|
Piranha Software Games
A piranha (, or ; ) is any of a number of freshwater fish species in the subfamily Serrasalminae, of the family Serrasalmidae, in the order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, floodplains, lakes and reservoirs. Although often described as extremely predatory and mainly feeding on fish, their dietary habits vary extensively, and they will also take plant material, leading to their classification as omnivorous. Etymology The name originates from Old Tupi '' pirãîa'', being first attested in the 1587 treatise ' by Portuguese explorer Gabriel Soares de Sousa. ''Piranha'' first appears in 1869 in English literature, likely borrowed from Portuguese. Taxonomy and evolution Piranhas belong to the family Serrasalmidae, which includes closely related omnivorous fish such as pacus. Traditionally, only the four genera ''Pristobrycon'', ''Pygocentrus'', ''Pygopristis'', and ''Serrasalmus'' are considered to be true piranhas, due to their specialized teeth. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
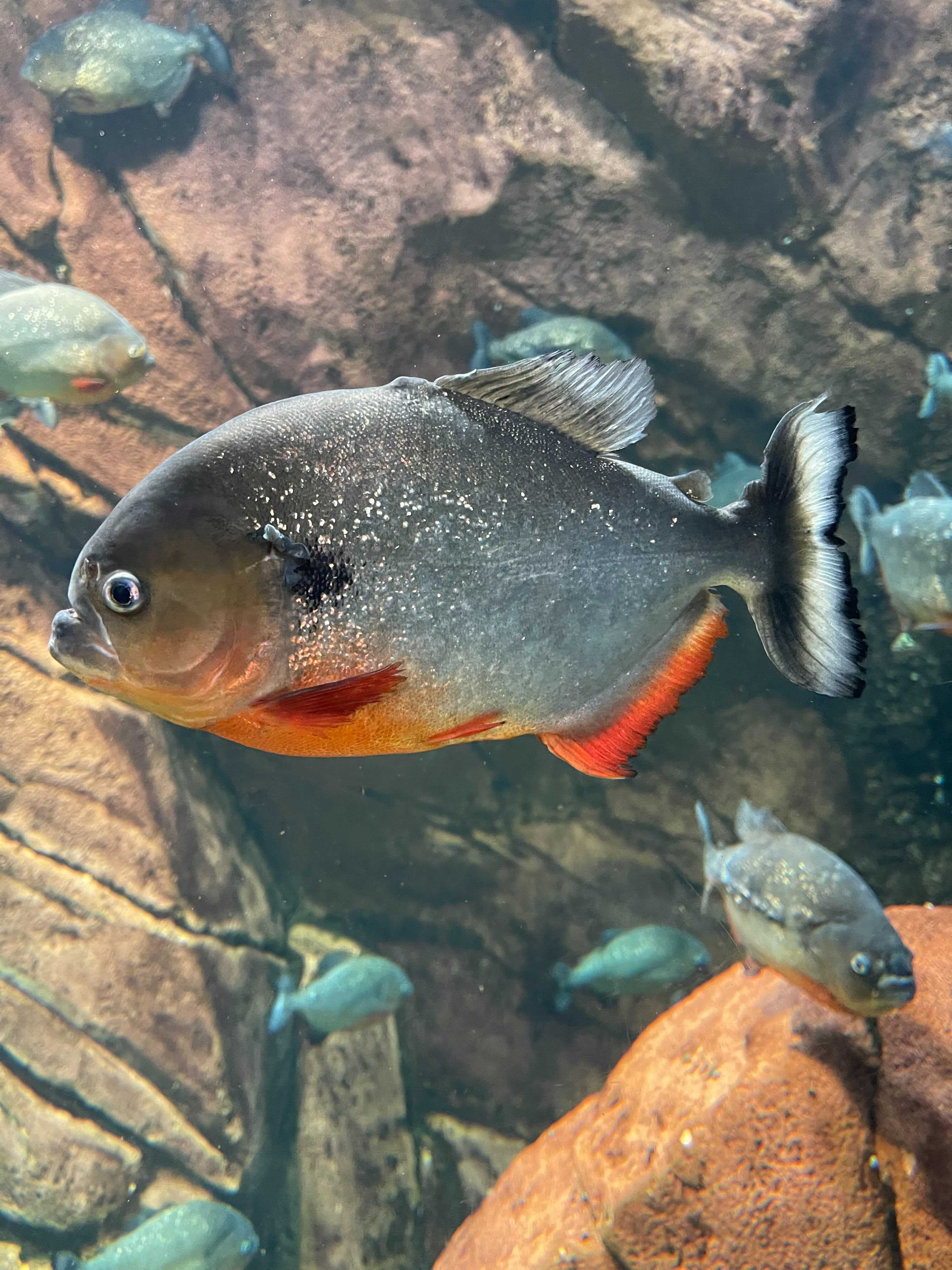
Red-bellied Piranha
The red-bellied piranha, also known as the red piranha (''Pygocentrus nattereri''), is a Type (biology), type of piranha native to South America, found in the Amazon basin, Amazon, Paraguay River, Paraguay, Paraná River, Paraná and Essequibo River, Essequibo basins, as well as coastal rivers of northeastern Brazil.''Pygocentrus nattereri''. Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan. Accessed 19 February 2016.Froese, R. and D. Pauly, Editors FishBase. 2015. This fish is locally abundant in its freshwater habitat. They are omnivorous foragers and feed on insects, worms, crustaceans, and fish. They are not a migratory species but do travel to seek o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
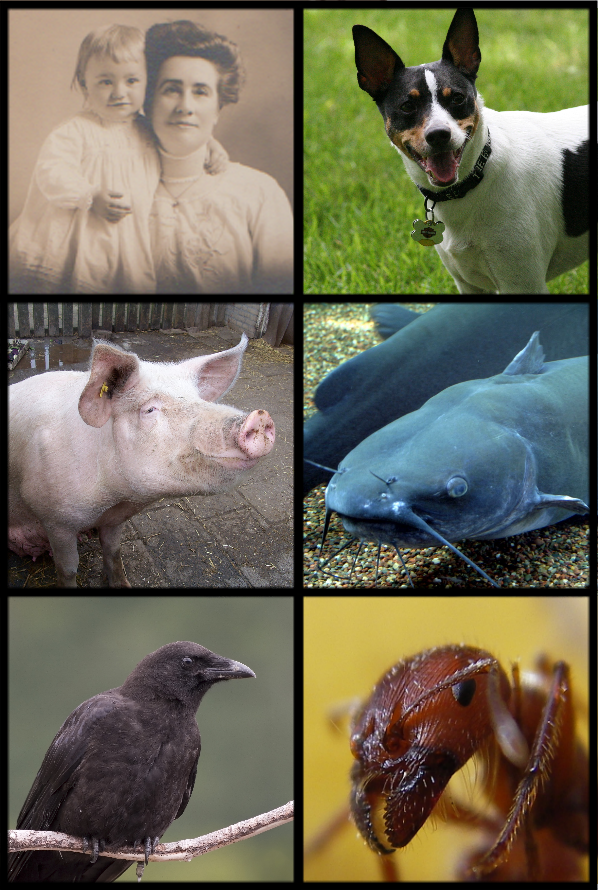
Omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms ( Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
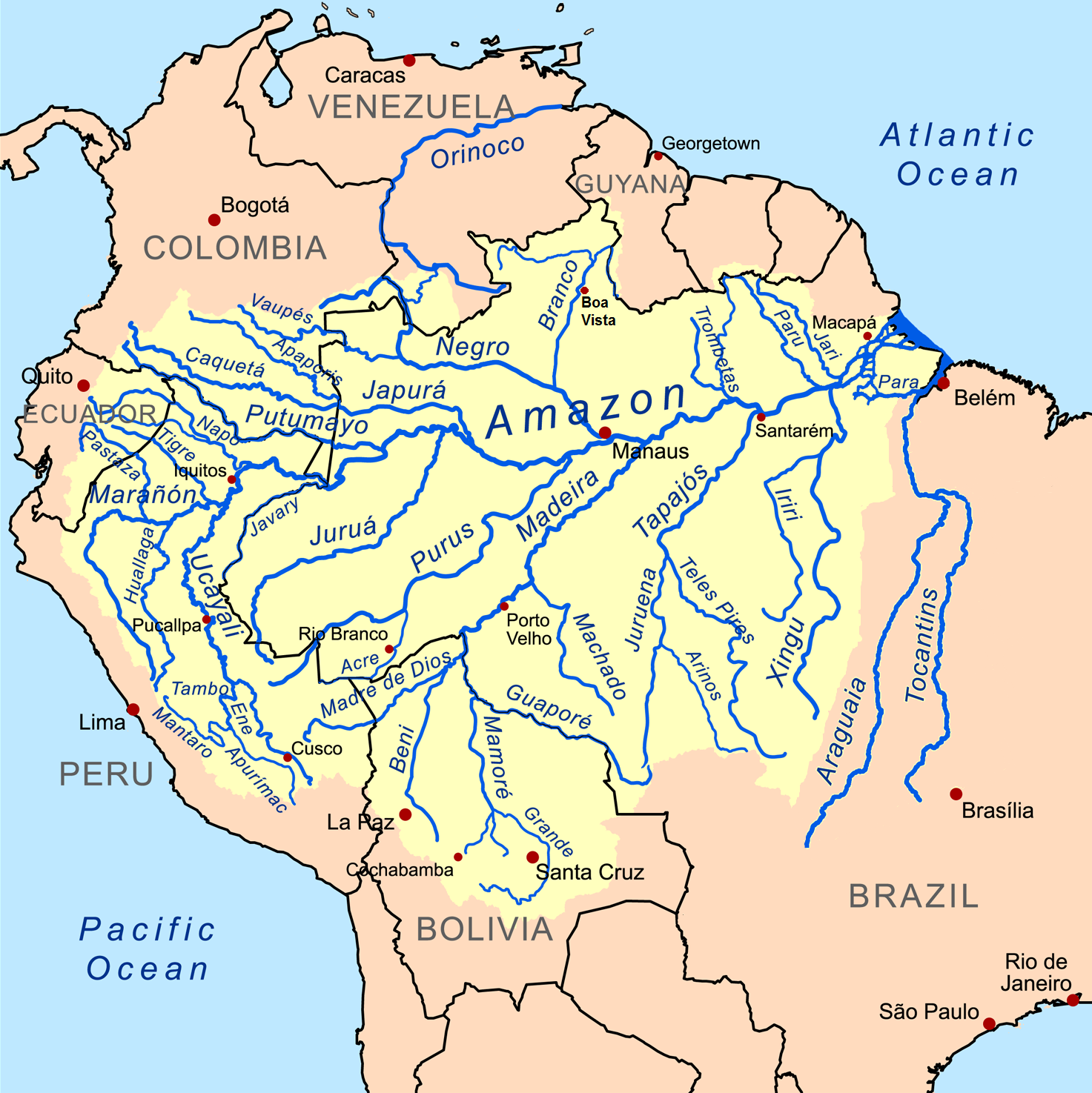
Orinoco
The Orinoco () is one of the longest rivers in South America at . Its drainage basin, sometimes known as the Orinoquia, covers approximately 1 million km2, with 65% of it in Venezuela and 35% in Colombia. It is the List of rivers by discharge, fourth largest river in the world by Discharge (hydrology), discharge volume of water (39,000 m3/s at Orinoco Delta, delta) due to the high precipitation throughout its catchment area (ca 2,300 mm/a). The Orinoco River and its tributaries are the major transportation system for eastern and interior Venezuela and the Llanos of Colombia. The environment and wildlife in the Orinoco's basin are extremely diverse. Etymology The river's name is derived from the Warao language, Warao term for "a place to paddle", itself derived from the terms ''güiri'' (paddle) and ''noko'' (place) i.e. a navigable place. History The mouth of the Orinoco River at the Atlantic Ocean was documented by Christopher Columbus on 1 August 1498, during his Christo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Dollar (fish)
Silver dollar is a common name given to a number of species of fishes, mostly in the genus '' Metynnis'', tropical fish belonging to the family Serrasalmidae which are closely related to piranha and pacu. Most commonly, the name refers to '' Metynnis argenteus''. Native to South America, these somewhat round-shaped silver fish are popular with fish-keeping hobbyists. The silver dollar is a peaceful schooling species that spends most of its time in the mid- to upper-level of the water. Its average lifespan is less than ten years but can live longer in captivity. A benthic spawner and egg scatterer, the adult fish will spawn around 2,000 eggs. This breeding occurs in soft, warm water in low light. Silver dollars natively live in a tropical climate in the sides of weedy rivers. They prefer water with a pH of 5–7, a water hardness of up to 15 dGH, and an ideal temperature range of 24–28 °C (75–82 °F). Their diet is almost exclusively vegetarian and in captivity they will o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pristobrycon Striolatus
''Pristobrycon striolatus'' is a species of serrasalmid fish. Range and habitat ''Pristobrycon striolatus'' inhabits mainly black or acidic waters in tributaries in the Orinoco and Amazon River Basins. Description This small and beautiful fish reaches . Its body is discoid with the anterodorsal profile slightly curved or straight. The head is robust and wide. Its snout is blunt. A preanal spine is absent. The adipose fin is wide. The head is silver with metallic orange to red at the mandibular and opercular regions. Its iris is yellow. Its body is greenish laterally and a mixture of orange and red at the abdominal area, covered with "pepper-like" spots. It has a single spot in the opercular area above the pectoral fin origin. The fins have reddish tones. Its caudal fin has an angled basal black band. Feeding Like other piranhas, ''P. striolatus'' is a predator, consuming smaller fish and attacking fins. Juveniles eat aquatic insects and crustacean Crustaceans (from L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria: # the grouping contains its own most recent common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population), i.e. excludes non-descendants of that common ancestor # the grouping contains all the descendants of that common ancestor, without exception Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic'' grouping meets 1. but not 2., thus consisting of the descendants of a common ancestor, excepting one or more monophyletic subgroups. A ''polyphyletic'' grouping meets neither criterion, and instead serves to characterize convergent relationships of biological features rather than genetic relationships – for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, or aquatic insects. As such, these characteristic features of a polyphyletic grouping are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacu
Pacu () is a common name used to refer to several species of omnivorous South American freshwater Serrasalmidae, serrasalmid fish related to piranhas. Pacu and piranha do not have similar teeth, the main difference being jaw alignment; piranha have pointed, razor-sharp teeth in a pronounced underbite, whereas pacu have squarer, straighter teeth and a less severe underbite, or a slight malocclusion, overbite. Pacu, unlike piranha, mainly feed on plant material and not flesh or Fish scale, scales. Additionally, the pacu can reach much larger sizes than piranha, at up to in total length and in weight. Name The common name ''pacu'' is generally applied to fish classified under the below listed Genus, genera. Among these, several genera contain species where commonly used English names include the word ''pacu'', as listed. *Subfamily Colossomatinae **''Colossoma'' – black pacu, black-finned pacu, giant pacu **''Mylossoma '' **''Piaractus'' – red-bellied pacu, small-scaled pacu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family (, : ) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". The delineation of what constitutes a family—or whether a described family should be acknowledged—is established and decided upon by active taxonomists. There are not strict regulations for outlining or acknowledging a family, yet in the realm of plants, these classifications often rely on both the vegetative and reproductive characteristics of plant species. Taxonomists frequently hold varying perspectives on these descriptions, leading to a lack of widespread consensus within the scientific community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaw Of The Piranha
The jaws are a pair of opposable articulated structures at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term ''jaws'' is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of humans and most animals. Arthropods In arthropods, the jaws are chitinous and oppose laterally, and may consist of '' mandibles'' or ''chelicerae''. These jaws are often composed of numerous mouthparts. Their function is fundamentally for food acquisition, conveyance to the mouth, and/or initial processing (''mastication'' or ''chewing''). Many mouthparts and associate structures (such as pedipalps) are modified legs. Vertebrates In most vertebrates, the jaws are bony or cartilaginous and oppose vertically, comprising an ''upper jaw'' and a ''lower jaw''. The vertebrate jaw is derived from the most anterior two pharyngeal arches supporting the gills, and usually bear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |