|
Premiership Of Boris Johnson
Boris Johnson's tenure as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom began on 24 July 2019 when he accepted an invitation of Queen Elizabeth II to form a government, succeeding Theresa May, and ended on 6 September 2022 upon his resignation. Johnson's premiership was dominated by Brexit, the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russian invasion of Ukraine, and the 2021–present United Kingdom cost-of-living crisis, cost of living crisis. As prime minister, Johnson also served simultaneously as First Lord of the Treasury, Minister for the Civil Service, Minister for the Union, and Leader of the Conservative Party (UK), Leader of the Conservative Party. Johnson defeated Jeremy Hunt in the 2019 Conservative Party leadership election on 23 July 2019, and was appointed prime minister the following day. He Brexit negotiations in 2019, re-opened Brexit negotiations with the European Union and in early September he 2019 British prorogation controversy, prorogued Parliament; the Supreme Court of the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Johnson Ministry
The first Johnson ministry began on 24 July 2019 when Queen Elizabeth II invited Boris Johnson to form a new government, following the resignation of the predecessor Prime Minister Theresa May. May had resigned as Leader of the Conservative Party on 7 June 2019; Johnson was elected as her successor on 23 July 2019. The Johnson ministry was formed from the 57th Parliament of the United Kingdom, as a Conservative minority government. It lost its working majority on 3 September 2019 when Tory MP Phillip Lee crossed the floor to the Liberal Democrats. An election was called for 12 December 2019, which led to the formation of a Conservative majority government, the second Johnson ministry. History Theresa May announced on 24 May 2019 that she would resign as Leader of the Conservative Party and therefore prime minister, after failing three times to secure passage through the House of Commons of her Withdrawal Agreement and Implementation Bill, which would have seen th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister For The Union
The Minister for the Union is a position in the United Kingdom which is held concurrently with the post of Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Prime Minister. History The position was created by Boris Johnson during his first Johnson ministry, first ministry, to be held concurrently with the duties of prime minister. Johnson proposed the position during the 2019 Conservative Party (UK) leadership election, 2019 Conservative Party leadership campaign. He was the first prime minister to adopt the title, and the post was retained by Johnson in his second Johnson ministry, second ministry, and subsequent prime ministers. On 4 September 2019, the HM Government, Government announced £10 million in funding to support the Prime Minister's work as Minister for the Union. Responsibilities Since September 2020, the stated responsibilities of the position have been: "As Minister for the Union, the Prime Minister works to ensure that all of government is acting on behalf of the entire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
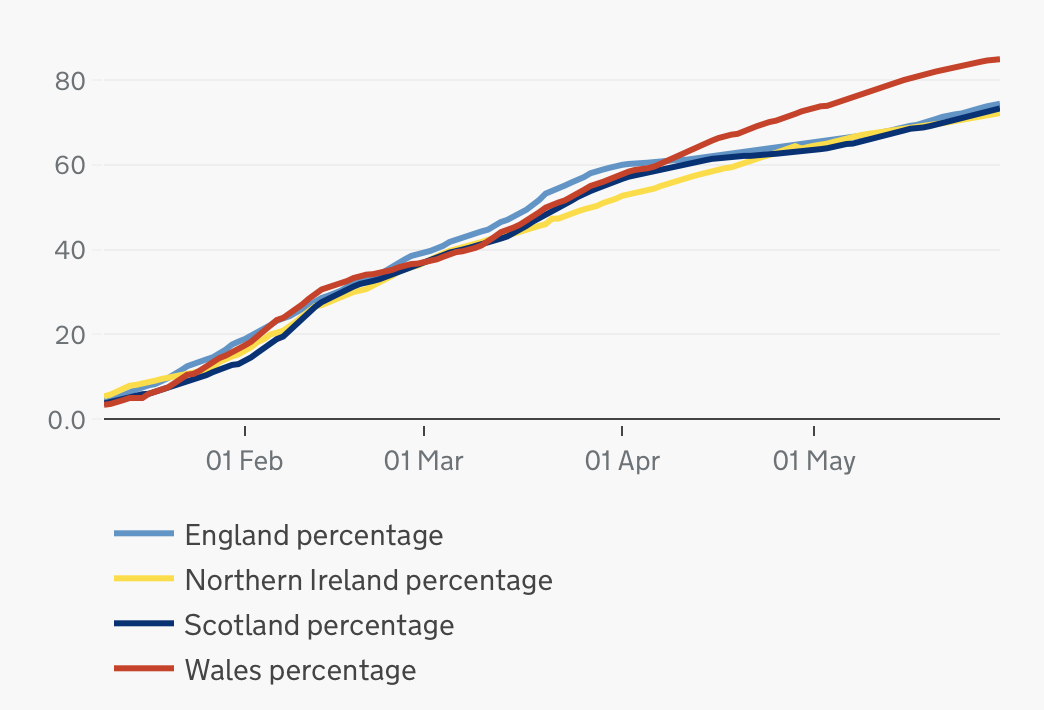
COVID-19 Vaccination In The United Kingdom
The COVID-19 vaccination programme in the United Kingdom is an ongoing mass immunisation campaign for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom. Vaccinations began on 8 December 2020 after Margaret Keenan became the first person in the world (outside trials) to receive her first dose of two of the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. There are three vaccines currently in use; following approval of the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine ( Comirnaty), vaccines developed by University of Oxford and AstraZeneca ( Vaxzevria), and the United States National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and Moderna ( Spikevax) have been rolled out. , there were four other COVID-19 vaccines on order for the programme, at varying stages of development. Phase 1 of the rollout prioritised the most vulnerable, in a schedule primarily based on age. The delivery plan was adjusted on 30 December 2020, delaying second doses so that more people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coronavirus Act 2020
The Coronavirus Act 2020 (c. 7) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that granted the government emergency powers to handle the COVID-19 pandemic. The act allowed the government the discretionary power to limit or suspend public gatherings, to detain individuals suspected to be infected by COVID-19, and to intervene or relax regulations in a range of sectors to limit transmission of the disease, ease the burden on public health services, and assist healthcare workers and the economically affected. Areas covered by the act included the National Health Service, social care, schools, police, Border Force, local councils, funerals and courts. The act was introduced to Parliament on 19 March 2020, and passed the House of Commons without a vote on 23 March, and the House of Lords on 25 March. The act received royal assent on 25 March 2020. The act specified a two-year time limit that could be shortened or lengthened by six months at ministerial discretion. Several of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic In The United Kingdom
The COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom is a part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). In the United Kingdom, it has resulted in confirmed cases, and is associated with deaths up to 26 January 2025. The virus began circulating in the country in early 2020, arriving primarily from travel elsewhere in Europe. Various sectors responded, with more widespread public health measures incrementally introduced from March 2020. The first wave was at the time one of the world's largest outbreaks. By mid-April the peak had been passed and restrictions were gradually eased. A second wave, with a new variant that originated in the UK becoming dominant, began in the autumn and peaked in mid-January 2021, and was deadlier than the first. The UK started a COVID-19 vaccination programme in early December 2020. Generalised restrictions were gradually lifted and were mostly ended by Augus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Government Response To The COVID-19 Pandemic
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom, the Government of the United Kingdom, UK Government introduced various public health and economic measures to mitigate its impact. Devolution in the United Kingdom, Devolution meant that the four nations' administrative responses to the pandemic differed; the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government, and the Northern Ireland Executive produced different policies to those that apply in England. United Kingdom legislation connected with the COVID-19 pandemic, Numerous laws were enacted or introduced throughout the crisis. The UK government had developed a pandemic response plan in previous years. In response to the first confirmed COVID-19 cases in January 2020, the UK introduced advice for travellers coming from affected countries in late January and February 2020, and began contact tracing, although this was later abandoned. The government incrementally introduced further societal restrictions on the public as the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1987 United Kingdom General Election
The 1987 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday 11 June 1987, to elect 650 members to the House of Commons. The election was the third consecutive general election victory for the Conservative Party, who won a majority of 102 seats and second landslide under the leadership of Margaret Thatcher, who became the first Prime Minister since the Earl of Liverpool in 1820 to lead a party into three successive electoral victories. The Conservatives ran a campaign focusing on lower taxes, a strong economy and strong defence. They also emphasised that unemployment had just fallen below the 3 million mark for the first time since 1981, and inflation was standing at 4%, its lowest level since the 1960s. National newspapers also continued to largely back the Conservative government, particularly ''The Sun'', which ran anti– Labour Party articles with headlines such as "Why I'm backing Kinnock, by Stalin". Labour, led by Neil Kinnock following Michael Foot's resigna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landslide Victory
A landslide victory is an election result in which the winning Candidate#Candidates in elections, candidate or political party, party achieves a decisive victory by an overwhelming margin, securing a very large majority of votes or seats far beyond the typical competitive outcome. The term became popular in the 1800s to describe a victory in which the opposition is "buried", similar to the way in which a geological landslide buries whatever is in its path. A landslide victory for one party is often accompanied by an electoral wipeout for the opposition, as the overwhelming support for the winning side inflicts a decisive loss on its rivals. What qualifies as a landslide victory can vary depending on the type of electoral system, as the term does not entail a precise, technical, or universally agreed-upon measurement. Instead, it is used informally in everyday language, making it subject to interpretation. Even within a single electoral system, there is no consensus on the exact mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliamentary Votes On Brexit
Parliamentary votes on Brexit, sometimes referred to as "meaningful votes", were the parliamentary votes under the terms of Section 13 of the United Kingdom's European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018, which requires the government of the United Kingdom to bring forward an amendable parliamentary motion at the end of the Article 50 negotiations between the government and the European Union in order to ratify the Brexit withdrawal agreement.Summary The wording of the clause was strongly contested by both the and the |
Supreme Court Of The United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC) is the final court of appeal for all civil cases in the United Kingdom and all criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, as well as some limited criminal cases from Scotland. Otherwise, the Court of Session is the Supreme court, supreme Civil law (common law), civil court of Scotland, and the High Court of Justiciary is the Supreme court, supreme Criminal justice, criminal court, and are collectively known as the Supreme Courts of Scotland. As the United Kingdom's highest appellate court for these matters, it hears cases of the greatest public or constitutional importance affecting the whole population. Additionally the Supreme Court hears cases on Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolution matters from Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. As a consequence, the court must include judges from the three distinct legal systems of the United Kingdom – English law, England and Wales, Scots law, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 British Prorogation Controversy
On 27 or 28 August 2019, the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Boris Johnson advised Queen Elizabeth II to prorogue Parliament from a date between 9 and 12 September 2019 until the State Opening of Parliament on 14 October 2019. As a result, Parliament was suspended from 9 September until 24 September, when the prorogation was ruled unlawful by the Supreme Court. Since Parliament was to be prorogued for five weeks and reconvene just 17 days before the United Kingdom's scheduled departure from the European Union on 31 October 2019, the move was seen by many opposition politicians and political commentators as a controversial and unconstitutional attempt by the prime minister to avoid parliamentary scrutiny of the Government's Brexit plans in the final weeks leading up to Brexit. Johnson and his Government defended the prorogation of Parliament as a routine political process that ordinarily follows the selection of a new prime minister and would allow the Government to refocus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brexit Negotiations In 2019
Brexit negotiations in 2019 started in August, after having originally concluded in November 2018 with the release of the withdrawal agreement. Negotiations took place between the United Kingdom and the European Union during 2017 and 2018 for the withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union following the referendum held on 23 June 2016. In March 2019, UK prime minister Theresa May and EU leaders negotiated a fortnight's delay for the Parliament of the United Kingdom to ratify the Brexit withdrawal agreement, moving the date from 29 March 2019 to 12 April 2019. On 10 April 2019, a further half-year extension was agreed between the UK and the EU27 at the EU summit, until 31 October 2019. At the time of the second extension, the EU position was that the negotiation of terms for withdrawal ended in November 2018 and that the extension was to give the UK Parliament more time to consider the agreement. During 2019, the UK Parliament debated whether to accept the Theres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |