cambridge's Earth Sciences department. First formed around 1731, the department incorporates the Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences. History The department's history can be traced back to 1731 when the 1st Woodwardian Professor of Geology was appointed, in accordance with the bequest of John Woodward. The present Department of Earth Sciences was formed by an amalgamation of the Department of Geology, Department of Geodesy and Geophysics and the Department of Mineralogy and Petrology in 1980. When the three departments were amalgamated the Chair of Geophysics and Chair of Mineralogy and Petrology, along with the Woodwardian Professorship, were assigned to the newly formed Department of Earth Sciences. The main location of the department is at the Downing Site, Downing St. The Bullard Laboratories, located in West Cambridge on Madingley Rd is a satellite department of the main building. The department incorpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Hutchinson (mineralogist)
Arthur Hutchinson (6 July 1866 – 12 December 1937) was a British mineralogist. During World War I, and at the request of the Admiralty, he was asked to design gas masks suitable for the Navy; for his work, he was awarded the OBE. Hutchinson was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1922. He was master of Pembroke College, Cambridge, from 1928 to 1937, served on the Council of the Royal Society from 1932 to 1934, and was the Royal Society, Society's Vice-President for the year 1933-34. Life Hutchinson was born in London on 6 July 1866. His father was George Hutchinson of Woodside, Westmorland, and his mother was Deborah Richardson of Culgaith in Cumberland. He was educated at Clifton College and Christ's College, Cambridge, where he obtained first classes in both parts of the Natural Sciences Tripos, taking Part II in Chemistry with Mineralogy as a subsidiary subject in 1888. He took his PhD on a chemical thesis 'On the reduction of aromatic amides'. During World ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professor Of Mineralogy (Cambridge)
The Professorship of Mineralogy was a professorship at the University of Cambridge. It was founded in 1808 and discontinued when its final holder retired in 1931. It was replaced by the Professorship of Mineralogy and Petrology. Professors of Mineralogy * Edward Daniel Clarke (1808) * John Stevens Henslow (1822) * William Whewell (1828) * William Hallowes Miller Prof William Hallowes Miller FRS HFRSE LLD DCL (6 April 180120 May 1880) was a Welsh mineralogist and laid the foundations of modern crystallography. Miller indices are named after him, the method having been described in his ''Treatise on Cr ... (1832) * William James Lewis (1881) * Arthur Hutchinson (1926-1931) References {{DEFAULTSORT:Mineralogy, Professor of, Cambridge, University of Professorships at the University of Cambridge Department of Earth Sciences, University of Cambridge 1808 establishments in England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrology
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks, their mineralogy, composition, texture, structure and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together because both make heavy use of chemistry, chemical methods, and phase diagrams. Sedimentary petrology is commonly taught together with stratigraphy because it deals with the processes that form sedimentary rock. Modern sedimentary petrology is making increasing use of chemistry. Background Lithology was once approximately synonymous with petrography, but in current usage, lithology focuses on macroscopic hand-sample or outcrop-scale description of rocks while petrography is the speciality that deals with microscopic details. In the petroleum industry, lithology, or more specifically mud logging, is the graphic representation of geological formations being drilled through and drawn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the branch of science devoted to the study of molecular and crystalline structure and properties. The word ''crystallography'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (; "clear ice, rock-crystal"), and (; "to write"). In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming 2014 the International Year of Crystallography.UN announcement "International Year of Crystallography" iycr2014.org. 12 July 2012 Crystallography is a broad topic, and many of its subareas, such as X-ray crystallography, are themselves important scientific topics. Crystallography ranges from the fundamentals of crystal structure to the mathematics of Crystal system, crystal geometry, including those that are Aperiodic crystal, not periodic or quasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cecil Edgar Tilley
Cecil Edgar Tilley FRS, Hon FRSE, PGS (14 May 1894 – 24 January 1973) was an Australian-British petrologist and geologist. Life He was born in Unley, Adelaide, the youngest child of John Thomas Edward Tilley, a civil engineer from London, and his wife South Australia-born wife, Catherine Jane Nicholas. Cecil was educated at Adelaide High School, then studied Chemistry and Geology under William Rowan Browne at the University of Adelaide, and the University of Sydney, graduating in 1915. In 1916, during the First World War, he went to South Queensferry near Edinburgh in Scotland to work as a chemist Department of Explosives Supply. He returned to Australia in December 1918. He won an Exhibition of 1851 scholarship to the University of Cambridge in 1919, where he studied petrology under Alfred Harker, and completed his PhD in 1922. From 1923 he was employed at Cambridge University, first as demonstrator in petrology, and then lecturer in petrology in 1929. In 1931, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Alexander Deer
William Alexander (Alex) Deer FRS (26 October 1910 – 8 February 2009) was a distinguished British geologist, petrologist and mineralogist. Biography Alex Deer was born in Rusholme, Manchester, the son of William Deer. He attended Manchester Central High School and then Manchester University, and took up a research studentship at St John's College, Cambridge in 1934, to study for a PhD. Career In 1937, after completing his PhD, Deer was appointed an assistant lecturer at the University of Manchester. On the outbreak of war in 1939, Deer joined the Chemical Warfare Section of the Royal Engineers, and later transferred to the Operations Staff. He served in the Middle East, Burma and North Africa, and was appointed to the rank of lieutenant-colonel. Deer returned to Cambridge in 1946, where he was appointed University Demonstrator in mineralogy and petrology, and Fellow and Junior Bursar at St John's College, Cambridge. He was appointed a Tutor in 1949. In 1950, he was elected t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Oxburgh, Baron Oxburgh
Ernest Ronald Oxburgh, Baron Oxburgh (born 2 November 1934) is an English geologist, geophysicist and politician. Lord Oxburgh is well known for his work as a public advocate in both academia and the business world in addressing the need to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and develop alternative energy sources as well as his negative views on the consequences of current oil consumption. Early life Oxburgh was born in Liverpool on 2 November 1934. He remained there with his family throughout World War II, despite Luftwaffe air raids. He attended Liverpool Institute High School for Boys from 1942 to 1950. He is a graduate of University College, Oxford and Princeton University (PhD) (1960) where he worked on the emerging theory of plate tectonics with the famous geologist Harry Hammond Hess. Career Oxburgh has taught geology and geophysics at the Universities of Oxford and Cambridge. At Cambridge he was Professor of Mineralogy and Petrology, head of the Department of Earth Scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodwardian Professor Of Geology
The Woodwardian Professor of Geology is a professorship held in the Department of Earth Sciences at the University of Cambridge. It was founded by John Woodward in 1728 under the title of Professor of Fossils. Woodward's will left to the University a large collection of fossils and also dictated that the professor should be elected by the Archbishop of Canterbury, the Bishop of Ely, the President of the Royal Society, the President of the Royal College of Physicians, the Member of Parliament for the University of Cambridge, and the University Senate. Incumbents of the Woodwardian Professorship of Geology * Conyers Middleton, 1731 * Charles Mason, 1734 (died 1770 and described on hitomb in Orwell churchas "Woodwardian Professor of Fossils") *John Michell, 1762 * Samuel Ogden, 1764 * Thomas Green, 1778 *John Hailstone, 1788 *Adam Sedgwick Adam Sedgwick FRS (; 22 March 1785 – 27 January 1873) was a British geologist and Anglican priest, one of the founders of modern geology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |