|
Panarthropoda
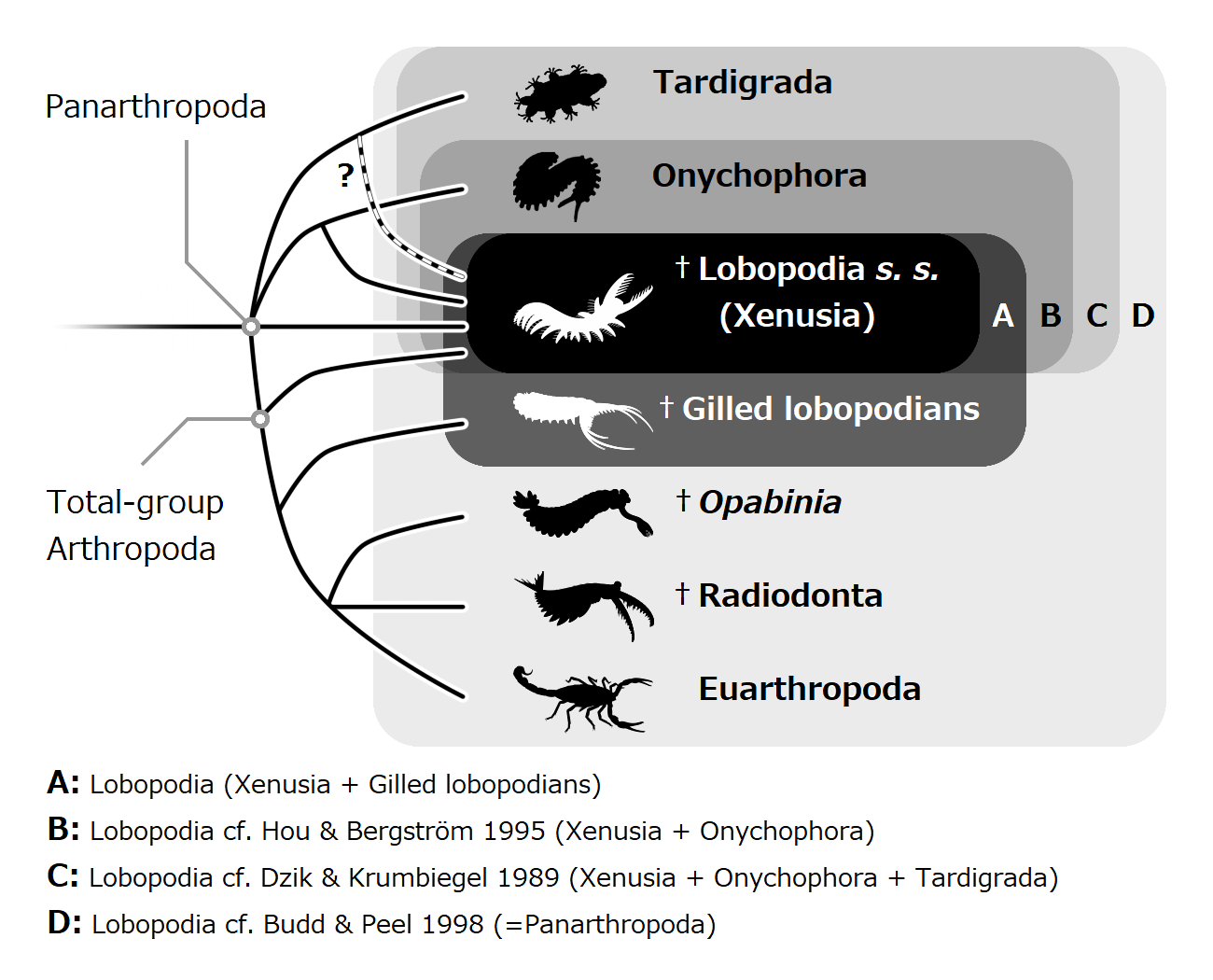
Panarthropoda is a clade comprising the greatest diversity of animal groups. It contains the extant phyla Arthropoda (Euarthropoda), Tardigrada (water bears) and Onychophora (velvet worms), although the precise relationships among these remained uncertain according to studies published in 2023 and 2024. Panarthropods also include extinct marine legged worms known as lobopodians (" Lobopodia"), a paraphyletic group where the last common ancestor and basal members ( stem-group) of each extant panarthropod phylum are thought to have risen. However the term "Lobopodia" is sometimes expanded to include tardigrades and onychophorans as well. Common characteristics of the Panarthropoda include a segmented body, paired ladder-like ventral nervous system, and the presence of paired appendages correlated with body segments. Taxonomy Not all studies support the monophyly of Panarthropoda, but most do, including neuroanatomical, phylogenomic and palaeontological studies. At l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
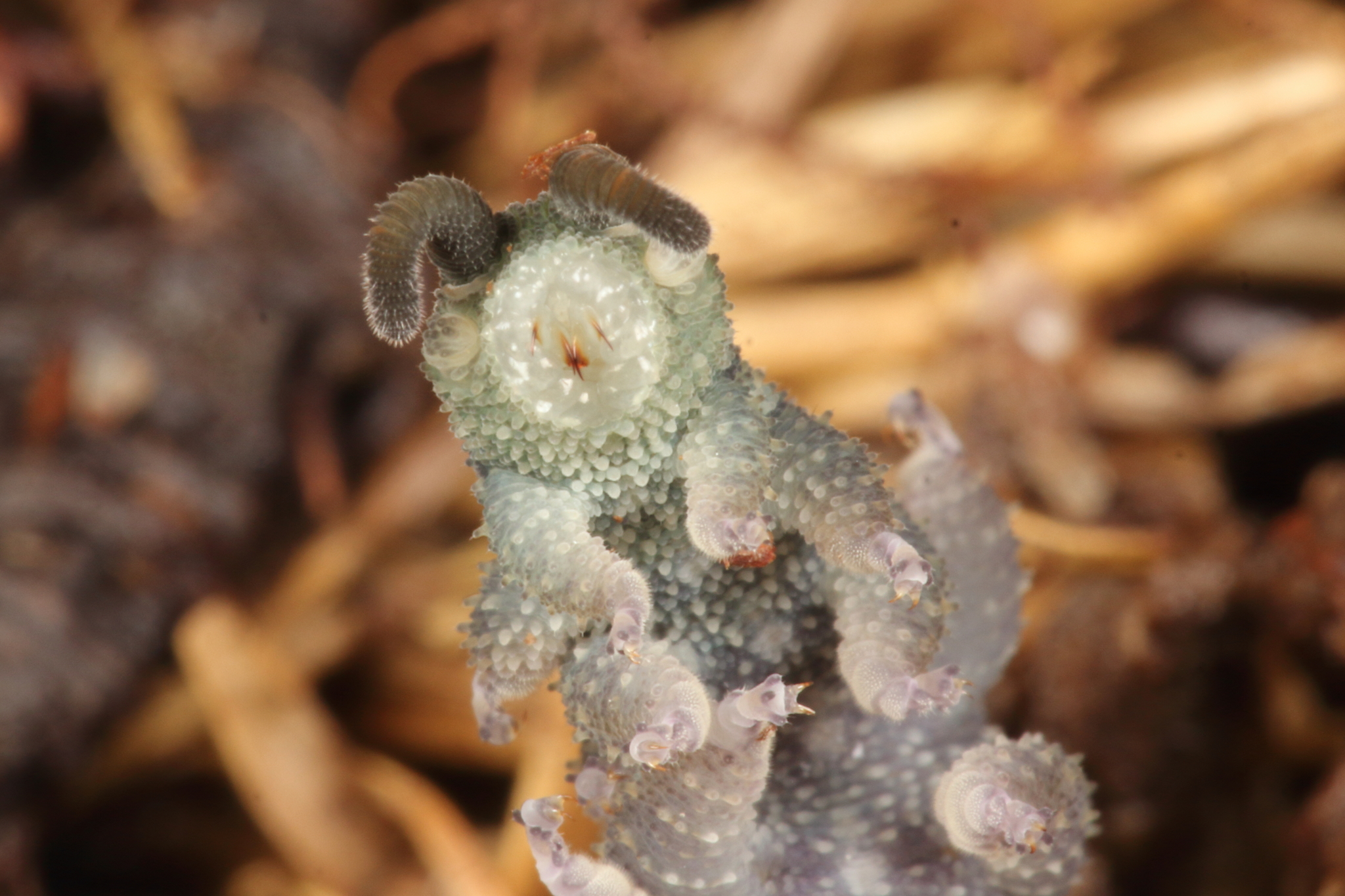
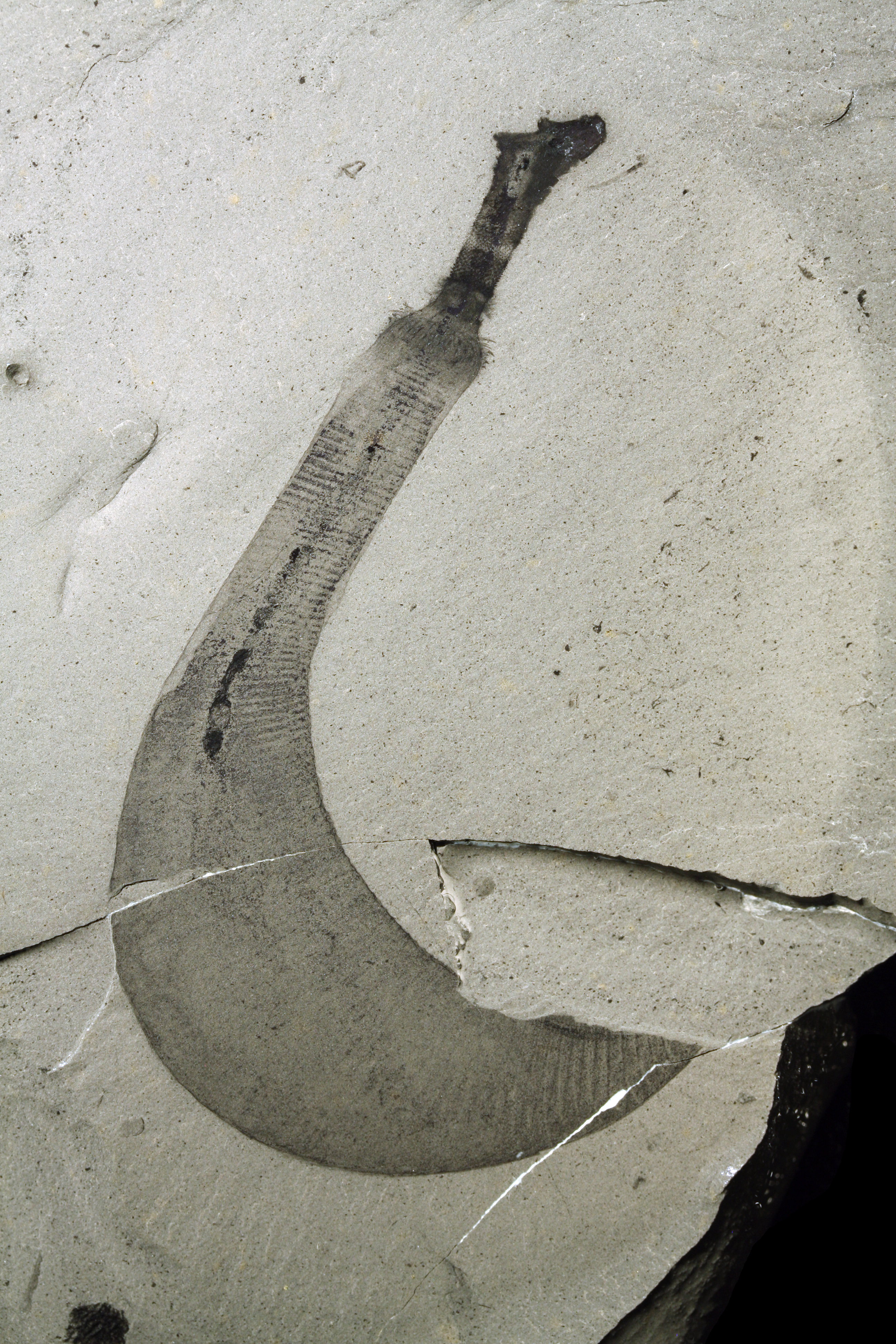
Lobopodia
Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia (), or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as '' Aysheaia'' and '' Hallucigenia''. However, other genera like '' Kerygmachela'' and '' Pambdelurion'' (which have features similar to other groups) are often referred to as “gilled lobopodians”. The oldest near-complete fossil lobopodians date to the Lower Cambrian; some are also known from Ordovician, Silurian and Carboniferous Lagerstätten. Some bear toughened claws, plates or spines, which are commonly preserved as carbonaceous or mineralized microfossils in Cambrian strata. The grouping is considered to be paraphyletic, as the three living panarthropod groups (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa () is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda (insects, chelicerates (including arachnids), crustaceans, and myriapods), Nematoda, and several smaller phylum (biology), phyla. The grouping of these animal phyla into a single clade was first proposed by Eernisse ''et al.'' (1992) based on a phylogenetic analysis of 141 morphological characters of ultrastructural and embryological phenotypes. This clade, that is, a group consisting of a common ancestor and all its descendants, was formally named by Aguinaldo ''et al.'' in 1997, based mainly on phylogenetic trees constructed using 18S ribosomal RNA genes. A large study in 2008 by Dunn ''et al.'' strongly supported the monophyly of Ecdysozoa. The group Ecdysozoa is supported by many Morphology (biology), morphological characters, including growth by ecdysis, with moulting of the cuticle – without mitosis in the epidermis – under control of the prohormone ecdysone, and internal fertilization. The group was i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onychophora
Onychophora (from , , "claws"; and , , "to carry"), commonly known as velvet worms (for their velvety texture and somewhat wormlike appearance) or more ambiguously as peripatus (after the first described genus, ''Peripatus''), is a phylum of elongate, soft-bodied, many-legged animals. In appearance they have variously been compared to worms with legs, caterpillars, and slugs. They prey upon other invertebrates, which they catch by ejecting an adhesive slime. Approximately 200 species of velvet worms have been described, although the true number is likely to be much greater. The two extant families of velvet worms are Peripatidae and Peripatopsidae. They show a peculiar distribution, with the peripatids being predominantly equatorial and tropical, while the peripatopsids are all found south of the equator. It is the only phylum within Animalia that is wholly endemic to terrestrial environments, at least among extant members. Velvet worms are generally considered close relatives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardigrade
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them . In 1776, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada, which means 'slow walkers'. They live in diverse regions of Earth's biospheremountaintops, the deep sea, tropical rainforests, and the Antarctic. Tardigrades are among the most resilient animals known, with individual species able to survive extreme conditions – such as exposure to extreme temperatures, extreme pressures (both high and low), air deprivation, radiation, dehydration, and starvation – that would quickly kill most other forms of life. Tardigrades have survived exposure to outer space. There are about 1,500 known species in the phylum Tardigrada, a part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa. The earliest known fossil is from the Cambrian, some 500 million years ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tardigrada
Tardigrades (), known colloquially as water bears or moss piglets, are a phylum of eight-legged Segmentation (biology), segmented micro-animals. They were first described by the German zoologist Johann August Ephraim Goeze in 1773, who called them . In 1776, the Italian biologist Lazzaro Spallanzani named them Tardigrada, which means 'slow walkers'. They live in diverse regions of Earth's biospheremountaintops, the deep sea, tropical rainforests, and the Antarctic. Tardigrades are among the most resilient animals known, with individual species able to survive extreme conditions – such as exposure to extreme temperatures, extreme pressures (both high and low), air deprivation, radiation, dehydration, and starvation – that would quickly kill most other forms of life. Tardigrades have survived exposure to outer space. There are about 1,500 known species in the phylum Tardigrada, a part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa. The earliest known fossil is from the Cambrian, some 500 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropoda
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated ( metameric) segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired ventral nerve cords running through all segments and forming paired ganglia in each segment. Their heads are formed by fusion of varying numbers of segments, and their brains are formed by fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metamerism (biology), metameric) Segmentation (biology), segments, and paired jointed appendages. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. They form an extremely diverse group of up to ten million species. Haemolymph is the analogue of blood for most arthropods. An arthropod has an open circulatory system, with a body cavity called a haemocoel through which haemolymph circulates to the interior Organ (anatomy), organs. Like their exteriors, the internal organs of arthropods are generally built of repeated segments. They have ladder-like nervous systems, with paired Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, ventral Ventral nerve cord, nerve cord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloneuralia
Cycloneuralia is a proposed clade of ecdysozoan animals including the Scalidophora ( Kinorhynchans, Loriciferans, Priapulids), the Nematoida (nematodes, Nematomorphs), and the extinct Palaeoscolecida. It may be paraphyletic, or may be a sister group to Panarthropoda. Or perhaps Panarthropoda is paraphyletic with respect to Cycloneuralia. The group has also been considered a single phylum, sometimes given the old name Nemathelminthes. The uniting character is the nervous system organization with a circumpharyngeal brain and somata–neuropil–somata pattern. The name derives from the position of the brain around the pharynx The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates .... References Ecdysozoa unranked clades {{protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Life
Marine life, sea life or ocean life is the collective ecological communities that encompass all aquatic animals, aquatic plant, plants, algae, marine fungi, fungi, marine protists, protists, single-celled marine microorganisms, microorganisms and associated marine virus, viruses living in the saline water of marine habitats, either the sea water of marginal seas and oceans, or the brackish water of coastal wetlands, lagoons, estuary, estuaries and inland seas. , more than 242,000 marine species have been documented, and perhaps two million marine species are yet to be documented. An average of 2,332 new species per year are being described. Marine life is studied scientifically in both marine biology and in biological oceanography. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on Earth, and served as the cradle of life and vital biotic sanctuaries throughout Earth's geological history. The earliest known life forms evolved as anaerobe, anaerobic prokaryotes (archaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostomia
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's members, although the reverse is typically true of its sister clade, Deuterostomia. Well-known examples of protostomes are arthropods, molluscs, annelids, flatworms and nematodes. They are also called schizocoelomates since schizocoely typically occurs in them. Together with the Deuterostomia and Xenacoelomorpha, these form the clade Bilateria, animals with bilateral symmetry, anteroposterior axis and three germ layers. Protostomy In animals at least as complex as earthworms, the first phase in gut development involves the embryo forming a dent on one side (the blastopore) which deepens to become its digestive tube (the archenteron). In the sister-clade, the deuterostomes (), the original dent becomes the anus while the gut event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priapulida
Priapulida (priapulid worms, from Gr. πριάπος, ''priāpos'' ' Priapus' + Lat. ''-ul-'', diminutive), sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility, because their general shape and their extensible spiny introvert (eversible) proboscis may resemble the shape of a human penis. They live in the mud, except for a few tropical meiobenthic species which live in medium- to coarse-grained sands, and are found in comparatively shallow waters to deep waters and no warmer than 12–13°C. Some species show a remarkable tolerance for hydrogen sulfide, anoxia and low salinity. ''Halicryptus spinulosus'' appears to prefer brackish shallow waters. They can be quite abundant in some areas. In an Alaskan bay as many as 85 adult individuals of '' Priapulus caudatus'' per square meter has been recorded, while the density of its larvae can be as high as 58,000 per square meter (5,390 per square foot). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterostomia
Deuterostomes (from Ancient Greek, Greek: ) are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia (), typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryogenesis, embryonic development. Deuterostomia comprises three Phylum, phyla: chordate, Chordata, Echinodermata, hemichordate, Hemichordata, and the extinct clade Cambroernida. In deuterostomes, the developing embryo's first opening (the blastopore) becomes the anus and cloaca, while the mouth is formed at a different site later on. This was initially the group's distinguishing characteristic, but deuterostomy has since been discovered among protostomes as well. The deuterostomes are also known as enterocoelomates, because their coelom develops through pouching of the gut, enterocoely. Deuterostomia's sister clade is Protostomia, animals that develop mouth first and whose digestive tract development is more varied. Protostomia includes the ecdysozoans and spiralians, as well as the extinct ''Kimberella'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |