|
Pilate Cycle
The Pilate cycle is a group of various pieces of early Christian literature that purport to either be written by Pontius Pilate, or else otherwise closely describe his activities and the Passion of Jesus. Unlike the four gospels, these later writings were not canonized in the New Testament, and hence relegated to a status of apocrypha. Some writings were quite obscure, with only a few ancient textual references known today; they merely survived through happenstance, and may not have been particularly widely read by early Christians in the Roman Empire and Christians in the Middle Ages. Others were more popular. The most notable example was the Gospel of Nicodemus (or "Acts of Pilate"), which proved quite popular and influential in medieval and Renaissance Christianity. The group is collectively known as the Pilate cycle by some scholars; this is not a term used by early Christians, many of whom might have had access to only one or two of these accounts at most. It is rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of Nicodemus
The Gospel of Nicodemus, also known as the Acts of Pilate (; ), is an apocryphal gospel purporting to be derived from an original work written by Nicodemus, who appears in the Gospel of John as an acquaintance of Jesus. The title "Gospel of Nicodemus" is medieval in origin. The dates of its accreted sections are uncertain, but the work in its existing form is thought to date to around the 4th or 5th century AD. The author was probably a Hellenistic Jew who converted to Christianity, or, as Constantin von Tischendorf and Maury conclude, a Christian imbued with Judaic and Gnostic beliefs. History and authenticity The oldest sections of the book appear first in Greek. The text contains multiple parts, which are uneven in style and would seem to be by different authors. A prologue found in some versions asserts that the text is a translation into Greek of eyewitness accounts found in the praetorium at Jerusalem. The question of the original language is debated. Beyond Greek, the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelium Nicodemi Manuscript
Evangelion refers to the gospel in Christianity, translated from the Ancient Greek word (; ) meaning "good news". Evangelion may also refer to: * Gospel, a book on the life and teachings of Jesus ** Gospel of Mani, originally called the Evangelion (), a Manichaean text ** Gospel of Marcion, called by its adherents the Gospel or Evangelion, a Marcionite text * Gospel Book, a codex containing one or more of the four Gospels ** Nestorian Evangelion (), a Gospel Book of the Church of the East Arts and entertainment * ''Neon Genesis Evangelion'' (franchise), a Japanese media franchise ** ''Neon Genesis Evangelion'', a Japanese anime television series ** ''Neon Genesis Evangelion'' (manga), a Japanese manga series partially based on the television series ** ''Neon Genesis Evangelion'' (video game), a 1999 video game based on the television series and the film ''The End of Evangelion'' ** Evangelion (mecha), a fictional cyborg and mecha in the franchise ** ''Evangelion'' movie, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Christianity
Eastern Christianity comprises Christianity, Christian traditions and Christian denomination, church families that originally developed during Classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations further east, south or north. The term does not describe a single Communion (Christian), communion or religious denomination. Eastern Christianity is a category distinguished from Western Christianity, which is composed of those Christian traditions and churches that originally developed further west. Major Eastern Christian bodies include the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Oriental Orthodox Churches, along with those groups descended from the historic Church of the East (also called the Assyrian Church (other), Assyrian Church), as well as the Eastern Catholic Churches (which are in communion with Holy See, Rome while maintaining Eastern Catholic liturgy, Eastern liturgies), and the Eastern Protestant Christianity, Eastern Protest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicodemus
Nicodemus (; ; ; ; ) is a New Testament figure venerated as a saint in a number of Christian traditions. He is depicted as a Pharisee and a member of the Sanhedrin who is drawn to hear Jesus's teachings. Like Lazarus of Bethany, Lazarus, Nicodemus is not mentioned in the synoptic Gospels, but only by John, who devotes more than half of John 3, Chapter 3 of his gospel and a few verses of John 7, Chapter 7 to Nicodemus; and, lastly, mentions him in John 19, Chapter 19. Nicodemus is considered in both Catholic and Eastern Orthodox traditions to have secretly been a Disciple (Christianity), disciple of Jesus on the basis of the narrative in John 19; there is no explicit mention of his discipleship in the Gospel of John. Owing to his insistence on a hearing for Jesus according to Jewish law, Nicodemus is sometimes called "defender of Jesus". Some scholars have identified the Nicodemus of the New Testament with a 1st-century historic Nicodemus ben Gurion, while others consider the da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christendom
The terms Christendom or Christian world commonly refer to the global Christian community, Christian states, Christian-majority countries or countries in which Christianity is dominant or prevails.SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> Following the spread of Christianity from the Levant to Europe and North Africa during the early Roman Empire, Christendom has been divided in the pre-existing Greek East and Latin West. After the Great schism of 1054, two main branches within Christianity emerged, centred around the cities of Rome (Western Christianity, whose community was called Western or Latin Christendom) and Constantinople (Eastern Christianity, whose community was called Eastern Christendom or Byzantine commonwealth). After the fall of Constantinople in 1453, Latin Christendom rose to a central role in the Western world. Following the reformation, protestantism emerged as the third main branch of Christianity in the 16th century. The history of the Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lost Works
A lost work is a work that is known about, but no longer exists, or cannot be found. Types *Lost literary work, where the text is unknown * Lost artworks, of visual art, which may be known through copies *Lost media, audiovisual media such as films, television and radio broadcasts, music, and video games **Lost film **Lost television broadcast See also * *Lost city In the popular imagination, a lost city is a real, once-prosperous and well-populated area of human habitation that fell into terminal decline and whose location was later forgotten. Lost City, The Lost City, or Lost Cities may also refer to: Pl ... Lost works {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justin Martyr
Justin, known posthumously as Justin Martyr (; ), also known as Justin the Philosopher, was an early Christian apologist and Philosophy, philosopher. Most of his works are lost, but two apologies and a dialogue did survive. The ''First Apology of Justin Martyr, First Apology'', his most well-known text, passionately defends the morality of the Christian life, and provides various ethical and philosophical arguments to convince the Roman emperor Antoninus Pius to abandon the persecution of the Church. Further, he also indicates, as Augustine of Hippo, St. Augustine would later, regarding the "true religion" that revealed itself as Christianity, that the "seeds of Christianity" (manifestations of the Logos (Christianity), Logos acting in history) actually predated Christ's Incarnation (Christianity), incarnation. This notion allows him to claim many historical Greek philosophers (including Socrates and Plato), in whose works he was well studied, as Virtuous pagan, unknowing Chris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bart Ehrman
Bart Denton Ehrman (born October 5, 1955) is an American New Testament scholar focusing on textual criticism of the New Testament, the historical Jesus, and the origins and development of early Christianity. He has written and edited 30 books, including three college textbooks. He has also authored six ''New York Times'' bestsellers. He is the James A. Gray Distinguished Professor of Religious Studies at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Biography Early life On October 5, 1955, Ehrman was born in Lawrence, Kansas, and subsequently grew up there before attending Lawrence High School, where he was on the state champion debate team in 1973. He began studying the Bible, biblical theology, and biblical languages at Moody Bible Institute, where he earned the school's three-year diploma in 1976.Ehrman, Bart D. '' Misquoting Jesus'', HarperSanFrancisco. 2005. He earned his BA from Wheaton College in Illinois in 1978. He later earned an MDiv from Princeton Theologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantin Von Tischendorf
Constantin is an Aromanian language, Aromanian, Megleno-Romanian language, Megleno-Romanian and Romanian language, Romanian male given name. It can also be a surname. For a list of notable people called Constantin, see Constantine (name). See also * Constantine (name) * Konstantin References {{Reflist Aromanian masculine given names Megleno-Romanian masculine given names Romanian masculine given names Masculine given names Romanian-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
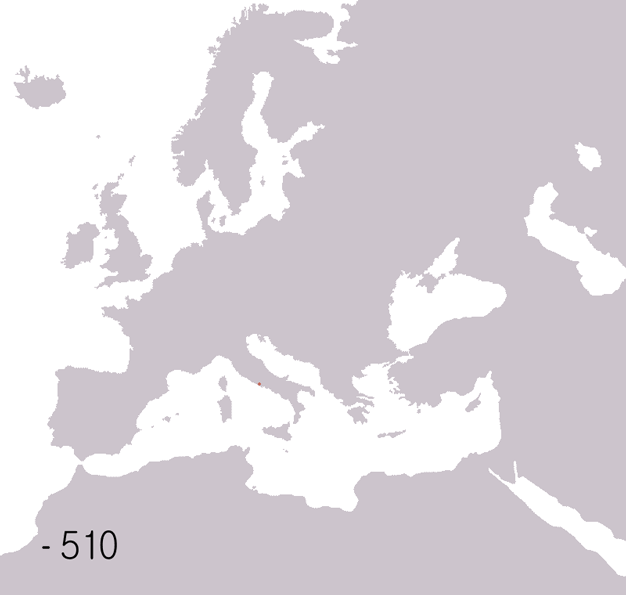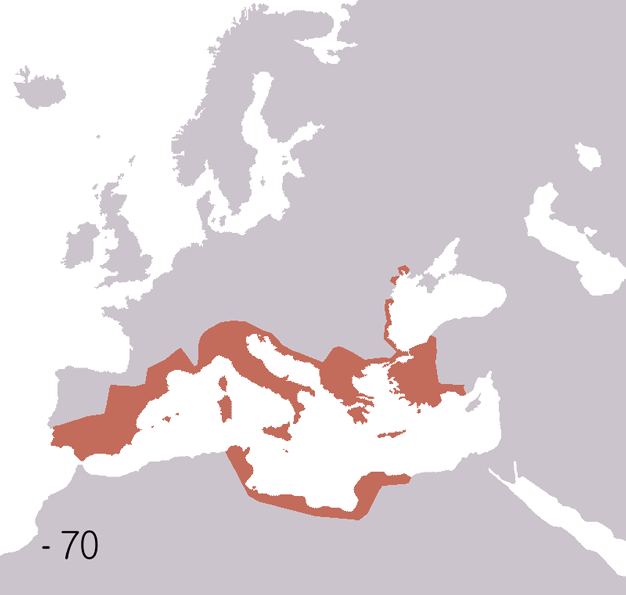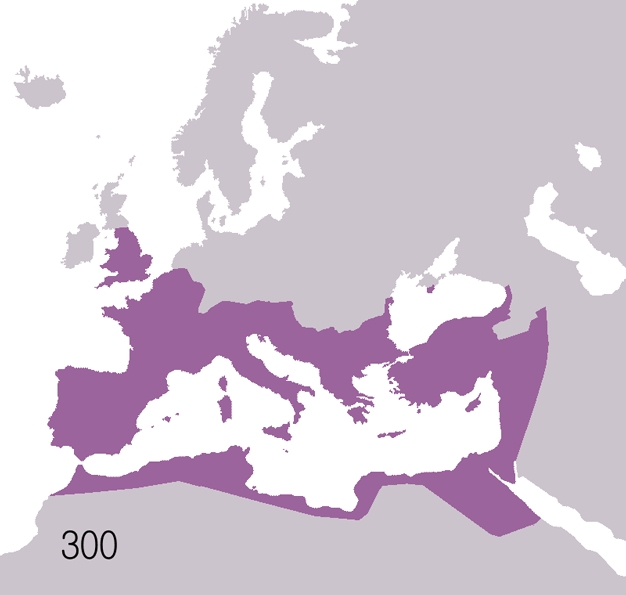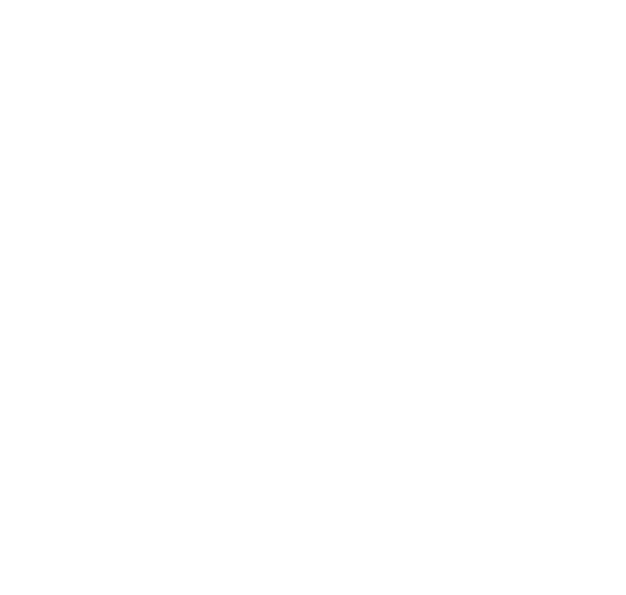
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided among several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading peoples outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Christianity
Western Christianity is one of two subdivisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Protestantism, Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic Church, Independent Catholicism and Restorationism. The large majority of the world's 2.3 billion Christians are Western Christians (about 2 billion: 1.2 billion Latin Catholic and 1.17 billion Protestant). One major component, the Latin Church, developed under the bishop of Rome. Out of the Latin Church emerged a wide variety of independent Protestant denominations, including Lutheranism and Anglicanism, starting from the Protestant Reformation in the 16th century, as did Independent Catholicism in the 19th century. Thus, the term "Western Christianity" does not describe a single Communion (Christian), communion or religious denomination but is applied to distinguish all these denominations collectively from Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synoptic Gospel
The gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical wording. They stand in contrast to John, whose content is largely distinct. The term ''synoptic'' (; ) comes via Latin from the Greek , ''synopsis'', i.e. "(a) seeing all together, synopsis". The modern sense of the word in English is of "giving an account of the events from the same point of view or under the same general aspect". , , , , , . It is in this sense that it is applied to the synoptic gospels. This strong parallelism among the three gospels in content, arrangement, and specific language is widely attributed to literary interdependence, though the role of orality and memorization of sources has also been explored by scholars. The question of the precise nature of their literary relationship—the synoptic problem—has been a topic of debate for centuries and has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |