|
Paleontology In Wyoming
Paleontology in Wyoming includes research into the prehistoric life of the U.S. state of Wyoming as well as investigations conducted by Wyomingite researchers and institutions into ancient life occurring elsewhere. The fossil record of the US state of Wyoming spans from the Precambrian to recent deposits. Many fossil sites are spread throughout the state. Wyoming is such a spectacular source of fossils that author Marian Murray noted in 1974 that " en today, it is the expected thing that any great museum will send its representatives to Wyoming as often as possible." Murray has also written that nearly every major vertebrate paleontologist in United States history has collected fossils in Wyoming. Wyoming is a major source of dinosaur fossils. Wyoming's dinosaur fossils are curated by museums located all over the planet. During the Precambrian, Wyoming was covered by a shallow sea inhabited by stromatolite-forming bacteria. This sea remained in place during the early Paleozoic e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of USA WY
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geography, geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscidean
Proboscidea (; , ) is a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family (Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. Three living species of elephant are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. Extinct members of Proboscidea include the deinotheres, mastodons, gomphotheres and stegodonts. The family Elephantidae also contains several extinct groups, including mammoths and ''Palaeoloxodon''. Proboscideans include some of the largest known land mammals, with the elephant '' Palaeoloxodon namadicus'' and mastodon ''"Mammut" borsoni'' suggested to have body masses surpassing , rivalling or exceeding paraceratheres (the otherwise largest known land mammals) in size. The largest extant proboscidean is the African bush elephant, with a world record of size of at the shoulder and . In addition to their eno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
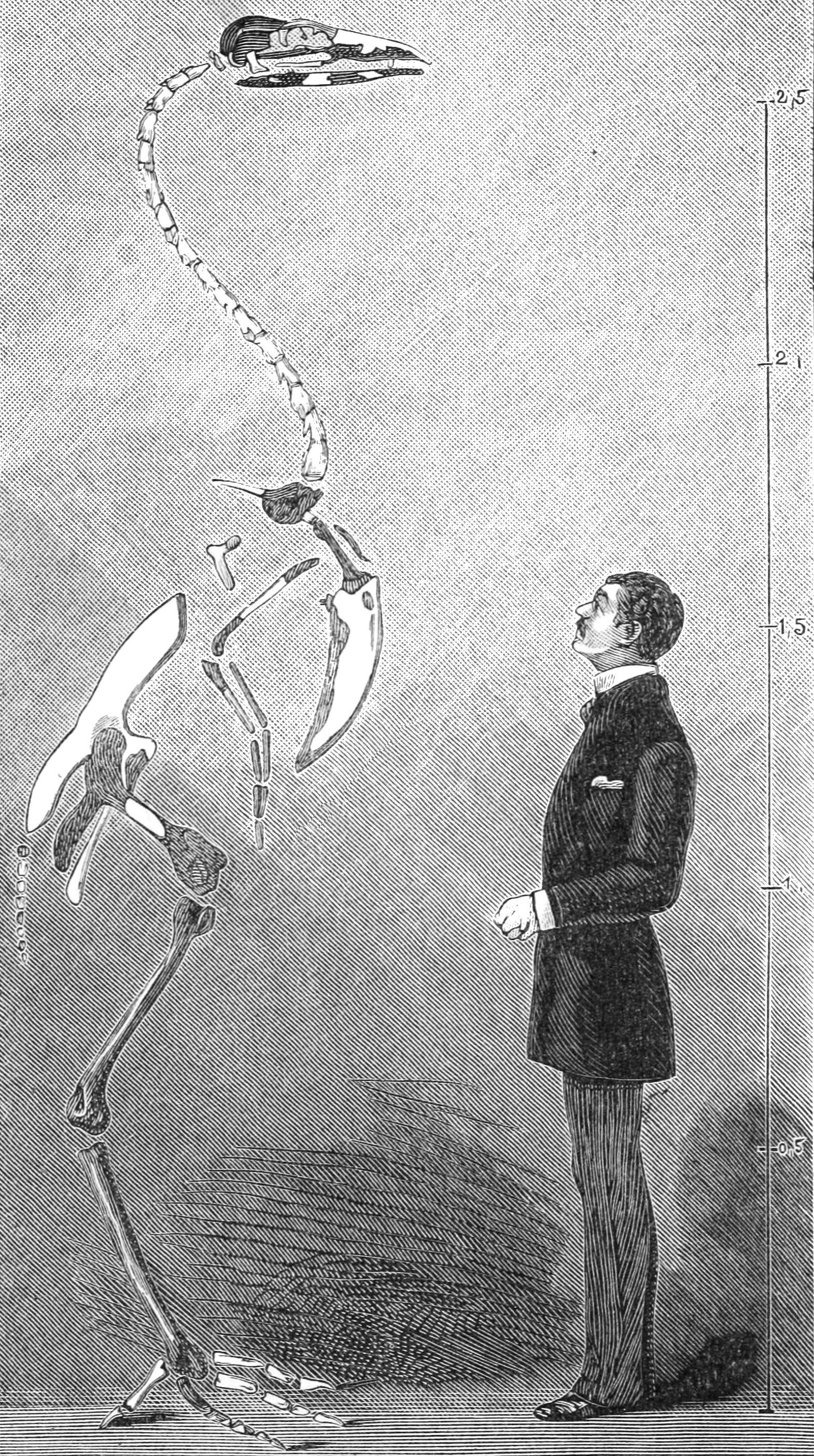
Gastornis
''Gastornis'' is an extinct genus of large, flightless birds that lived during the mid-Paleocene to mid-Eocene epochs of the Paleogene period. Most fossils have been found in Europe, and some species typically referred to the genus are known from North America and Asia. Several genera, including the well-studied genus ''Diatryma'', have historically been considered junior synonyms of ''Gastornis''. However, this interpretation has been challenged recently, and some researchers currently consider ''Diatryma'' to be a valid genus. ''Gastornis'' species were very large birds that were traditionally thought to have been predators of various smaller mammals, such as ancient, diminutive equids. However, several lines of evidence, including the lack of hooked claws (in known ''Gastornis'' footprints), studies of their beak structure and isotopic signatures of their bones, have caused scientists to now consider that these birds were probably herbivorous, feeding on tough plant material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creodont
Creodonta ("meat teeth") is a former order of extinct carnivorous placental mammals that lived from the early Paleocene to the late Miocene epochs in North America, Europe, Asia and Africa. Originally thought to be a single group of animals ancestral to the modern Carnivora, this order is now usually considered a polyphyletic assemblage of two different groups, the oxyaenids and the hyaenodonts, not a natural group. Oxyaenids are first known from the Palaeocene of North America, while hyaenodonts hail from the Palaeocene of Africa. Creodonts were the dominant carnivorous mammals from , peaking in diversity and prevalence during the Eocene. The first large, obviously carnivorous mammals appeared with the radiation of the oxyaenids in the late Paleocene. During the Paleogene, "creodont" species were the most abundant terrestrial carnivores in the Old World. In Oligocene Africa, hyaenodonts were the dominant group of large flesh-eaters, persisting until the middle of the Miocene. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivorans
Carnivora ( ) is an Order (biology), order of Placentalia, placental mammals specialized primarily in eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the sixth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species. Carnivorans are found on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, ranging from the cold polar regions of Earth to the hyper-arid region of the Sahara Desert and the open seas. Carnivorans exhibit a wide array of body plans, varying greatly in size and shape. Carnivora are divided into two suborders, the Feliformia, containing the true felids and several animals; and the Caniformia, containing the true canids and many animals. The feliforms include the Felidae, Viverridae, hyena, and mongoose families, the majority of which live only in the Old World; cats are the only exception, occurring in the Old World and the New World, entering the Americas via the Bering land bridge. The caniforms include the Caninae, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camelid
Camelids are members of the biological family (biology), family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant taxon, extant members of this group are: dromedary, dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos. Camelids are even-toed ungulates classified in the order (biology), order Artiodactyla, along with species including whales, pigs, deer, cattle, and antelopes. Characteristics Camelids are large, strictly herbivorous animals with slender necks and long legs. They differ from ruminants in a number of ways.Fowler, M.E. (2010). ''Medicine and Surgery of Camelids'', Ames, Iowa: Wiley-Blackwell. Chapter 1 "General Biology and Evolution" addresses the fact that camelids (including camels and llamas) are not ruminants, pseudo-ruminants, or modified ruminants. Their dentition show traces of vestigial central incisors in the incisive bone, and the third incisors have developed into canine-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knightia
''Knightia'' is an extinct genus of clupeid bony fish that lived in the freshwater lakes and rivers of North America and Asia during the Eocene epoch. The genus was erected by David Starr Jordan in 1907, in honor of the late University of Wyoming professor Wilbur Clinton Knight, "an indefatigable student of the paleontology of the Rocky Mountains." It is the official state fossil of Wyoming, and the most commonly excavated fossil fish in the world. Taxonomy ''Knightia'' belongs to the same taxonomic family as herring and sardines, and resembled the former closely enough that both ''Knightia alta'' and ''Knightia eocaena'' were originally described as species of true herring in the genus '' Clupea''. As with modern-day clupeids, ''Knightia'' spp. likely fed on algae and diatoms, as well as insects and occasionally smaller fish. In a 2022 paper, researchers announced they had detected biological residues in ''Knightia'' fossils from the Green River Formation. The genus is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon, preceded by the Mesozoic and Paleozoic. The Cenozoic started with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, when many species, including the non-avian dinosaurs, became extinct in an event attributed by most experts to the impact of a large asteroid or other celestial body, the Chicxulub impactor. The Cenozoic is also known as the Age of Mammals because the terrestrial animals that dominated both hemispheres were mammalsthe eutherians ( placentals) in the Northern Hemisphere and the metatherians (marsupials, now mainly restricted to Australia and to some extent South America) in the Southern Hemisphere. The extinction of many groups allowed mammals and birds to greatly diversify so that large m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, or the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea (geology), inland sea that existed roughly over the present-day Great Plains of North America, splitting the continent into two landmasses, i.e. Laramidia to the west and Appalachia (landmass), Appalachia to the east. The ancient sea, which existed for 34 million years from the early Late Cretaceous (100 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma) to the earliest Paleocene (66 Ma), connected the Gulf of Mexico (then a marginal sea of the Central American Seaway) to the Arctic Ocean. At its largest extent, the seaway was deep, wide and over long. Origin and geology By the late Cretaceous, Eurasia and the Americas had separated along the south Atlantic, and subduction on the west coast of the Americas had commenced, resulting in the Laramide orogeny, the early phase of growth of the modern Rocky Mountains. The Western Interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Dunes
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, flat regions covered with wind-swept sand or dunes, with little or no vegetation, are called '' ergs'' or ''sand seas''. Dunes occur in different shapes and sizes, but most kinds of dunes are longer on the stoss (upflow) side, where the sand is pushed up the dune, and have a shorter ''slip face'' in the lee side. The valley or trough between dunes is called a ''dune slack''. Dunes are most common in desert environments, where the lack of moisture hinders the growth of vegetation that would otherwise interfere with the development of dunes. However, sand deposits are not restricted to deserts, and dunes are also found along sea shores, along streams in semiarid climates, in areas of glacial outwash, and in other areas where poorly cemented sand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |