|
Pemmican War
The Pemmican War was a series of violent confrontations between the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) and the North West Company (NWC) in the Canadas from 1812 to 1821. It started after the establishment of the Red River Colony by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk in 1812, and ended in 1821 when the NWC was merged into the HBC. The conflict was sparked by the Pemmican Proclamation issued by Governor Miles Macdonell, which disallowed any person from exporting pemmican, a key foodstuff for those involved in the North American fur trade, out of the Red River Colony. This was fiercely opposed by the Métis, who were mostly affiliated with the NWC and opposed to both the colony and the HBC's dominance in the region. Background At the beginning of the 19th century, Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk attempted to resettle his fellow Scotsmen in North America. By 1808, Selkirk had founded two colonies, one on Prince Edward Island, another at Baldoon in Western Ontario, and was looking to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Colonization Of The Americas
The British colonization of the Americas is the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and, after 1707, Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain. Colonization efforts began in the late 16th century with failed attempts by England to establish permanent colonies in the North. The first permanent English overseas possessions, English colony in the Americas was established in Jamestown, Virginia, in 1607. Colonies were established in North America, Central America, South America, and the Caribbean. Though most British colonies in the Americas eventually gained independence, some colonies have remained under Britain's jurisdiction as British Overseas Territories. The first documented settlement of Europeans in the Americas was established by Norsemen, Norse people around 1000 AD in what is now Newfoundland, called Vinland by the Norse. Later European explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saulteaux
The Saulteaux (pronounced , or in imitation of the French pronunciation , also written Salteaux, Saulteau and Ojibwa ethnonyms, other variants), otherwise known as the Plains Ojibwe, are a First Nations in Canada, First Nations band government in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. They are a branch of the Ojibwe who pushed west. They formed a mixed culture of Woodland Indians, woodlands and Plains Indian, plains Indigenous customs and traditions. Ethnic classification The Saulteaux are a branch of the Ojibwe Indigenous peoples in Canada, Nations within Canada. They are sometimes called the Anihšināpē (Anishinaabe). ''Saulteaux'' is a French language, French term meaning 'waters ("eaux") - fall ("sault")', and by extension "People of the rapids/water falls", referring to their former location in the area of Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario, on the St. Marys River (Michigan–Ontario) which connects Lake Superior with Lake Huron. They are prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bois-Brûlés
Bois-Brûlés (''burnt wood'') are Métis. The name is most frequently associated with the French-speaking Métis of the Red River Colony in the Red River valley of Canada and the United States. The Bois-Brûlés, led by their leader Cuthbert Grant, took part in the Battle of Seven Oaks (1816). The "Chanson de la Grenouillère", composed in 1816 by Métis bard Pierre Falcon in honour of the Battle of Seven Oaks, also called "Falcon's Song" or "la Bataille des sept chênes", refers to the Métis participants as victorious "Bois-Brûlés", and the song remained central to Métis lore for generations. In 1837 Pierre Falcon also wrote "The Dickson Song" or "''Ballade du Général Dickson''". The song is about "General" James Dickson who planned to raise an army of Bois-Brûlés for the purpose of setting up a kingdom in California. William H. Keating described a group of Métis buffalo hunters he encountered at Pembina by the Red River of the North in 1823 as ''Bois brulés''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athabasca Country
In fur trade days the term Athabasca Country was used for the fur-producing region around Lake Athabasca. The area was important for two reasons. The cold climate produced some of the densest and thickest beaver fur in North America. The number of furs produced was somewhat greater than its only rival, the Saskatchewan River fur trade. Secondly, the great distance from Montreal and Hudson Bay required the highly developed and efficient transportation system that characterized the Hudson's Bay Company in the nineteenth century.Catton, Ted. (2000) ''The environment and the fur trade experience in Voyageurs National Park, 1730-1870.'' National Park Service. Midwest Region, pp. 8-9. The natural centre of the trade was the Peace-Athabasca Delta at the west end of Lake Athabasca. The lake itself led eastward into relatively poor country. To the north, the Slave River and Mackenzie River led to the Arctic Ocean. To the west, the Peace River led to the Rocky Mountains. To the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
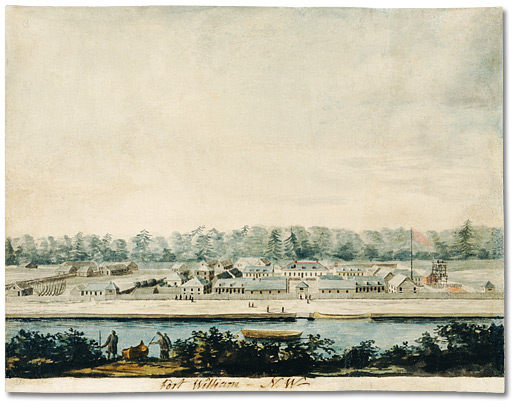
Fort William, Ontario
Fort William was a city in Ontario, Canada, located on the Kaministiquia River, at its entrance to Lake Superior. Incorporated as a town in 1892 and as a city in 1907, it was amalgamated with Port Arthur and the townships of Neebing and McIntyre to form the city of Thunder Bay in January 1970. Coat of arms and motto The city's Latin motto was ''A posse ad esse'' (''From a possibility to an actuality''), featured on its coat of arms designed in 1900 by town officials, "On one side of the shield stands an Indian dressed in the paint and feathers of the early days; on the other side is a French voyageur; the cent econtains a grain elevator, a steamship and a locomotive, while the beaver surmounts the whole." History Fur trade era 1671–1884 Fort William and Grand Portage were the two starting points for the canoe route from the Great Lakes to Western Canada. For details of the route inland see Kaministiquia River. French regime (Fort Kamanistigouian, Caministogoyan) Kamanistigo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bas De La Rivière
Bas may refer to: People * Bas (name), a given name and a surname * Bas (rapper) (born 1987) Chemistry * Boron arsenide (BAs), a chemical compound * Barium sulfide (BaS), a chemical compound Other uses * ''bas'' (French for "low"), as in bas-relief sculpture * Tamburica, a stringed instrument sometimes known as bas * BAS (accounting) The Swedish BAS chart of accounts (Basic chart), represents the Swedish accounting generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and is an open to use chart of accounts for accounting in Sweden available in Swedish, English and German language t ..., the Swedish accounting principles and chart of accounts See also * * BAS (other) * Bass (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis Buffalo Hunt
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They have a shared history and culture, deriving from specific mixed European (primarily French, Scottish, and English) and Indigenous ancestry (primarily Cree with strong kinship to Cree people and communities), which became distinct through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three legally recognized Indigenous peoples in the ''Constitution Act, 1982'', along with the First Nations and Inuit. The term ''Métis'' (uppercase 'M') typically refers to the specific community of people defined as the Métis Nation, which originated largely in the Red River Valley and organized politically in the 19th century, radiating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffalo Meat Drying, White Horse Plains, Red River
Buffalo most commonly refers to: * True buffalo or Bubalina, a subtribe of wild cattle, including most "Old World" buffalo, such as water buffalo * Bison, a genus of wild cattle, including the American buffalo * Buffalo, New York, a city in the northeastern United States Buffalo or buffaloes may also refer to: Animals * Bubalina, a subtribe of the tribe Bovini within the subfamily Bovinae **African buffalo or Cape Buffalo (''Syncerus caffer'') ** ''Bubalus'', a genus of bovines including various water buffalo species ***Wild water buffalo (''Bubalus arnee'') *** Water buffalo (''Bubalus bubalis'') ****Buffalo meat, the meat of the water buffalo **** Italian Mediterranean buffalo, a breed of water buffalo *** Anoa *** Tamaraw (''Bubalus mindorensis'') ***''Bubalus murrensis'', an extinct species of water buffalo that occupied riverine habitats in Europe in the Pleistocene * Bison, large, even-toed ungulates in the genus ''Bison'' within the subfamily Bovinae **American bison (''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saskatchewan River
The Saskatchewan River (Cree: , "swift flowing river") is a major river in Canada. It stretches about from where it is formed by the joining of the North Saskatchewan River and South Saskatchewan River just east of Prince Albert, Saskatchewan. It flows roughly eastward across Saskatchewan and Manitoba to empty into Lake Winnipeg. Through its tributaries the North Saskatchewan and South Saskatchewan, its watershed encompasses much of the prairie regions of Canada, stretching westward to the Rocky Mountains in Alberta and north-western Montana in the United States. Including its tributaries, it reaches to its farthest headwaters on the Bow River, a tributary of the South Saskatchewan in Alberta. Description It is formed in central Saskatchewan, approximately east of Prince Albert, Saskatchewan, Prince Albert, by the confluence of its two major branches, the North Saskatchewan River, North Saskatchewan and the South Saskatchewan River, South Saskatchewan, at the Saskatchewa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland House, Saskatchewan
Cumberland House () is a community in Division No. 18, Saskatchewan, Census Division No. 18 in northeast Saskatchewan, Canada on the Saskatchewan River. It is the oldest community in Saskatchewan and has a population of about 2,000 people. Cumberland House Provincial Park, which provides tours of an 1890s powder house built by the Hudson's Bay Company, is located nearby. The community is on Cumberland Island (Saskatchewan), Cumberland Island and consists of the Northern village (Saskatchewan), Northern Village of Cumberland House with a population of 772 and the adjoining Cumberland House Cree Nation with a population of 715. The community is served by the Cumberland House Airport and by Saskatchewan Highway 123, Highway 123. Cumberland House Cree Nation The population of Cumberland House consists of mostly First Nations in Canada, First Nations people, including Cree and Métis people (Canada), Métis. Cumberland House was and is a Cree "n" dialect community, known in Cree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast of Nunavut, but politically entirely part of Nunavut. It is an inland sea, inland List of seas on Earth#Marginal seas by ocean, marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. The Hudson Strait provides a connection between the Labrador Sea and the Atlantic Ocean in the northeast, while the Foxe Channel connects Hudson Bay with the Arctic Ocean in the north. The Hudson Bay drainage basin drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of southeastern Nunavut, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, all of Manitoba, and parts of the U.S. states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota, and Montana. Hudson Bay's southern arm is called James Bay. The East Cree, Eastern Cree name for Hudson and James Bay is (southern dialect) or (northern dialect), m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |