|
Phenylpropanoids Metabolism
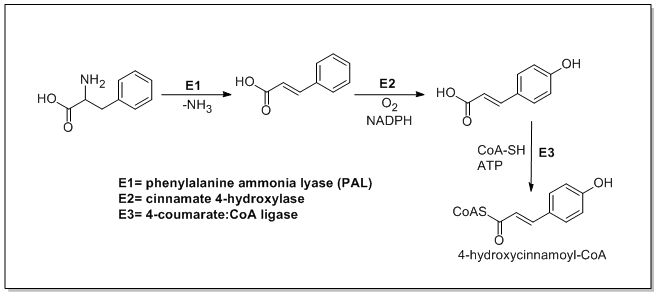
The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes. From amino acids to cinnamates In plants, all phenylpropanoids are derived from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, a.k.a. phenylalanine/tyrosine ammonia-lyase) is an enzyme that transforms L-phenylalanine and tyrosine into trans-cinnamic acid and p-coumaric acid, ''p''-coumaric acid, respectively. Trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (cinnamate 4-hydroxylase) is the enzyme that transforms trans-cinnamate into 4-hydroxycinnamate (''p''-coumaric acid). 4-Coumarate-CoA ligase is the enzyme that transforms 4-coumarate (''p''-coumaric acid) into 4-coumaroyl-CoA. Enzymes associated with biosynthesis of hydroxycinnamic acids * Cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD), an enzyme that transforms cinnamyl alcohol into cinnamaldehyde * Sinapine esterase, an enzyme that transforms sinapoylcholine into sinapate (sinapic acid) and choline * Trans-cinnamate 2-monooxygenase, an enzyme that tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis, i.e., chemical synthesis occurring in biological contexts, is a term most often referring to multi-step, enzyme-Catalysis, catalyzed processes where chemical substances absorbed as nutrients (or previously converted through biosynthesis) serve as enzyme substrate (chemistry), substrates, with conversion by the living organism either into simpler or more complex Product (chemistry), products. Examples of biosynthetic pathways include those for the production of amino acids, lipid membrane components, and nucleotides, but also for the production of all classes of biological macromolecules, and of acetyl-coenzyme A, adenosine triphosphate, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and other key intermediate and transactional molecules needed for metabolism. Thus, in biosynthesis, any of an array of Chemical compound, compounds, from simple to complex, are converted into other compounds, and so it includes both the catabolism and anabolism (building up and breaking down) of comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choline
Choline is a cation with the chemical formula . Choline forms various Salt (chemistry), salts, such as choline chloride and choline bitartrate. An essential nutrient for animals, it is a structural component of phospholipids and cell membranes. Choline is used to synthesize acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter involved in muscle control and numerous functions of the nervous system. Choline is involved in early development of the brain, gene expression, cell membrane Signaling peptide receptor, signaling, and brain metabolism. Although humans synthesize choline in the liver, the amount produced naturally is insufficient to meet cellular functions, requiring that some choline be obtained from foods or dietary supplements. Foods rich in choline include meats, poultry, eggs, and other animal-based products, cruciferous vegetables, beans, nuts, and whole grains. Choline is present in breast milk and is commonly added as an food additive, ingredient to baby foods. Chemistry Choline i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinapoylglucose—choline O-sinapoyltransferase
In enzymology, a sinapoylglucose---choline O-sinapoyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :1-O-sinapoyl-beta-D-glucose + choline \rightleftharpoons D-glucose + sinapoylcholine Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 1-O-sinapoyl-beta-D-glucose and choline, whereas its two products are D-glucose and sinapoylcholine (sinapine). This enzyme belongs to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 1-O-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxycinnamoyl)-beta-D-glucose:choline 1-O-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxycinnamoyl)transferase. This enzyme is also called sinapine synthase. This enzyme participates in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis The biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids involves a number of enzymes. From amino acids to cinnamates In plants, all phenylpropanoids are derived from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL, a.k.a. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate 3'-monooxygenase
In enzymology, a 5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate 3'-monooxygenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :trans-5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate + NADPH + H+ + O2 \rightleftharpoons trans-5-O-caffeoyl-D-quinate + NADP+ + H2O The 4 substrates of this enzyme are trans-5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate, NADPH, H+, and O2, whereas its 3 products are trans-5-O-caffeoyl-D-quinate, NADP+, and H2O. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on paired donors, with O2 as oxidant and incorporation or reduction of oxygen. The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2 with NADH or NADPH as one donor, and incorporation of one atom o oxygen into the other donor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is trans-5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (3'-hydroxylating). Other names in common use include 5-O-(4-coumaroyl)-D-quinate/shikimate 3'-hydroxylase, and coumaroylquinate(coumaroylshikimate) 3'-monooxygenase. This enzyme pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase
In enzymology, a caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase () is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes the chemical reaction :S-adenosyl-L-methionine + caffeoyl-CoA \rightleftharpoons S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine + feruloyl-CoA Thus, the two substrate (biochemistry), substrates of this enzyme are S-Adenosyl methionine, S-adenosyl methionine and caffeoyl-CoA, whereas its two product (chemistry), products are S-adenosylhomocysteine and feruloyl-CoA. A large number of natural products are generated via a step involving this enzyme.Wout Boerjan, John Ralph, Marie Baucher "Lignin Biosynthesis" Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, vol. 54, pp. 519–46. This enzyme is classified to the family of transferases, specifically those transferring one-carbon group methyltransferases. The List of enzymes, systematic name of this enzyme class is S-adenosyl-L-methionine:caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase. Other names in common use include caffeoyl coenzyme A methyltransferase, caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-methyltransferase, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferulic Acid
Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid derivative and a phenolic compound. It is an organic compound with the formula (CH3O)HOC6H3CH=CHCO2H. The name is derived from the genus '' Ferula'', referring to the giant fennel ('' Ferula communis''). Classified as a phenolic phytochemical, ferulic acid is an amber colored solid. Esters of ferulic acid are found in plant cell walls, covalently bonded to hemicellulose such as arabinoxylans. Salts and esters derived from ferulic acid are called ferulates. Occurrence in nature Ferulic acid is ubiquitous in the plant kingdom, including a number of vegetable sources. It occurs in particularly high concentrations in popcorn and bamboo shoots. It is a major metabolite of chlorogenic acids in humans along with caffeic and isoferulic acid, and is absorbed in the small intestine, whereas other metabolites such as dihydroferulic acid, feruloylglycine and dihydroferulic acid sulfate are produced from chlorogenic acid in the large intestine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeic Acid
Caffeic acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a polyphenol with a key role in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated in energy metabolism. Caffeic acid is also one major polyphenol responsible for maintaining normal levels of nitric oxide (NO) within cells. Caffeic acid is a yellow, solid chemical compound that is structually classified as a hydroxycinnamic acid, and the molecule consists of both phenolic and acrylic functional groups. Caffeic acid is found in all plants as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of lignin, a naturally occurring complex carbohydrate representing the principal components of biomass and its residues. It is chemically unrelated to caffeine; instead, the shared name is related to its presence in coffee. Natural occurrences Caffeic acid can be found in the bark of ''Eucalyptus globulus'' the barley grain ''Hordeum vulgare'' and the herb '' Dipsacus asperoides''. It can also be found in the freshwater fern '' Salvinia molest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |