|
Ophiuchus
Ophiuchus () is a large constellation straddling the celestial equator. Its name comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping a snake. The serpent is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations. An old alternative name for the constellation was Serpentarius. Location Ophiuchus lies between Aquila (constellation), Aquila, Serpens, Scorpius, Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius, and Hercules (constellation), Hercules, northwest of the center of the Milky Way. The southern part lies between Scorpius to the west and Sagittarius (constellation), Sagittarius to the east. In the northern hemisphere, it is best visible in summer. It is opposite of Orion (constellation), Orion. Ophiuchus is depicted as a man grasping a Serpens, serpent; the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpens Caput
Serpens () is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in ''Serpens Caput'' and Nu Serpentis in ''Serpens Cauda''. The brightest List of stars in Serpens, star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variable star, variabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpens Cauda
Serpens () is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations designated by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the "Serpent-Bearer". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in ''Serpens Caput'' and Nu Serpentis in ''Serpens Cauda''. The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnard's Star
Barnard's Star is a small red dwarf star in the constellation of Ophiuchus. At a distance of from Earth, it is the fourth-nearest-known individual star to the Sun after the three components of the Alpha Centauri system, and is the closest star in the northern celestial hemisphere. Its stellar mass is about 16% of the Sun's, and it has 19% of the Sun's diameter. Despite its proximity, the star has a dim apparent visual magnitude of +9.5 and is invisible to the unaided eye; it is much brighter in the infrared than in visible light. Barnard's Star is among the most studied red dwarfs because of its proximity and favorable location for observation near the celestial equator. Historically, research on Barnard's Star has focused on measuring its stellar characteristics, its astrometry, and also refining the limits of possible extrasolar planets. Although Barnard's Star is ancient, it still experiences stellar flare events, one being observed in 1998. Barnard's Star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rasalhague
Alpha Ophiuchi (α Ophiuchi, abbreviated Alpha Oph, α Oph), also named Rasalhague , is a binary star and the brightest star in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Nomenclature The name Alpha Ophiuchi is a Romanisation of the star's Bayer designation, ''α Ophiuchi''. It is also known by the traditional name ''Rasalhague'', from the Arabic رأس الحواء ''raʼs al-ḥawwāʼ'' "the head of the serpent collector". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a IAU Working Group on Star Names, Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two collections of approved names, formally listing Alpha Ophiuchi as ''Rasalhague''. Properties Alpha Ophiuchi is a binary star system with an orbital period of about 8.62 years. The orbital parameters were only poorly known until 2011 when observations using adaptive optics produced a better orbital fit, allo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eta Ophiuchi
Eta Ophiuchi (η Ophiuchi, abbreviated Eta Oph, η Oph) is a binary star in the constellation of Ophiuchus. With a combined apparent magnitude of +2.43, it is the second-brightest of the constellation and one of the brightest stars in the night sky. Based on parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 88 light-years away. Eta Ophiuchi is part of a multiple star system designated WDS J17104-1544. It itself is designated WDS J17104-1544AB and its two components WDS J17104-1544A (also called Sabik , the traditional name for the system) and WDS J17104-1544B. The 'C' component is UCAC4 372-080717 and 'D' is UCAC2 26022336. Nomenclature ''η Ophiuchi'' ( Latinised to ''Eta Ophiuchi'') is the system's Bayer designation. WDS J17104-1544AB is its designation in the Washington Double Star Catalog. The designations of the two components as WDS J17104-1544 A and B derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Ophiuchi
Alpha Ophiuchi (α Ophiuchi, abbreviated Alpha Oph, α Oph), also named Rasalhague , is a binary star and the brightest star in the constellation of Ophiuchus. Nomenclature The name Alpha Ophiuchi is a Romanisation of the star's Bayer designation, ''α Ophiuchi''. It is also known by the traditional name ''Rasalhague'', from the Arabic رأس الحواء ''raʼs al-ḥawwāʼ'' "the head of the serpent collector". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included a table of the first two collections of approved names, formally listing Alpha Ophiuchi as ''Rasalhague''. Properties Alpha Ophiuchi is a binary star system with an orbital period of about 8.62 years. The orbital parameters were only poorly known until 2011 when observations using adaptive optics produced a better orbital fit, allowing the individual masses of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules Family
Constellation families are collections of constellations sharing some defining characteristic, such as proximity on the celestial sphere, common historical origin, or common mythological theme. In the Western tradition, most of the northern constellations stem from Ptolemy's list in the ''Almagest'' (which in turn has roots that go back to Mesopotamian astronomy), and most of the far southern constellations were introduced by sailors and astronomers who traveled to the south in the 16th to 18th centuries. Separate traditions arose in India and China. Menzel's families Donald H. Menzel, director of the Harvard Observatory, gathered several traditional groups in his popular account, ''A Field Guide to the Stars and Planets'' (1975), and adjusted and regularized them so that his handful of groups covered all 88 of the modern constellations. Of these families, one (Zodiac) straddles the ecliptic which divides the sky into north and south; one (Hercules) has nearly equal porti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
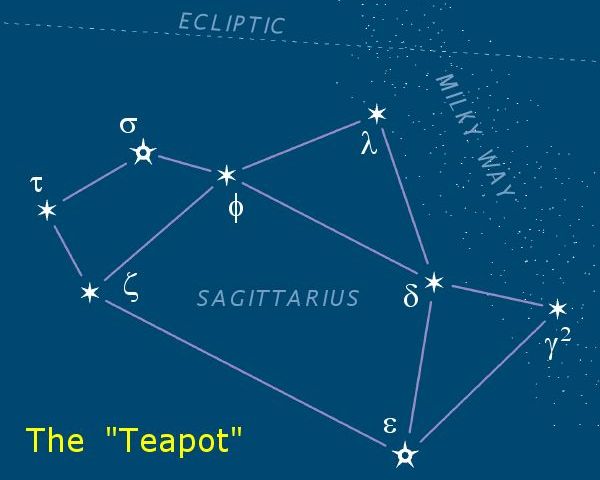
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archery, archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism (astronomy), asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars Delta Sagittarii, δ Sgr (Kaus Media), Epsilon Sagittarii, ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), Zeta Sagittarii, ζ Sgr (Ascella), and Phi Sagittarii, φ Sgr form the body of the pot; Lambda Sagittarii, λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules (constellation)
Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythology hero adapted from the Greek mythology, Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the second-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations today. It is the fifth-largest of the modern constellations and is the largest of List of brightest stars, the 50 which have no stars brighter than apparent Magnitude (astronomy), magnitude +2.5. Characteristics Hercules is bordered by Draco (constellation), Draco to the north; Boötes, Corona Borealis, and Serpens, Serpens Caput to the west; Ophiuchus to the south; Aquila (constellation), Aquila to the southwest; and Sagitta, Vulpecula, and Lyra to the east. Covering 1225.1 square degrees and 2.970% of the night sky, it ranks fifth among the 88 constellations in size. The three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, as adopted by the International Astronomical Union in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorpius
Scorpius is a zodiac constellation located in the Southern celestial hemisphere, where it sits near the center of the Milky Way, between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east. Scorpius is an ancient constellation whose recognition predates Greek culture; it is one of the 48 constellations identified by the Greek astronomer Ptolemy in the second century. Notable features Stars Scorpius contains many bright stars, including Antares (α Sco), "rival of Mars," so named because of its distinct reddish hue; β1 Sco (Graffias or Acrab), a triple star; δ Sco ( Dschubba, "the forehead"); θ Sco ( Sargas, of Sumerian origin); ν Sco (Jabbah); ξ Sco; π Sco (Fang); σ Sco (Alniyat); and τ Sco (Paikauhale). Marking the tip of the scorpion's curved tail are λ Sco ( Shaula) and υ Sco (Lesath), whose names both mean "sting." Given their proximity to one another, λ Sco and υ Sco are sometimes referred to as the Cat's Eyes. The constellation's bright stars form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion (constellation)
Orion is a prominent set of stars visible during winter in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the IAU designated constellations, 88 modern constellations; it was among :Constellations listed by Ptolemy, the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is named after Orion (mythology), a hunter in Greek mythology. Orion is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism (astronomy), asterism. Orion's two brightest stars, Rigel (β) and Betelgeuse (α), are both among the List of brightest stars, brightest stars in the night sky; both are supergiants and slightly variable star, variable. There are a further six stars brighter than magnitude 3.0, including three making the short straight line of the Orion's Belt asterism (astronomy), asterism. Orion also hosts the radiant (meteor shower), radiant of the annual Orionids, the strongest meteor shower as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |