|
Order Of Saint Olav
The Royal Norwegian Order of Saint Olav (; or ''Sanct Olafs Orden'', the old Norwegian name) is a Norwegian order of chivalry instituted by King Oscar I on 21 August 1847. It is named after King Olav II, known to posterity as St. Olav. Just before the union with Sweden was dissolved in 1905, the Order of the Norwegian Lion was instituted in 1904 by King Oscar II, but no appointments were awarded by his successor, King Haakon VII. The Order of St. Olav thus became the kingdom's only order of chivalry for the next 80 years. The Grand Master of the order is the reigning monarch of Norway. It is used to reward individuals for remarkable accomplishments on behalf of the country and humanity. Since 1985, appointments to the order has only been conferred upon Norwegian citizens, though foreign heads of state and royalty may be appointed as a matter of courtesy. Grades and classes The reigning monarch of Norway is the order's Grand Master. The order consists of three grades, of whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Royal Coat Of Arms Of Norway
Greater may refer to: *Greatness, the state of being great *Greater than, in inequality (mathematics), inequality *Greater (film), ''Greater'' (film), a 2016 American film *Greater (flamingo), the oldest flamingo on record *Greater (song), "Greater" (song), by MercyMe, 2014 *Greater Bank, an Australian bank *Greater Media, an American media company See also *Irredentism usually named as Greater ''Nation''. Examples include Hungarian irredentism, Greater Hungary, Greater Romania * * {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Order Of Precedence
{{precedence The Norwegian order of precedence is the hierarchy of officials in the Government of Norway used to direct seating and ranking on formal occasions, decided by the King, which came into effect from 1 July 1993. I. The President of the National Assembly, the Prime Minister, the Chief of the Supreme Court, the Vice President of the National Assembly and members of the Cabinet with spouses have, in the Royal Court, rank and seat second to the Royal Family and foreign royal and princely persons. Following these, the Lord Chamberlain, ambassadors of foreign powers, the presidents and vice presidents of the Lagting and Odelsting with spouses. II. Officials of the Court have rank and file as such: #The Mistress of the Robes - with generals #Marshal of the Court, Cabinet Secretary - with lieutenant generals #Chamberlain, Directors of the Royal Administration, the Royal Household and the King's and the Crown Prince's attendant staff - with major generals. #Members of The Civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Cross (Norway)
The War Cross with Sword ( Norwegian Bokmål: ''Krigskorset med sverd, '' Norwegian Nynorsk: ''Krigskrossen med sverd'') is the highest ranking Norwegian gallantry decoration. It is awarded for extraordinary brave actions or extraordinary leadership during combat. A recipient deemed worthy of additional citations will receive up to an additional two swords on the medal ribbon in addition to the "standard" single sword. Additional citations are rare: Gunnar Sønsteby is the only person to have received the War Cross with three swords (more appropriately known as "War Cross with sword and two swords"). History The medal was established on 23 May 1941 by royal resolution of King Haakon VII, who was in London with the government in exile due to the German occupation of Norway. At that time, "royal" awards were made (to members of the British Royal family for example) and awards could be made for meritorious activities not associated with combat (extraordinary achievements or cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Majority
The age of majority is the threshold of legal adulthood as recognized or declared in law. It is the moment when a person ceases to be considered a minor (law), minor, and assumes legal control over their person, actions, and decisions, thus terminating the control and legal responsibilities of their parents or guardian over them. Most countries set the age of majority at 18, but some jurisdictions have a higher age and others lower. The word ''majority'' here refers to having greater years and being of full age as opposed to ''minority'', the state of being a minor. The law in a given jurisdiction may not actually use the term "age of majority". The term refers to a collection of laws bestowing the status of adulthood. Explanation The term ''age of majority'' can be confused with the similar concept of the ''age of license''. As a legal term, ''license'' means ''permission'', referring to a legally enforceable right or privilege. Thus, the age of license for a specific activit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of Norway
There are 15 counties in Norway. The 15 county, counties are administrative division, administrative regions that are the first-level administrative divisions of Norway. The counties are further subdivided into 357 municipalities of Norway, municipalities (). The island territories of Svalbard and Jan Mayen are outside the county divisions and they are ruled directly from the national level. The capital city of Oslo is both a county and a municipality. In 2017, the Solberg's Cabinet, Solberg government decided to abolish some of the counties and to merge them with other counties to form larger ones, reducing the number of counties from 19 to 11, which was implemented on 1 January 2020. This sparked popular opposition, with some calling for the reform to be reversed. The Storting voted to partly undo the reform on 14 June 2022, with Norway to have 15 counties from 1 January 2024. Three of the newly merged counties, namely Vestfold og Telemark, Viken (county), VikenLars R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Chamberlain (Norway)
The Lord Chamberlain of Norway () is a traditional officer of the Royal Household of Norway. The title was introduced in 1866. In Denmark the equivalent title is ''Hofmarskallen'' (the Court Marshal), and in Sweden it is ''Förste Hovmarskalken'' (the First Marshal of the Court). The Lord Chamberlain of Norway is the highest administrative leader at the Royal Court and is responsible for the business vis-à-vis the King. The chief justice has the ultimate responsibility for personnel matters, the court's organization and operations, and has ceremonial and protocol duties. The court chief is a member of the council of the Order of St. Olav, where they are the treasurer. In the Royal Norwegian Order of Merit, the head of court is the chancellor of the order. In Norway, the court marshal is subordinate to the head of the court and functions as head of finance and administration at the court. Lords Chamberlain of Norway *1815–1870: Herman Severin Løvenskiold *1890-1904: Theodor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
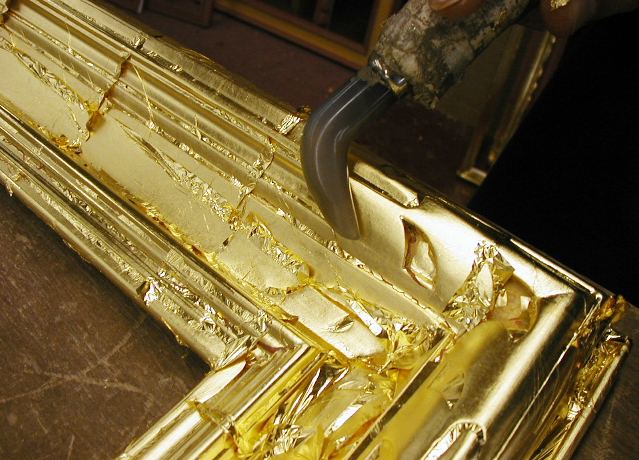
Gilding
Gilding is a decorative technique for applying a very thin coating of gold over solid surfaces such as metal (most common), wood, porcelain, or stone. A gilded object is also described as "gilt". Where metal is gilded, the metal below was traditionally silver in the West, to make silver-gilt (or ''vermeil'') objects, but gilt-bronze is commonly used in China, and also called ormolu if it is Western. Methods of gilding include hand application and gluing, typically of gold leaf, chemical gilding, and electroplating, the last also called gold plating. Parcel-gilt (partial gilt) objects are only gilded over part of their surfaces. This may mean that all of the inside, and none of the outside, of a chalice or similar vessel is gilded, or that patterns or images are made up by using a combination of gilt and ungilted areas. Gilding gives an object a gold appearance at a fraction of the cost of creating a solid gold object. In addition, a solid gold piece would often be too soft or to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltese Cross
The Maltese cross is a cross symbol, consisting of four " V" or arrowhead shaped concave quadrilaterals converging at a central vertex at right angles, two tips pointing outward symmetrically. It is a heraldic cross variant which developed from earlier forms of eight-pointed crosses in the 16th century. Although chiefly associated with the Knights Hospitaller (Order of St. John, now the Sovereign Military Order of Malta), and by extension with the island of Malta, it has come to be used by a wide array of entities since the early modern period, notably the Order of Saint Stephen, the city of Amalfi, the Polish Order of the White Eagle (1709), the Prussian order ''Pour le Mérite'' (1740), and the Bavarian Military Merit Order (1866). Unicode defines a character named "Maltese cross" in the Dingbats range at code point U+2720 (✠); however, most computer fonts render the code point as a cross pattée. History The Knights Hospitaller during the Crusades used a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Norway
The Church of Norway (, , , ) is an Lutheranism, evangelical Lutheran denomination of Protestant Christianity and by far the largest Christian church in Norway. Christianity became the state religion of Norway around 1020, and was established as a separate church intimately integrated with the state as a result of the Reformation in Denmark–Norway and Holstein, Lutheran reformation in Denmark–Norway which broke ties with the Holy See in 1536–1537; the Monarchy_of_Norway#Church_of_Norway, Norwegian monarch was the church's titular head from 1537 to 2012. Historically, the church was one of the main instruments of state authority, and an important part of the state's administration. Local government was based on the church's parishes with significant official responsibility held by the parish priest. In the 19th and 20th centuries, the Church of Norway gradually ceded most administrative functions to the secular civil service. The modern Constitution of Norway describes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottony
A number of cross symbols were developed for the purpose of the emerging system of heraldry, which appeared in Western Europe in about 1200. This tradition is partly in the use of the Christian cross an emblem from the 11th century, and increasingly during the age of the Crusades. Many cross variants were developed in the classical tradition of heraldry during the late medieval and early modern periods. Heraldic crosses are inherited in modern iconographic traditions and are used in numerous national flags. History The Christian cross emblem ( Latin cross or Greek cross) was used from the 5th century, deriving from a T-shape representing the gibbet ('' stauros'', ''crux'') of the crucifixion of Jesus in use from at least the 2nd century. The globus cruciger and the staurogram is used in Byzantine coins and seals during the Heraclian period (6th century). Under the Heraclian dynasty (7th century), coins also depict simply crosses potent, patty, or pommy. The cross was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collier Ordre De Saint Olaf Type 1906
Collier or colliers may refer to: Coal industry * Collier, coal miner or coal merchant * Colliery, coal mining and selling; or a coal mine *Collier (ship), a bulk cargo ship which carried coal * Charcoal maker, in colonial United States and also in Sussex, England Places * Collier Row, a place in the London Borough of Havering * Colliers Wood, an area in the London Borough of Merton *Collier County, Florida, a county of Florida's southwest coast * Collier, Georgia, an unincorporated community *Colliers, West Virginia, a small town in the northern panhandle area of West Virginia * Colliers, Newfoundland and Labrador, a town on the Avalon Peninsula * Collier Township, Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, a suburb of Pittsburgh * Collier Range National Park, Australian park * Collier High School (New Jersey), a school in Wickatunk, New Jersey People * Collier (surname) * Collier Twentyman Smithers (1867–1943), British portrait artist Other * Collier Baronets, a title in the Briti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |