|
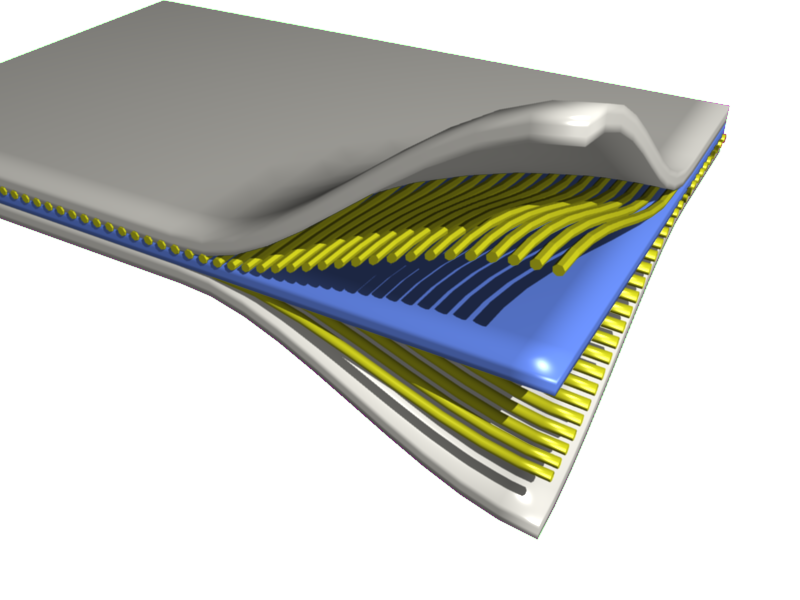
Plywood
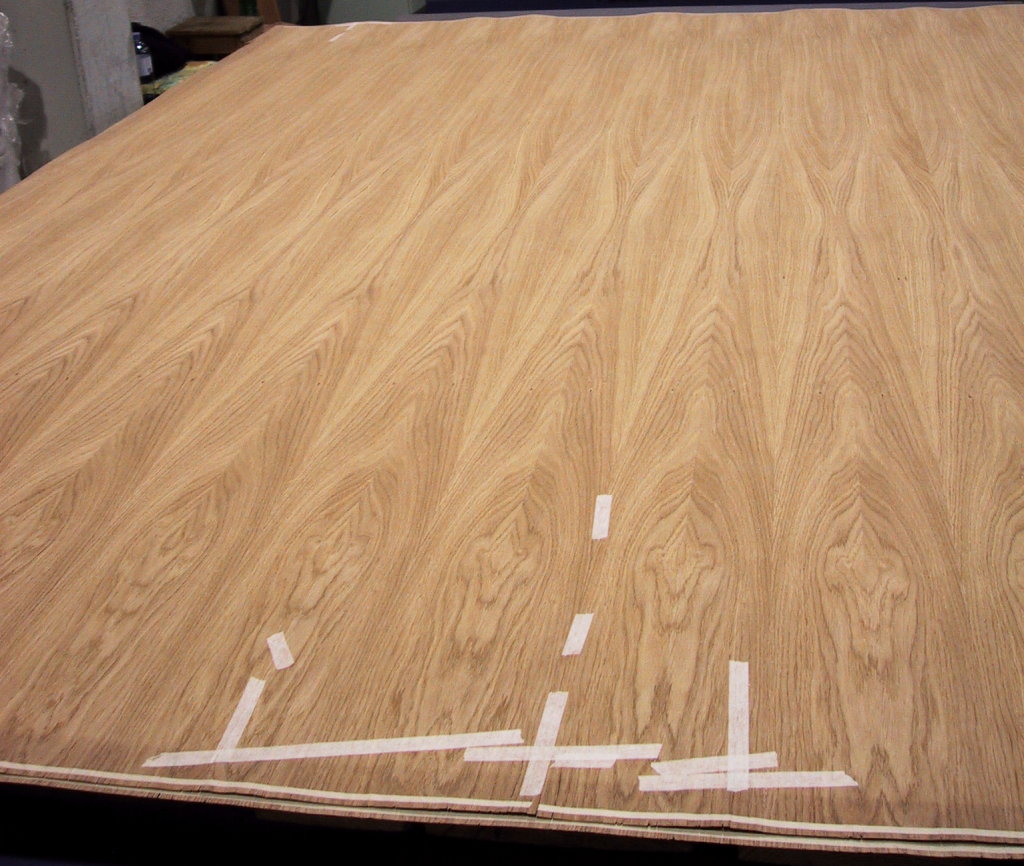
Plywood is a composite material manufactured from thin layers, or "plies", of wood veneer that have been stacked and glued together. It is an engineered wood from the family of manufactured boards, which include plywood, medium-density fibreboard (MDF), oriented strand board (OSB), and particle board (or chipboard). All plywoods bind resin and wood fibre sheets (cellulose cells are long, strong and thin) to form a composite material. The sheets of wood are stacked such that each layer has its grain set typically (see below) perpendicular to its adjacent layers. This alternation of the grain is called ''cross-graining'' and has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces thickness swelling and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions. There is usually an odd number of plies, so that the sheet is balanced, that is, the surface layers ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineered Wood
Engineered wood, also called mass timber, composite wood, man-made wood, or manufactured board, includes a range of derivative wood products which are manufactured by binding or fixing the strands, particles, fibres, veneers, or boards of wood, together with adhesives, or other methods of fixation to form composite material. The panels vary in size but can range upwards of and in the case of cross-laminated timber (CLT) can be of any thickness from a few inches to or more. These products are engineered to precise design specifications, which are tested to meet national or international standards and provide uniformity and predictability in their structural performance. Engineered wood products are used in a variety of applications, from home construction to commercial buildings to industrial products. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tego Film
Tego film is an adhesive sheet used in the manufacture of waterproof plywood. It is applied dry and cured by heat, which allows for high-quality laminates that are free from internal voids and warping. Tego film plywood products were used in aircraft manufacture in Germany during World War II, and the loss of the plant during a 1943 bombing raid was a serious blow to several aircraft projects. Tego film was an invention of the Essen, Germany, firm of Th. Goldschmidt AGlater Evonik Industrie) Development and use for plywood Tego film was developed as a glue for waterproof plywood. It comprised a paper sheet impregnated with a resole phenolic resin, which was heated, assembled between s and then compressed, form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medium-density Fibreboard
Medium-density fibreboard (MDF) is an engineered wood product made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibre, often in a defibrator, combining it with wax and a resin binder, and forming it into panels by applying high temperature and pressure. MDF is generally denser than plywood. It is made up of separated fibre but can be used as a building material similar in application to plywood. It is stronger and denser than particle board. The name derives from the distinction in densities of fibreboard. Large-scale production of MDF began in the 1980s, in both North America and Europe. Over time, the term "MDF" has become a generic name for any dry-process fibreboard. Physical properties MDF is typically made up of 82% wood fibre, 9% urea-formaldehyde resin glue, 8% water, and 1% paraffin wax. The density is typically between . The range of density and classification as light-, standard-, or high-density board is a misnomer and confusing. The density of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriented Strand Board
Oriented strand board (OSB) is a type of engineered wood, formed by adding adhesives and then compressing layers of wood strands (flakes) in specific orientations. It was invented by Armin Elmendorf in California in 1963. OSB may have a rough and variegated surface with the individual strips of around , lying unevenly across each other, and is produced in a variety of types and thicknesses. Oriented strand board is sometimes confused with ''chipboard'', a synonym for particle board, whose "chips" are of a size that a lay person would likely describe as "particles". Uses OSB's mechanical properties make it suitable for load-bearing applications in construction. In North America, it is more popular than plywood, commanding 66% of the structural panel market in 2016. The most common uses are as sheathing in walls, flooring, and roof decking. For exterior walls, panels are available with a radiant-barrier layer laminated to one side; this eases installation and increases energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Board
Particle board, also known as particleboard or chipboard, is an engineered wood product, belonging to the wood-based panels, manufactured from wood chips and a synthetic, mostly formaldehyde-based resin or other suitable binder, which is pressed under a hot press, batch- or continuous- type, and produced. Particle board is often confused with oriented strand board (OSB, also known as flakeboard, or waferboard), a different type of fiberboard that uses machined wood flakes and offers more strength. Characteristics Particle board is cheaper, denser, and more uniform than conventional wood and plywood and is substituted for them when cost is more important than strength and appearance. Particleboard can be made more appealing by painting or the use of wood veneers on visible surfaces. Though it is denser than conventional wood, it is the lightest and weakest type of fiberboard, except for insulation board. Medium-density fibreboard and hardboard, also called high-density fibe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Nobel
Alfred Bernhard Nobel ( ; ; 21 October 1833 – 10 December 1896) was a Swedish chemist, inventor, engineer, and businessman. He is known for inventing dynamite, as well as having bequeathed his fortune to establish the Nobel Prizes. He also made several other important contributions to science, holding 355 patents during his life. Born into the prominent Nobel family in Stockholm, Nobel displayed an early aptitude for science and learning, particularly in chemistry and languages; he became fluent in six languages and filed his first patent at the age of 24. He embarked on many business ventures with his family, most notably owning the company Bofors, which was an iron and steel producer that he had developed into a major manufacturer of cannons and other armaments. Nobel's most famous invention, dynamite, was an explosive made using nitroglycerin, which was patented in 1867. He further invented gelignite in 1875 and ballistite in 1887. Upon his death, Nobel donated his fortun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Material
A composite or composite material (also composition material) is a material which is produced from two or more constituent materials. These constituent materials have notably dissimilar chemical or physical properties and are merged to create a material with properties unlike the individual elements. Within the finished structure, the individual elements remain separate and distinct, distinguishing composites from mixtures and solid solutions. Composite materials with more than one distinct layer are called ''composite laminates''. Typical engineered composite materials are made up of a binding agent forming the ''matrix'' and a Filler (materials), filler material (particulates or fibres) giving ''substance'', e.g.: * Concrete, reinforced concrete and masonry with cement, lime or Mortar (masonry), mortar (which is itself a composite material) as a binder * Composite wood such as glulam and plywood with wood glue as a binder * Reinforced plastics, such as fiberglass and fibre-rein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glue
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation. The use of adhesives offers certain advantages over other binding techniques such as sewing, mechanical fastenings, and welding. These include the ability to bind different materials together, the more efficient distribution of stress across a joint, the cost-effectiveness of an easily mechanized process, and greater flexibility in design. Disadvantages of adhesive use include decreased stability at high temperatures, relative weakness in bonding large objects with a small bonding surface area, and greater difficulty in separating objects during testing. Adhesives are typically organized by the method of adhesion followed by ''reactive'' or ''non-reactive'', a term which refers to whether the adhesive chemically reacts in order to harden. Alternatively, they can be organized eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immanuel Nobel
Immanuel Nobel the Younger ( , ; 24 March 1801 – 3 September 1872) was a Swedish people, Swedish engineer, architect, inventor and industrialist. He was the inventor of the Lathe (tool), rotary lathe used in plywood manufacturing. He was a member of the Nobel family and the father of Robert Nobel, Ludvig Nobel, Alfred Nobel and Emil Oskar Nobel. In 1827 he married the children's mother, Andriette Nobel, Andriette Ahlsell. He also often experimented with nitroglycerin with his sons, which led to his son Emil Oskar's death because of an explosion at his father's factory Heleneborg in Stockholm in 1864. Nobel moved to Russia from Sweden in 1838, to sell his inventions in Saint Petersburg, where he lived for two decades with his family. In Saint Petersburg he was attached to the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Saint Katarina along with other Swedes such as Johan Patrik Ljungström, with whom he may have collaborated. Among his successful creations was an improved version of an un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Veneer
Veneer refers to thin slices of wood and sometimes bark that typically are glued onto core panels (typically, wood, particle board or medium-density fiberboard) to produce flat panels such as doors, tops and panels for cabinets, parquet floors and parts of furniture. They are also used in marquetry. Unlike laminates, no two veneer sheets look the same. Plywood consists of three or more layers of veneer. Normally, each is glued with its grain at right angles to adjacent layers for strength. Veneer beading is a thin layer of decorative edging placed around objects, such as jewelry boxes. Veneer is also used to replace decorative papers in wood veneer high pressure laminate. Background Veneering dates back to at least the ancient Egyptians who used expensive and rare wood veneers over cheaper timbers to produce their furniture and sarcophagi. During the Roman Empire, Romans also used veneered work in mass quantities. Production Veneer is obtained either by "peeling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplex
Multiplex may refer to: Science and technology * Multiplex communication, combining many signals into one transmission circuit or channel ** Multiplex (television), a group of digital television or radio channels that are combined for broadcast * Multiplex (assay), a biological assay which measures several components at the same time * Multiplex, another name for plywood, a composite material manufactured from thin layers of wood veneer Other uses * Multiplex (automobile), a former American car make * Multiplex (comics), a DC comic book supervillain * Multiplex (company), a global contracting and development company * Multiplex (highway) or concurrency, a single road designated by multiple highway numbers * Multiplex (juggling), a juggling action with multiple balls thrown or caught at one time by the same hand * Multiplex (movie theater), a theater with many screens * Multiplex (webcomic), ''Multiplex'' (webcomic), an online comic about the staff of a movie theater See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |