|
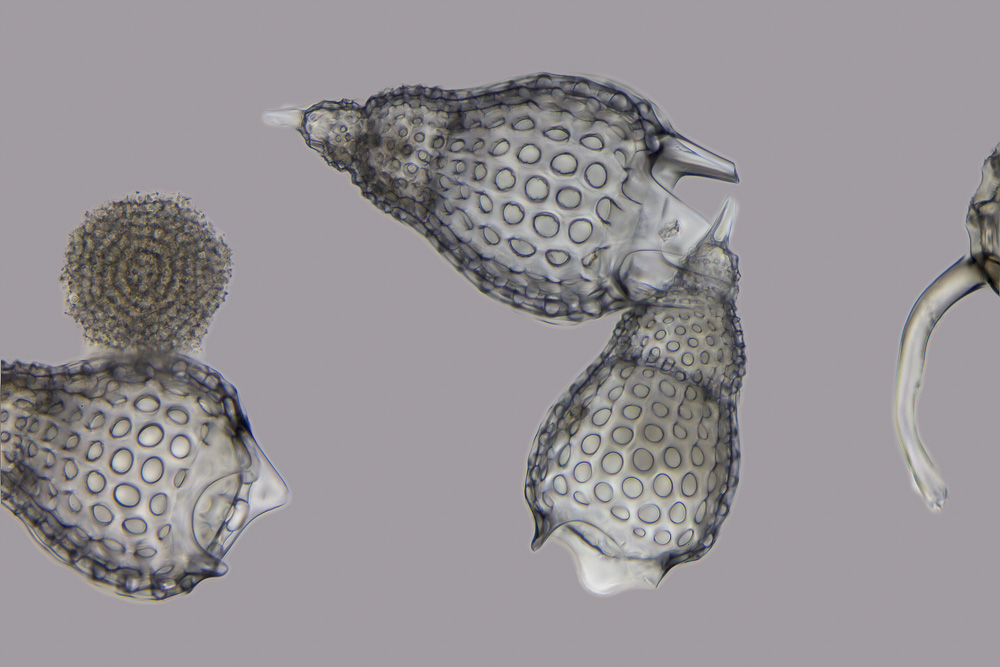
Phaeodaria
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell. The term "Radiozoa" has been used to refer to radiolaria when Phaeodarea is explicitly excluded. Phaeodarea produce hollow skeletons composed of amorphous silica and organic material, which rarely fossilize. The endoplasm is divided by a cape with three openings, of which one gives rise to feeding pseudopods, and the others let through bundles of microtubules that support the axopods. Unlike true radiolarians, there are no cross-bridges between them. They also lack symbiotic algae, generally living below the photic zone, and do not produce any Celestine (mineral), strontium sulfate. Character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cercozoa
Cercozoa (now synonymised with Filosa) is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by phylogeny, molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or Ubiquitin#Polyubiquitin chains, polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through phylogeny, molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of bacteria. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria. Characteristics The group includes most amoeboids and flagellates that feed by means of filose pseudopods. These may be restricted to part of the cell surface, but there is never a true cytostome or mouth as found in many other protozoa. They show a variety of forms and have proven difficult to define in terms of structural characteristics, although their unity is strongly supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolaria
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are unicellular eukaryotes of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any Eukaryote, eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, Embryophyte, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a Clade, natural group, or clade, but are a Paraphyly, paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancestor excluding land plants, animals, and fungi. Protists were historically regarded as a separate taxonomic rank, taxonomic kingdom (biology), kingdom known as Protista or Protoctista. With the advent of phylogenetic analysis and electron microscopy studies, the use of Protista as a formal taxon was gradually abandoned. In modern classifications, protists are spread across several eukaryotic clades called supergroup (biology), supergroups, such as Archaeplastida (photoautotrophs that includes land plants), SAR supergroup, SAR, Obazoa (which includes fungi and animals), Amoebozoa and "Excavata". Protists represent an extremely large genetic diversity, genetic and ecological diversity in all environments, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeboid
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose members share common descent. Consequently, amoeboid organisms are no longer classified together in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protist Shell
Many protists have protective shells or tests, usually made from silica (glass) or calcium carbonate (chalk). Protists are a diverse group of eukaryote organisms that are not plants, animals, or fungi. They are typically microscopic unicellular organisms that live in water or moist environments. Protists shells are often tough, mineralised forms that resist degradation, and can survive the death of the protist as a microfossil. Although protists are typically very small, they are ubiquitous. Their numbers are such that their shells play a huge part in the formation of ocean sediments and in the global cycling of elements and nutrients. The role of protist shells depends on the type of protist. Protists such as diatoms and radiolaria have intricate, glass-like shells made of silica that are hard and protective, and serve as a barrier to prevent water loss. The shells have small pores that allow for gas exchange and nutrient uptake. Coccolithophores and foraminifera also have h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeosphaerida
Phaeosphaerida is an order of cercozoans in the class Phaeodarea Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They a .... References * Report on the Radiolaria. E Haeckel, 1887 * Report on the scientific results of the voyage of the HMS Challenger during the years 1873–1876. E Haeckel, Zoology series, 1887 External links * Phaeosphaeridaat the World Register of Marine Spacies (WoRMS) Phaeodaria Rhizaria orders {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeogromida
Phaeogromida is an order of cercozoans in the class Phaeodarea Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They a .... References * Report on the Radiolaria. E Haeckel, 1887 * Report on the scientific results of the voyage of HMS Challenger during the years 1873–1876. E Haeckel, Zoology series, 1887 External links * Phaeogromidaat the World Register of Marine Spacies (WoRMS) Phaeodaria Rhizaria orders {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeodendrida
Phaeodendrida is an order of cercozoans in the class Phaeodarea Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They a .... References * Report on the Radiolaria. E Haeckel, 1887 * Report on the scientific results of the voyage of the HMS Challenger during the years 1873–1876. E Haeckel, Zoology series, 1887 External links * Phaeodendridaat the World Register of Marine Spacies (WoRMS) Phaeodaria Rhizaria orders {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeocalpida
Phaeocalpida is an order of cercozoans in the class Phaeodarea Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They a .... References * Report on the Radiolaria. E Haeckel, 1887 * Report on the scientific results of the voyage of the HMS Challenger during the years 1873-1876. E Haeckel, Zoology series, 1887 External links * Phaeocalpidaat the World Register of Marine Spacies (WoRMS) Phaeodaria Rhizaria orders {{Cercozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |