|
Organocobalt Compounds
Organocobalt chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to cobalt chemical bond. Organocobalt compounds are involved in several organic reactions and the important biomolecule vitamin B12, vitamin B12 has a cobalt-carbon bond. Many organocobalt compounds exhibit useful catalytic properties, the preeminent example being dicobalt octacarbonyl. Alkyl complexes Most fundamental are the cobalt complexes with only alkyl ligands. Examples include Co(4-norbornyl)4 and its cation. Alkylcobalt is represented by vitamin B12, vitamin B12 and related enzymes. In methylcobalamin the ligand is a methyl group, which is electrophilic. in vitamin B12, the alkyl ligand is an adenosyl group. Related to vitamin B12 are cobalt porphyrins, dimethylglyoxime, dimethylglyoximates, and related complexes of Schiff base ligands. These synthetic compounds also form alkyl derivatives that undergo diverse reactions reminiscent of the biological processes. The weak cobalt(III) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalamin Skeletal
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It plays an essential role in the nervous system by supporting myelinogenesis, myelin synthesis and is critical for the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. While animals require B12, plants do not, relying instead on alternative enzymatic pathways. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and is synthesized exclusively by certain archaea and bacteria. Natural food sources include meat, shellfish, liver, fish, poultry, Egg as food, eggs, and dairy products. It is also added to many breakfast cereals through food fortification and is available in dietary supplement and pharmaceutical forms. Supplements are commonly taken orally but may be administered via intramuscular injection to treat defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrylic Acid
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually. History The word "acrylic" was coined in 1843, for a chemical derivative of acrolein, an acrid-smelling oil derived from glycerol. Production Acrylic acid is produced by oxidation of propylene, which is a byproduct of the production of ethylene and gasoline: : Historical methods Because acrylic acid and its esters have long been valued commercially, many other methods have been developed. Most have been abandoned for economic or environmental reasons. An early method was the hydrocarboxylation of acetylene (" Reppe chemistry"): : This method requires nickel carbonyl, high pressures of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobaltocene
Cobaltocene, known also as bis(cyclopentadienyl)cobalt(II) or even "bis Cp cobalt", is an organocobalt compound with the formula Co(C5H5)2. It is a dark purple solid that sublimes readily slightly above room temperature. Cobaltocene was discovered shortly after ferrocene, the first metallocene. Due to the ease with which it reacts with oxygen, the compound must be handled and stored using air-free techniques. Synthesis Cobaltocene is prepared by the reaction of sodium cyclopentadienide (NaC5H5) with anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride in THF solution. Sodium chloride is cogenerated, and the organometallic product is usually purified by vacuum sublimation. Structure and bonding In Co(C5H5)2 the Co centre is "sandwiched" between two cyclopentadienyl (Cp) rings. The Co–C bond lengths are about 2.1 Å, slightly longer than the Fe–C bond in ferrocene. Co(C5H5)2 belongs to a group of organometallic compounds called metallocenes or sandwich compounds. Cobaltocene has 19 valen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandwich Compound
In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by hapticity, haptic, covalent bonds to two arene compound, arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula , substituted derivatives (for example ) and heterocycle, heterocyclic derivatives (for example ). Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes. The term ''sandwich compound'' was introduced in organometallic nomenclature in 1956 in a report by J. D. Dunitz, L. E. Orgel and R. A. Rich, who confirmed the structure of ferrocene by X-ray crystallography. The correct structure, in which the molecule features an iron atom ''sandwiched'' between two parallel cyclopentadienyl rings, had been proposed several years previously by Robert Burns Woodward and, separately, by Ernst Otto Fischer. The structure helped explain puzzles about ferrocene's conformational isomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Co(C8H12)(C8H13)
CO or variants may refer to: Chemistry * Carbon monoxide (CO), a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas * Carbonyl group, composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O * Cobalt, a chemical element, symbol Co Computing and telecommunications * .co (second-level domain), the Internet second-level domain meaning "commercial" * .co, the Internet country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Colombia * Commitment ordering (CO), a concurrency control technique for databases * Telephone exchange, or central office (CO) Mathematics * Cofunction, or Co, in trigonometry * Cuboctahedron, a uniform polyhedron People * Nguyễn Hữu Có (1925–2012), Vietnamese general * Conrado Co (born 1940), Filipino badminton player * Alfredo Co (born 1949), Filipino Sinologist * Atoy Co (born 1951), Filipino actor and basketball coach * Leonard Co (1953–2010), Filipino botanist * Nando Có (born 1973), Bissau-Guinean footballer * Kenedy Có (born 1998), Bissau-Guinean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Reaction
The Nicholas reaction is an organic reaction where a dicobalt octacarbonyl-stabilized propargylic cation is reacted with a nucleophile. Oxidative demetallation gives the desired alkylated alkyne. It is named after Kenneth M. Nicholas. Several reviews have been published. Reaction mechanism The addition of dicobalt octacarbonyl to the alkyne of propargylic ether (1) gives the dicobalt intermediate 2. Reaction with tetrafluoroboric acid or a Lewis acid gives the key dicobalt octacarbonyl-stabilized propargylic cation (3a and 3b). Addition of a nucleophile followed by a mild oxidation gives the substituted alkyne (5). The likely reaction intermediate in the process, propargylium)Co2(CO)6sup>+ cation 3, possesses considerable stability. It was, in fact, possible to observe these cations by 1H-NMR at 10 °C when generated using ''d''-trifluoroacetic acid. Later, Richard E. Connor and Nicholas were able to isolate salts of such cations 3 as stable, dark red solids by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
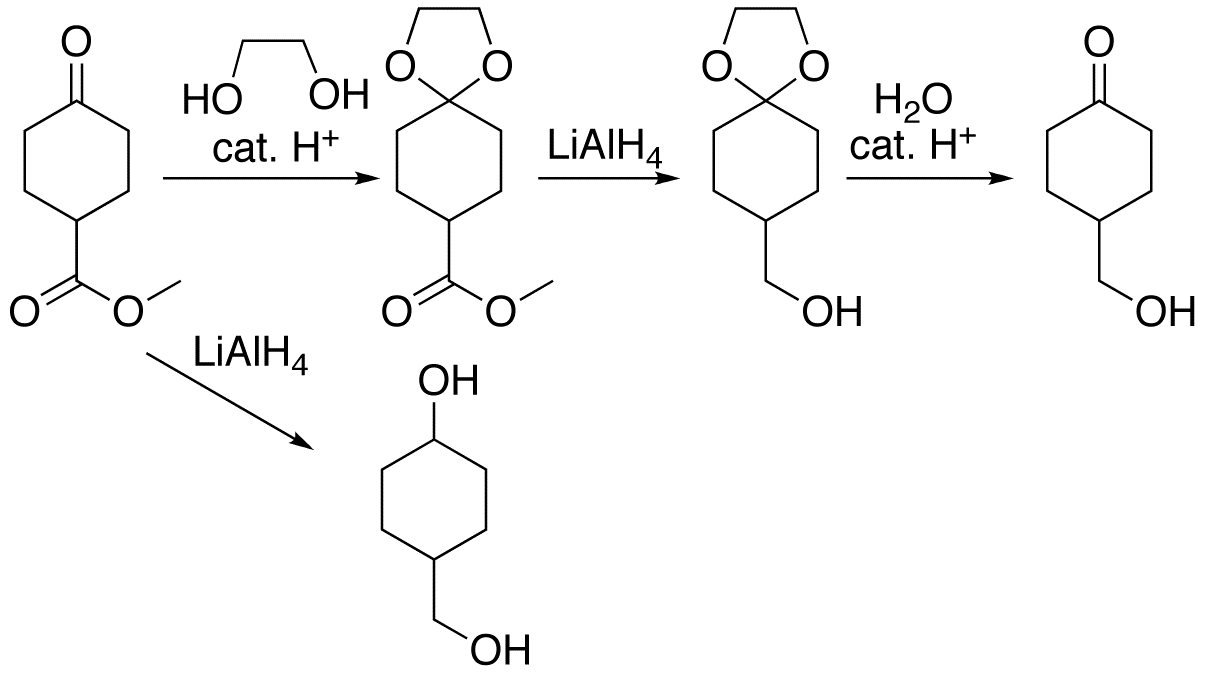
Protective Group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction. It plays an important role in multistep organic synthesis. In many preparations of delicate organic compounds, specific parts of the molecules cannot survive the required reagents or chemical environments. These parts (functional groups) must be protected. For example, lithium aluminium hydride is a highly reactive reagent that usefully reduces esters to alcohols. It always reacts with carbonyl groups, and cannot be discouraged by any means. When an ester must be reduced in the presence of a carbonyl, hydride attack on the carbonyl must be prevented. One way to do so converts the carbonyl into an acetal, which does not react with hydrides. The acetal is then called a protecting group for the carbonyl. After the hydride step is complete, aqueous acid removes the acetal, restoring the carbonyl. This step i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicobalt Hexacarbonyl Acetylene Complex
Dicobalt hexacarbonyl acetylene complexes are a family of In organocobalt compounds with the formula . A large variety of R groups are tolerated. They are red compounds that are soluble in organic solvents. They arise from the reaction of alkynes and dicobalt octacarbonyl: : According to X-ray crystallography, the two Co atoms and two alkyne carbons form the vertices of a distorted tetrahedron. The C-C distance for the bridging alkyne ligand is 1.33 Å, and the Co-Co distance is 2.47 Å. The core has C2v symmetry.{{cite journal , doi=10.1021/om00161a029, title=Diastereoselective Ligand and Vertex Substitutions in Bimetallic Bridged Alkyne Clusters: X-Ray Crystal Structure of .mu.2-(endo-2-Propynylborneol)hexacarbonyldicobalt , year=1990 , last1=d'Agostino , first1=Michael F. , last2=Frampton , first2=Christopher S. , last3=McGlinchey , first3=Michael J. , journal=Organometallics , volume=9 , issue=11 , pages=2972–2984 The structure is related to that of methylidynetricoba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylidynetricobaltnonacarbonyl
Methylidynetricobaltnonacarbonyl is an Organometallic chemistry, organometallic cobalt cluster with the chemical formula Co3(CO)9CH that contains a metal carbonyl core with the Methylidyne group, methylidyne ligand, first discovered in the late 1950s. A variety of substituents can be added to the methylidyne group to form derivatives of the parent compound that have unique spectroscopic properties and reactivity. This page will explore the discovery and synthesis of methylidynetricobaltnonacarbonyl, the structure and bonding of the parent compound, as well as some examples reactivity and catalysis with the cluster. Synthesis Methylidynetricobaltnonacarbonyl and derivatives were discovered in the late 1950s by Markby and Wender by reactions of the alkyne complexes with acids. The structure of the cluster was however misformulated. In 1962, the class of compounds were properly formulated methylidynetricobaltnonacarbonyl as well as several derivatives. The synthetic procedure deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoform
Bromoform is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is a colorless liquid at room temperature, with a high refractive index and a very high density. Its sweet odor is similar to that of chloroform. It is one of the four haloforms, the others being fluoroform, chloroform, and iodoform. It is a brominated organic solvent. Currently its main use is as a laboratory reagent. It is very slightly soluble in water (one part bromoform in 800 parts water) and is miscible with alcohol, benzene, chloroform, ether, petroleum ether, acetone and oils. Structure The molecule adopts tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry. Synthesis Bromoform was discovered in 1832 by Löwig who distilled a mixture of bromal and potassium hydroxide, as analogous to preparation of chloroform from chloral. Bromoform can be prepared by the haloform reaction using acetone and sodium hypobromite, by the electrolysis of potassium bromide in ethanol, or by treating chloroform with aluminium brom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal Phosphine Complex
A metal-phosphine complex is a coordination complex containing one or more phosphine ligands. Almost always, the phosphine is an organophosphine of the type R3P (R = alkyl, aryl). Metal phosphine complexes are useful in homogeneous catalysis. Prominent examples of metal phosphine complexes include Wilkinson's catalyst (Rh(PPh3)3Cl), Grubbs' catalyst, and tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(0). Preparation Many metal phosphine complexes are prepared by reactions of metal halides with preformed phosphines. For example, treatment of a suspension of palladium chloride in ethanol with triphenylphosphine yields monomeric bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium(II) chloride units. : dCl2sub>n + 2PPh3 → PdCl2(PPh3)2 The first reported phosphine complexes were ''cis''- and ''trans''-PtCl2(PEt3)2 reported by Cahours and Gal in 1870. Often the phosphine serves both as a ligand and as a reductant. This property is illustrated by the synthesis of many platinum-metal complexes of triphenylpho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbonylation
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains. Organic chemistry Several industrially useful organic chemicals are prepared by carbonylations, which can be highly selective reactions. Carbonylations produce organic carbonyls, i.e., compounds that contain the functional group such as aldehydes (), carboxylic acids () and esters (). Carbonylations are the basis of many types of reactions, including hydroformylation and Reppe reactions. These reactions require metal catalysts, which bind and activate the CO. These processes involve transition metal acyl complexes as intermediates. Much of this theme was developed by Walter Reppe. Hydroformylation Hydroformylation entails the addition of both carbon monoxide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |