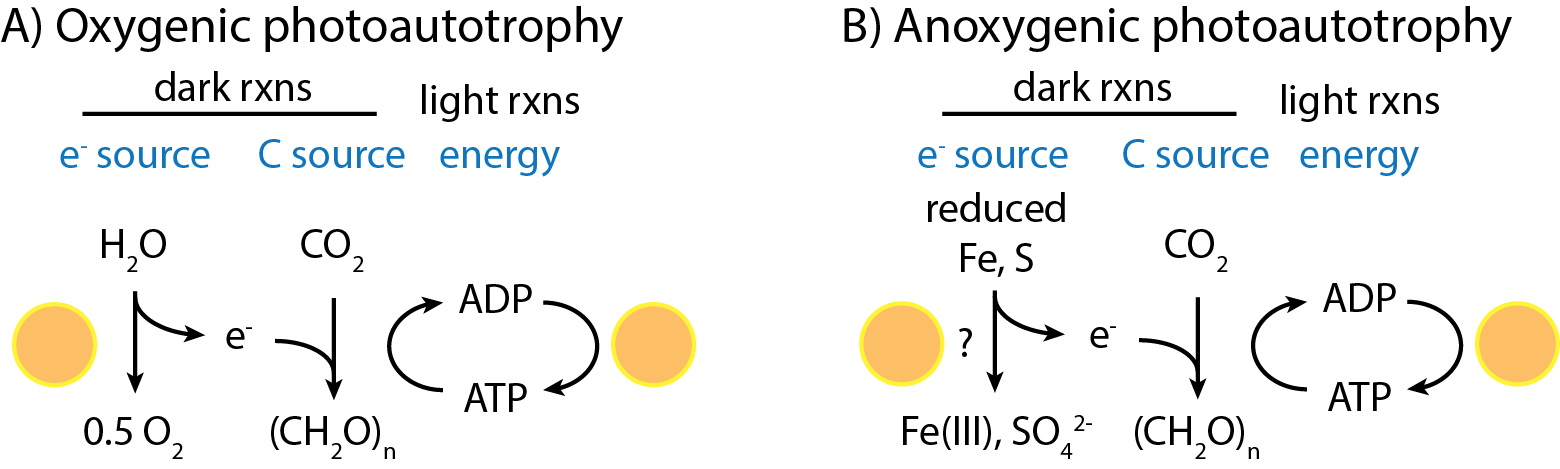
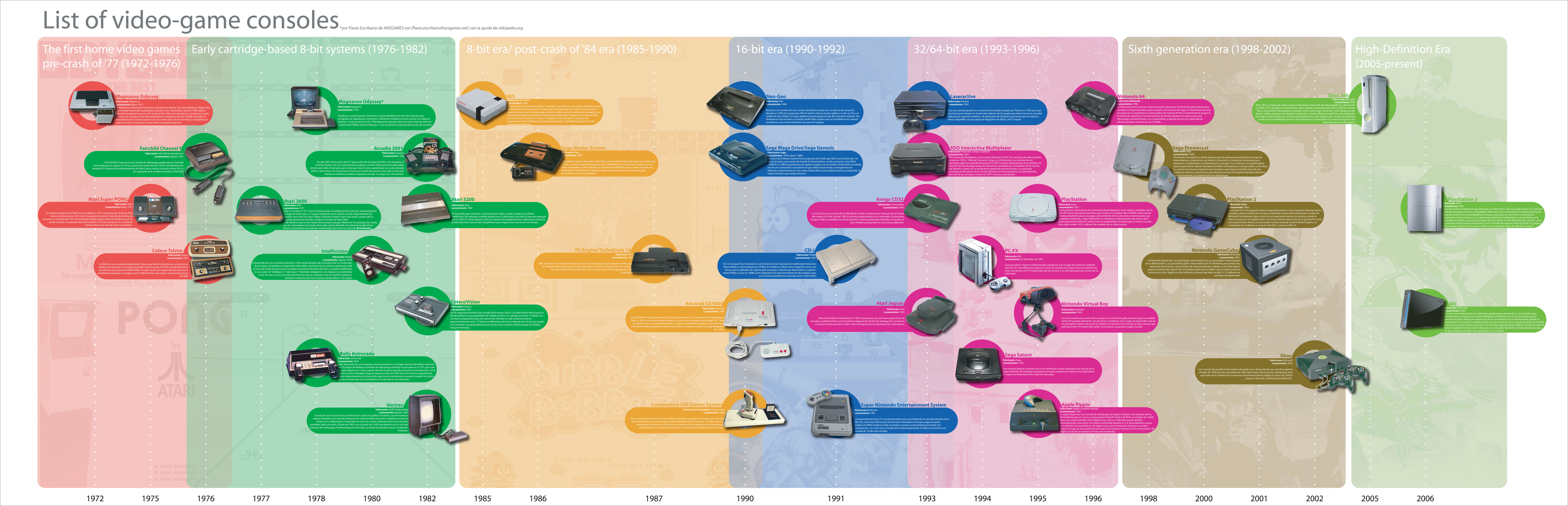
|
Production And Manufacturing
Production may refer to: Economics and business * Production (economics) * Production, the act of manufacturing goods * Production, in the outline of industrial organization, the act of making products (goods and services) * Production as a statistic, gross domestic product * Production line Arts, entertainment, and media * Production, the act or role of assembling, crafting, creating, or presenting, a work of art, or the work of art itself. Motion pictures * Production, film distributor of a company * Production, phase of filmmaking * Production, video production Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Production'' (album), by Mirwais, 2000 * Production, category of illusory magic trick * Production, phase of video games development * Production, Record producer's role * Production, theatrical performance Science and technology * Production, deployment environment where changes go "live" and users interact with it * Production (computer science), formal-gramm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production (economics)
Production is the process of combining various inputs, both material (such as metal, wood, glass, or plastics) and immaterial (such as plans, or knowledge) in order to create output. Ideally this output (economics), output will be a goods and services, good or service which has value (economics), value and contributes to the utility (economics), utility of individuals. The area of economics that focuses on production is called production theory, and it is closely related to the consumption (or consumer) theory of economics. The production process and output directly result from productively utilising the original inputs (or factors of production). Known as primary producer goods or services, land, labour, and capital are deemed the three fundamental factors of production. These primary inputs are not significantly altered in the output process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Producer
A record producer or music producer is a music creating project's overall supervisor whose responsibilities can involve a range of creative and technical leadership roles. Typically the job involves hands-on oversight of recording sessions; ensuring artists deliver acceptable and quality performances, supervising the technical engineering of the recording, and coordinating the production team and process. The producer's involvement in a musical project can vary in depth and scope. Sometimes in popular genres the producer may create the recording's entire sound and structure. However, in classical music recording, for example, the producer serves as more of a liaison between the conductor and the engineering team. The role is often likened to that of a film director, though there are important differences. It is distinct from the role of an executive producer, who is mostly involved in the recording project on an administrative level, and from the audio engineer who operates the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Product (other)
Product may refer to: Business * Product (business), an item that can be offered to a market to satisfy the desire or need of a customer. * Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution Mathematics * Product (mathematics) Algebra * Direct product Set theory * Cartesian product of sets Group theory * Direct product of groups * Semidirect product * Product of group subsets * Wreath product * Free product * Zappa–Szép product (or knit product), a generalization of the direct and semidirect products Ring theory * Product of rings * Ideal operations, for product of ideals Linear algebra * Scalar multiplication * Matrix multiplication * Inner product, on an inner product space * Exterior product or wedge product * Multiplication of vectors: ** Dot product ** Cross product ** Seven-dimensional cross product ** Triple product, in vector calculus * Tensor product Topology * Product topology Algebraic topology * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Producer (other)
Producer(s), The Producer(s), or co-producer(s) may refer to: Occupations *Producer (agriculture), a farm operator *Producer, a stakeholder of economic production * Film producer, supervises the making of films **Executive producer, contributes to a film's budget and usually does not work on set * Impresario, a producer or manager in the theatre and music industries * Line producer, manager during daily operations of a film or TV series * News producer, person who compiles all items of a news programme into a cohesive show * Online producer, person who oversees the making of content for websites *Radio producer, person who oversees the making of a radio show *Record producer, person who manages sound recording * Television producer, person who oversees all aspects of video production on a television program *Theatrical producer, person who oversees the staging of theatre productions * Video game producer, person in charge of overseeing development of a video game Film and televi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Means Of Production
In political philosophy, the means of production refers to the generally necessary assets and resources that enable a society to engage in production. While the exact resources encompassed in the term may vary, it is widely agreed to include the classical factors of production (land, labour, and capital) as well as the general infrastructure and capital goods necessary to reproduce stable levels of productivity. It can also be used as an abbreviation of the "means of production and distribution" which additionally includes the logistical distribution and delivery of products, generally through distributors; or as an abbreviation of the "means of production, distribution, and exchange" which further includes the exchange of distributed products, generally to consumers. The concept of "Means of Production" is used by researchers in various fields of study — including politics, economics, and sociology — to discuss, broadly, the relationship between anything that can have p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption refers to the use of resources to fulfill present needs and desires. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economics, mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced Good (economics), goods and Service (economics), services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g., the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity (ecology)
In ecology, the term productivity refers to the rate of generation of biomass in an ecosystem, usually expressed in units of mass per volume (unit surface) per unit of time, such as grams per square metre per day (g m−2 d−1). The unit of mass can relate to dry matter or to the mass of generated carbon. The productivity of autotrophs, such as plants, is called primary productivity, while the productivity of heterotrophs, such as animals, is called secondary productivity. The productivity of an ecosystem is influenced by a wide range of factors, including nutrient availability, temperature, and water availability. Understanding ecological productivity is vital because it provides insights into how ecosystems function and the extent to which they can support life. Primary production Primary production is the synthesis of organic material from inorganic molecules. Primary production in most ecosystems is dominated by the process of photosynthesis, In which organisms synthesiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as '' primary producers'' or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either ''net'' or ''gross'', the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not. Overview Primary production is the production of chemical energy, in organic compounds by living organisms. The main source of such energy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production (computer Science)
In computer science, a production or production rule is a rewrite rule that replaces some symbols with other symbols. A finite set of productions P is the main component in the specification of a formal grammar (specifically a generative grammar). The other components are a finite set N of nonterminal symbols, a finite set (known as an alphabet) \Sigma of terminal symbols that is disjoint from N and a distinguished symbol S \in N that is the ''start symbol''. In an unrestricted grammar, a production is of the form u \to v, where u and v are arbitrary strings of terminals and nonterminals, and u may not be the empty string. If v is the empty string, this is denoted by the symbol \epsilon, or \lambda (rather than leaving the right-hand side blank). So productions are members of the cartesian product :V^*NV^* \times V^* = (V^*\setminus\Sigma^*) \times V^*, where V := N \cup \Sigma is the ''vocabulary'', ^ is the Kleene star operator, V^*NV^* indicates concatenation, \cup deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deployment Environment
In software deployment, an environment or tier is a computer system or set of systems in which a computer program A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to Execution (computing), execute. It is one component of software, which also includes software documentation, documentation and other intangibl ... or software component is deployed and executed. In simple cases, such as developing and immediately executing a program on the same machine, there may be a single environment, but in industrial use, the ''development'' environment (where changes are originally made) and ''production'' environment (what end users use) are separated, often with several stages in between. This structured release management process allows phased deployment (rollout), testing, and rollback in case of problems. Environments may vary significantly in size: the development environment is typically an individual developer's workstation, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a Stage (theatre), stage. The performers may communicate this experience to the audience through combinations of gesture, speech, song, music, and dance. It is the oldest form of drama, though live theatre has now been joined by modern recorded forms. Elements of art, such as painted scenery and stagecraft such as lighting are used to enhance the physicality, presence and immediacy of the experience. Places, normally buildings, where performances regularly take place are also called "theatres" (or "theaters"), as derived from the Ancient Greek θέατρον (théatron, "a place for viewing"), itself from θεάομαι (theáomai, "to see", "to watch", "to observe"). Modern Western theatre comes, in large measure, from the theatre of ancient Greece, from which it borrows tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Game Development
Video game development (sometimes shortened to gamedev) is the process of creating a video game. It is a multidisciplinary practice, involving programming, design, art, audio, user interface, and writing. Each of those may be made up of more specialized skills; art includes 3D modeling of objects, character modeling, animation, visual effects, and so on. Development is supported by project management, production, and quality assurance. Teams can be many hundreds of people, a small group, or even a single person. Development of commercial video games is normally funded by a video game publisher, publisher and can take two to five years to reach completion. Game creation by small, self-funded teams is called indie game, independent development. The technology in a game may be written from scratch or use proprietary software specific to one company. As development has become more complex, it has become common for companies and independent developers alike to use off-the-shelf "engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |