 |
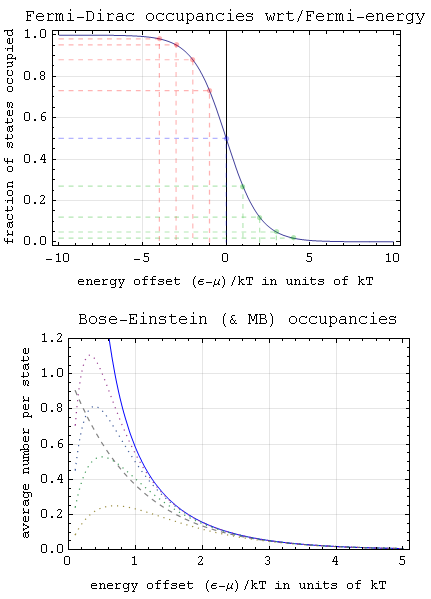
Particle Statistics
Particle statistics is a particular description of multiple particles in statistical mechanics. A key prerequisite concept is that of a statistical ensemble (an idealization comprising the state space of possible states of a system, each labeled with a probability) that emphasizes properties of a large system as a whole at the expense of knowledge about parameters of separate particles. When an ensemble describes a system of particles with similar properties, their number is called the particle number and usually denoted by ''N''. Classical statistics In classical mechanics, all particles ( fundamental and composite particles, atoms, molecules, electrons, etc.) in the system are considered distinguishable. This means that individual particles in a system can be tracked. As a consequence, switching the positions of any pair of particles in the system leads to a different configuration of the system. Furthermore, there is no restriction on placing more than one particle in any given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic particles like powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun '' particulate'' is most frequently used to refer to pollutants in the Earth's atmosphere, which are a suspension of unconnected particles, rather than a connected particle aggregation. Conceptual properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Lepton
In particle physics, a lepton is an elementary particle of half-integer spin (Spin (physics), spin ) that does not undergo strong interactions. Two main classes of leptons exist: electric charge, charged leptons (also known as the electron-like leptons or muons), including the electron, muon, and tauon, and neutral leptons, better known as neutrinos. Charged leptons can combine with other particles to form various composite particles such as atoms and positronium, while neutrinos rarely interact with anything, and are consequently rarely observed. The best known of all leptons is the electron. There are six types of leptons, known as ''flavour (particle physics), flavours'', grouped in three ''Generation (particle physics), generations''. The Standard Model, first-generation leptons, also called ''electronic leptons'', comprise the electron () and the electron neutrino (); the second are the ''muonic leptons'', comprising the muon () and the muon neutrino (); and the third a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Permutation Group
In mathematics, a permutation group is a group ''G'' whose elements are permutations of a given set ''M'' and whose group operation is the composition of permutations in ''G'' (which are thought of as bijective functions from the set ''M'' to itself). The group of ''all'' permutations of a set ''M'' is the symmetric group of ''M'', often written as Sym(''M''). The term ''permutation group'' thus means a subgroup of the symmetric group. If then Sym(''M'') is usually denoted by S''n'', and may be called the ''symmetric group on n letters''. By Cayley's theorem, every group is isomorphic to some permutation group. The way in which the elements of a permutation group permute the elements of the set is called its group action. Group actions have applications in the study of symmetries, combinatorics and many other branches of mathematics, physics and chemistry. Basic properties and terminology A ''permutation group'' is a subgroup of a symmetric group; that is, its elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Spin–statistics Theorem
The spin–statistics theorem proves that the observed relationship between the intrinsic spin of a particle (angular momentum not due to the orbital motion) and the quantum particle statistics of collections of such particles is a consequence of the mathematics of quantum mechanics. According to the theorem, the many-body wave function for elementary particles with integer spin ( bosons) is symmetric under the exchange of any two particles, whereas for particles with half-integer spin ( fermions), the wave function is antisymmetric under such an exchange. A consequence of the theorem is that non-interacting particles with integer spin obey Bose–Einstein statistics, while those with half-integer spin obey Fermi–Dirac statistics. Background The statistics of indistinguishable particles is among the most fundamental of physical effects. The Pauli exclusion principle that every occupied quantum state contains at most one fermion controls the formation of matter. The basic bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Symmetry (physics)
The symmetry of a physical system is a physical or mathematical feature of the system (observed or intrinsic) that is preserved or remains unchanged under some Transformation (function), transformation. A family of particular transformations may be ''continuous'' (such as rotation of a circle) or ''discrete space, discrete'' (e.g., Reflection (physics), reflection of a bilaterally symmetric figure, or rotation of a regular polygon). Continuous and discrete transformations give rise to corresponding types of symmetries. Continuous symmetries can be described by Lie groups while discrete symmetries are described by finite groups (see ''Symmetry group''). These two concepts, Lie and finite groups, are the foundation for the fundamental theories of modern physics. Symmetries are frequently amenable to mathematical formulations such as representation of a Lie group, group representations and can, in addition, be exploited to simplify many problems. Arguably the most important examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physical examples of macromolecules. Common macromolecules are biopolymers (nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates). and polyolefins (polyethylene) and polyamides (nylon). Synthetic macromolecules Many macromolecules are synthetic polymers (plastics, synthetic fibers, and synthetic rubber. Polyethylene is produced on a particularly large scale such that ethylene is the primary product in the chemical industry. Macromolecules in nature * Proteins are polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds. * DNA and RNA are polymers of nucleotides joined by phosphodiester bonds. These nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a sugar ( ribose in the case of RNA, deoxyribose in the case of DNA), and a nucleotide base (either adenine, guan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pungent smell. It is widely used in fertilizers, refrigerants, explosives, cleaning agents, and is a precursor for numeous chemicals. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to fertilisers. Around 70% of ammonia produced industrially is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil. Ammonia, either directly or indirectly, is also a building block for the synthesis of many chemicals. In many countries, it is classified as an List of extremely hazardous substances, extremely hazardous substance. Ammonia is toxic, cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Liquid Helium
Liquid helium is a physical state of helium at very low temperatures at standard atmospheric pressures. Liquid helium may show superfluidity. At standard pressure, the chemical element helium exists in a liquid form only at the extremely low temperature of . Its boiling point and critical point depend on the isotope of helium present: the common isotope helium-4 or the rare isotope helium-3. These are the only two stable isotopes of helium. See the table below for the values of these physical quantities. The density of liquid helium-4 at its boiling point and a pressure of one atmosphere (101.3 kilopascals) is about , or about one-eighth the density of liquid water. Liquefaction Helium was first liquefied on July 10, 1908, by the Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes at the University of Leiden in the Netherlands. At that time, helium-3 was unknown because the mass spectrometer had not yet been invented. In more recent decades, liquid helium has been used as a cryogenic refriger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Quantum State
In quantum physics, a quantum state is a mathematical entity that embodies the knowledge of a quantum system. Quantum mechanics specifies the construction, evolution, and measurement of a quantum state. The result is a prediction for the system represented by the state. Knowledge of the quantum state, and the rules for the system's evolution in time, exhausts all that can be known about a quantum system. Quantum states may be defined differently for different kinds of systems or problems. Two broad categories are * wave functions describing quantum systems using position or momentum variables and * the more abstract vector quantum states. Historical, educational, and application-focused problems typically feature wave functions; modern professional physics uses the abstract vector states. In both categories, quantum states divide into pure versus mixed states, or into coherent states and incoherent states. Categories with special properties include stationary states for tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element. Atoms are extremely small, typically around 100 picometers across. A human hair is about a million carbon atoms wide. Atoms are smaller than the shortest wavelength of visible light, which means humans cannot see atoms with conventional microscopes. They are so small that accurately predicting their behavior using classical physics is not possible due to quantum mechanics, quantum effects. More than 99.94% of an atom's mass is in the nucleus. Protons hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Quantum Number
In quantum physics and chemistry, quantum numbers are quantities that characterize the possible states of the system. To fully specify the state of the electron in a hydrogen atom, four quantum numbers are needed. The traditional set of quantum numbers includes the principal, azimuthal, magnetic, and spin quantum numbers. To describe other systems, different quantum numbers are required. For subatomic particles, one needs to introduce new quantum numbers, such as the flavour of quarks, which have no classical correspondence. Quantum numbers are closely related to eigenvalues of observables. When the corresponding observable commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system, the quantum number is said to be " good", and acts as a constant of motion in the quantum dynamics. History Electronic quantum numbers In the era of the old quantum theory, starting from Max Planck's proposal of quanta in his model of blackbody radiation (1900) and Albert Einstein's adaptation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |