|
Parasite Aircraft
A parasite aircraft is a component of a composite aircraft which is carried aloft and air launched by a larger carrier aircraft or mother ship to support the primary mission of the carrier. The carrier craft may or may not be able to later recover the parasite during flight. The first parasite aircraft flew in 1916, when the United Kingdom, British launched a Bristol Scout from a Felixstowe Porte Baby flying boat. The idea eventually developed into jet bombers carrying fully capable parasite fighters. With the advent of long-range fighters equipped with Air-to-air missile, air-to-air missiles, and aerial refueling, parasite fighters fell out of use. Parasite fighters Until the middle of the 20th century there was military interest in parasite fighters – fighter aircraft intended to be carried into a combat zone by a larger aircraft, such as a bomber aircraft, bomber. If the bomber were threatened, the parasite would be released to defend it. Parasite fighters have never bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cyril Porte
Lieutenant Colonel John Cyril Porte, (26 February 1884 – 22 October 1919) was a British flying boat aviation pioneer, pioneer associated with the First World War Seaplane Experimental Station at Felixstowe. Early life and career Porte was born on 26 February 1884 to Reverend John Robert Porte (1849–1922) Trinity College, Dublin, TCD and Henrietta (née Scott) in Bandon, County Cork,Notice of Death. ''Flight'' 30 October 1919 Ireland. Reverend Doctor of Divinity, Dr. Porte served as Rector (ecclesiastical), Rector of St Peter's, Ballymodan, Bandon before moving to England with his family as Vicar of St Matthew's church, Denmark Hill in 1890. Rev. Porte's father, George Porte (1819–1892) was a Civil Engineer and Schoolmaster, master of The H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
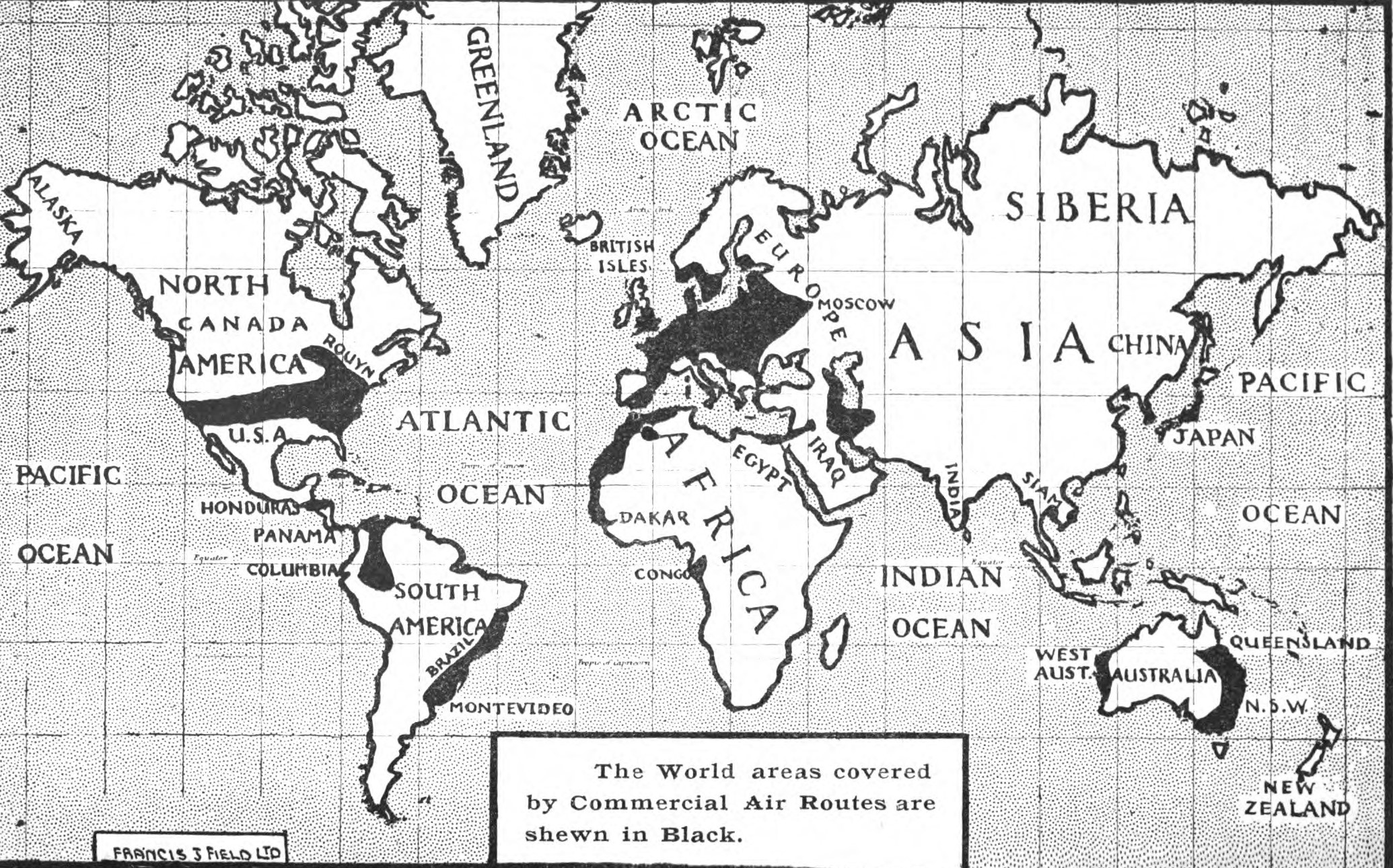
1925 In Aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1925. Events * In the United Kingdom, the first Royal Auxiliary Air Force squadrons are formed. * The Eberhart Steel Products Company of Buffalo, New York, forms an aircraft design and manufacturing subsidiary, the Eberhart Aeroplane and Motor Company. * Summer 1925 – Two Breguet 19 G.R. aircraft owned by the Japanese ''Asahi Shimbun'' newspaper group fly from Tokyo, Japan, to Paris, France. January * January 1 – The French airline CIDNA is formed. February * February 3–4 – In a Breguet 19 G.R., the French aviators Henri Lemaître and Ludovic Arrachart set a world distance record, flying from Étampes, Paris, France, to Villa Cisneros, Spanish Sahara. * February 12 – Sabena establishes the first airline connection between Belgium and the Belgian Congo, pioneering a long-haul route to Léopoldville. March * March 1 – Ryan Airline Company begins regular services. *March 2 – Huff Dal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Airship Scheme
The British Imperial Airship Scheme was a project conceived in 1924 to improve communication and provide transportation between Great Britain and distant countries of the vast British Empire by establishing regular air service using passenger airships. The first phase was the construction of two large and technically advanced airships, the R100 and the R101; the R100 made a successful transatlantic trial flight to Canada and back during the summer of 1930. In October 1930, the R101, beset with several design and manufacturing flaws, crashed and burned in France while attempting its first flight to India. In 1931, following the loss of the R101, the entire British airship scheme was terminated. Early proposals In July 1921, Alfred Henry Ashbolt, the Agent-General for Tasmania, proposed the creation of an Imperial Airship Company to the Imperial Conference being held in London. The use of heavier-than-air craft over such distances was seen as impractical at this time. The comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roosevelt Field (airport)
Roosevelt Field is a former airport, located in the East Garden City section of Uniondale, on Long Island, New York, United States. Originally called the Hempstead Plains Aerodrome, or sometimes Hempstead Plains field or the Garden City Aerodrome, it was a training field (Hazelhurst Field) for the Air Service, United States Army during World War I. In 1919, it was renamed in honor of President Theodore Roosevelt's son, Quentin, who was killed in air combat during World War I. Roosevelt Field was the takeoff point for many historic flights in the early history of aviation, including Charles Lindbergh's 1927 solo transatlantic flight. It was also used by other pioneering aviators, including Amelia Earhart and Wiley Post. History The Hempstead Plains Aerodrome originally encompassed east of and abutting Clinton Road, south of and adjacent to Old Country Road, and west of Merrick Avenue. A bluff 15 feet in elevation divided the plain into two large fields. The U.S. Army ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Tilden
Fort Tilden, also known as Fort Tilden Historic District, is a former United States Army installation on the coast in the New York City borough of Queens. Fort Tilden now forms part of the Gateway National Recreation Area, and is administered by the National Park Service. Fort Tilden Historic District is located on the Rockaway Peninsula, between Jacob Riis Park to the east and Breezy Point Tip to the west. All three of these sites are operated by the National Park Service. Since its decommissioning, the former installation has largely become a natural area of beaches, dunes and maritime forest. Most of the old military installations are abandoned, and military structures which formerly housed artillery (batteries) and ammunition (magazines) are covered in graffiti. A few buildings have been renovated and are used by local arts groups, and some large open areas are used as sports grounds. Atop one of the old batteries, Battery Harris East, a viewing platform has 360-degr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curtiss JN-4
The Curtiss JN "Jenny" is a series of biplanes built by the Glenn Curtiss Aeroplane Company of Hammondsport, New York, later the Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. Although the Curtiss JN series was originally produced as a training aircraft for the US Army, the "Jenny" (the common nickname derived from "JN") continued after World War I as a civilian aircraft, becoming the "backbone of American postwar ivilaviation". Thousands of surplus Jennys were sold at bargain prices to private owners in the years after the war, and became central to the barnstorming era that helped awaken the US to civil aviation through much of the 1920s. Design and development Curtiss combined the best features of the model J and model N trainers, built for the US Army and US Navy, and began producing the JN or "Jenny" series of aircraft in 1915. Curtiss built only a limited number of the JN-1 and JN-2 biplanes. The design was commissioned by Glenn Curtiss from Englishman Benjamin Douglas Thom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-class Blimp
The C-class blimp was a patrol airship developed by the US Navy near the end of World War I, a systematic improvement upon the B class blimp, B-type which was suitable for training, but of limited value for patrol work. Larger than the B-class, the C-class blimps had two motors and a longer endurance. As with the B-class, the envelope production was split between Goodyear Aerospace, Goodyear and Goodrich Corporation, Goodrich, with control cars being built by the Burgess Company, Burgess division of Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company. Originally the Navy ordered 30 but reduced the number to 10 after the armistice in November 1918.Althoff, William F, ''SkyShips'', New York: Orion Books, 1990, , p. 6. All ten of the "C" type airships were delivered in late 1918, and examples served at all of the Navy's airship stations from 1918 to 1922. In 1921, the C-7 was the first airship ever to be inflated with helium.Clark, Basil, ''The History of Airships'', New York: St Martin's Press, 1961, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23-class Airship
The 23 class were rigid airships produced in the United Kingdom during the First World War. Development of the 23 class began in August 1915 when Vickers was asked to improve the 9r design by increasing its gas capacity by adding a bay and increasing the capacity of the bow and stern gas cells. The 23-class was designed by H.B. Pratt and Barnes Wallis of Vickers. Vickers built the first and last of the four ships. The other two were built by William Beardmore and Company and Armstrong-Whitworth. While the 23 class airships were never used in combat, the four ships provided many hours of valuable training and experimental data for British airship crews and designers. Although a total of 17 of these ships were contemplated at one time, only four were ever built.Higham 1961, pp. 135 The 23 class was found to be significantly overweight, leading to its cancellation in favour of the more-refined R23X class. Design and development Following proposals in July 1915 to order more ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopwith Camel
The Sopwith Camel is a British First World War single-seat biplane fighter aircraft that was introduced on the Western Front in 1917. It was developed by the Sopwith Aviation Company as a successor to the Sopwith Pup and became one of the best-known fighter aircraft of the Great War. Pilots flying Camels were credited with downing 1,294 enemy aircraft, more than any other Allied fighter of the conflict. Towards the end of the war, Camels lost their edge as fighters and were also used as a ground-attack aircraft. The Camel was powered by a single rotary engine and was armed with twin synchronized Vickers machine guns. It was difficult to fly, with 90% of its weight in the front two metres (seven feet) of the aircraft, but it was highly manoeuvrable in the hands of an experienced pilot, a vital attribute in the relatively low-speed, low-altitude dogfights of the era. Its pilots joked that their fates would involve "a wooden cross, the Red Cross, or a Victoria Cross". T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allies of World War I, Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has played History of the Royal Air Force, a significant role in Military history of the United Kingdom, British military history. In particular, during the Second World War, the RAF established Air supremacy, air superiority over Nazi Germany's Luftwaffe during the Battle of Britain, and led the Allied strategic bombing effort. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities nee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |