|
Odia Literature
Odia literature is literature written in the Odia language, mostly from the Indian state of Odisha. The modern Odia language is mostly formed from Tadbhava words with significant Sanskrit (Tatsama) influences, along with loanwords from Desaja, English, Hindustani (Hindi/Urdu), Persian, and Arabic. Its earliest written texts date from around 1000 CE. The earliest Odia newspaper was '' Utkala Deepika'', first published on August 4, 1866. Historians have divided Odia literature into five main stages: Old Odia (800 AD to 1300 AD), Early Medieval Odia (1300 AD to 1500 AD), Medieval Odia (1500 AD to 1700 AD), Late Medieval Odia (1700 AD to 1850 AD) and Modern Odia (1870 AD to present). Further subdivisions, as seen below, more precisely chart the language's development. 4th century BC The creativity and development of the Odia language and literature can be seen in its spoken forms, such as folk tales, and in written forms, such as rock edicts and manuscripts. Songs sung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charyapada
The Charyapada is a collection of mystical poems, songs of realization in the Vajrayāna tradition of Buddhism from the tāntric tradition in Assam, Bengal, Bihar and Odisha. It was compiled between the 8th and 12th centuries in late Apabhraṃśa or various Abahaṭṭhas and represents the formative period of the eastern Indo-Aryan languages. It was written during a period when the northeastern Prākrit languages had not yet differentiated into later forms, or they were just getting differentiated. Scholars of many eastern Indo-Aryan languages, such as Assamese, Bengali, Maithili, and Odia find features of these languages in the language of this work. A palm-leaf manuscript of the ''Charyāpada'' was rediscovered in the early 20th century by Haraprasād Shāstrī at the Nepal Royal Court Library. The ''Charyāpada'' was also preserved in the Tibetan Buddhist canon. Manuscripts The original palm-leaf manuscript of the Charyapada, or ''Caryācaryāviniścaya'', sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapilendradeva
Kapilendra Deva (died 1467) was the founder of the Suryavamsa Gajapati dynasty that ruled parts of eastern and southern India with present-day Odisha as the center of the kingdom. He ascended to the throne after staging a military coup against the preceding and the last ruler from the Eastern Ganga dynasty, ''Bhanudeva IV''. Kapilendra claimed descent from the ''Surya Vamsha'' of the ''Mahābhārata'' and was conferred the regnal title ''Shri Shri ...(108 times) Gajapati Gaudeshwara NabaKoti Karnata Kalabargeswara'' i.e. the Lord of Bengal ( Gauda), the lord of the Karnataka region or Vijayanagara, the Lord of Kalaburagi and of nine crore (90 million) subjects. He defeated the Muslim forces like the Sultan of Jaunpur (Mahmud Shah), Bahmani Sultanate and the young ruler of Bengal Samsuddin Ahmad Shah who were continuously preparing to invade Odisha and had continuous rivalries with powerful kings such as Deva Raya II of Vijayanagara along with Reddys of Rajmahendri. Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gajapati Kingdom
The Gajapati dynasty refers to the ruling dynasty from the region of modern Odisha in the Indian subcontinent, whose monarch carries the regnal title of Gajapati. The institution of Gajapati dynasty or lordship was founded by the monarchs of the Eastern Ganga dynasty and was used by the succeeding dynasties. A major religious function included the patronisation of Lord Jagannath as the deity of the Odia cultural realm. Till date, four ruling dynasties from the region of Odisha have presided over the institution of Gajapati dynasty. The current titular Gajapati belongs to the head of the Bhoi dynasty, which the dynasty had inherited the legacy of the historical ruling lords of Odisha invested in the title of ''Gajapati''. They also exercised administrative control of the Jagannath Temple at Puri. History The ruling monarchs of the wider Kalinga, Utkala and Dakshina Kosala used various regnal titles upon coronation or conquest of regions, chiefly being the titles of ''Kali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kurukshetra War, a war of succession between two groups of princely cousins, the Kauravas and the Pandava, Pāṇḍavas. It also contains Hindu philosophy, philosophical and devotional material, such as a discussion of the four "goals of life" or ''puruṣārtha'' (12.161). Among the principal works and stories in the ''Mahābhārata'' are the ''Bhagavad Gita'', the story of Damayanti, the story of Shakuntala, the story of Pururava and Urvashi, the story of Savitri and Satyavan, the story of Kacha (sage), Kacha and Devayani, the story of Rishyasringa and an Ramopakhyana, abbreviated version of the ''Rāmāyaṇa'', often considered as works in their own right. Traditionally, the authorship of the ''Mahābhārata'' is attributed to Vyasa, Vy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
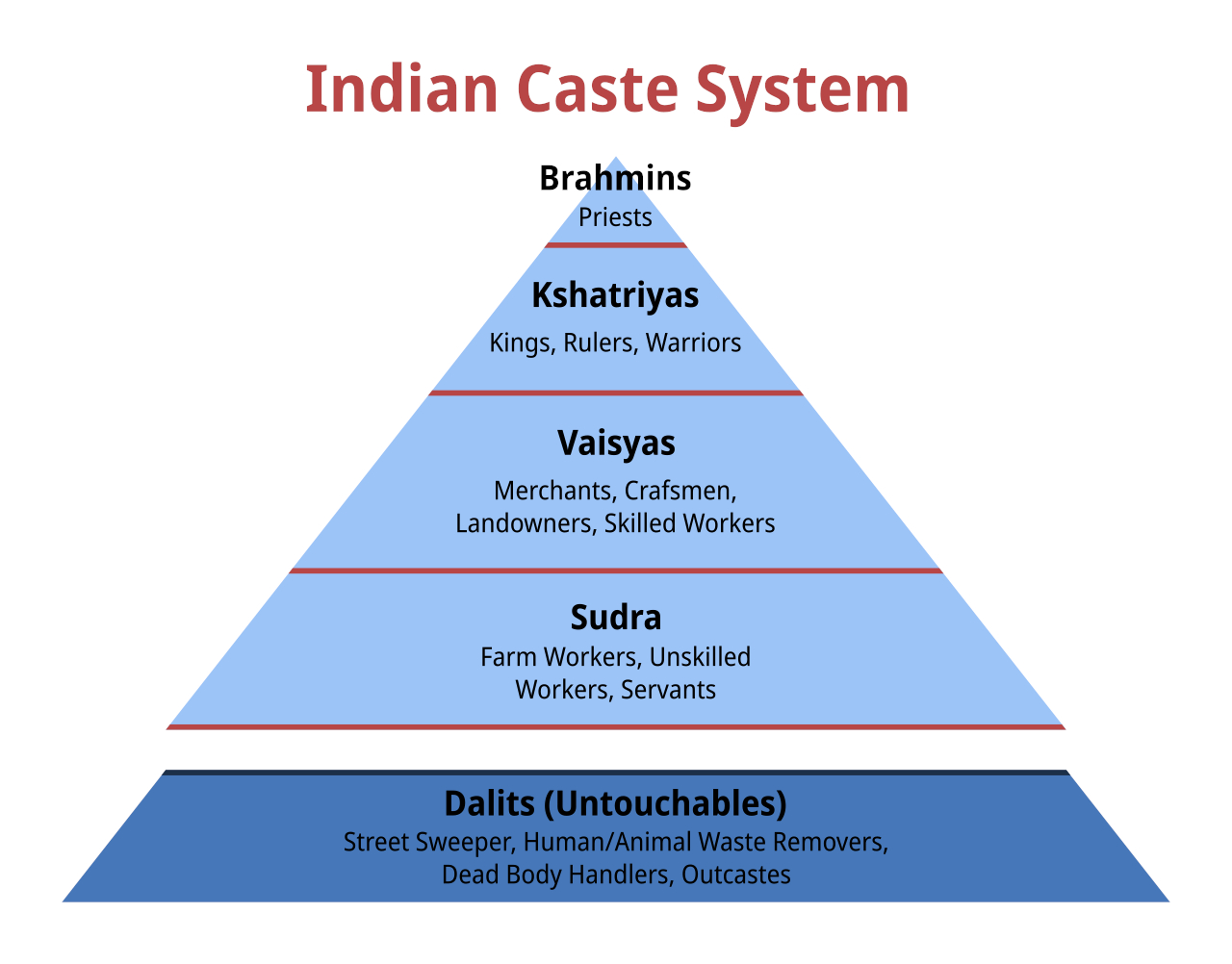
Dalit
Dalit ( from meaning "broken/scattered") is a term used for untouchables and outcasts, who represented the lowest stratum of the castes in the Indian subcontinent. They are also called Harijans. Dalits were excluded from the fourfold varna of the caste hierarchy and were seen as forming a fifth varna, also known by the name of ''Panchama''. Several scholars have drawn parallels between Dalits and the '' Burakumin'' of Japan, the '' Baekjeong'' of Korea and the peasant class of the medieval European feudal system. Dalits predominantly follow Hinduism with significant populations following Buddhism, Sikhism, Christianity, and Islam. The constitution of India includes Dalits as one of the Scheduled Castes; this gives Dalits the right to protection, positive discrimination (known as reservation in India), and official development resources. Terminology The term ''Dalit'' is for those called the "untouchables" and others that were outside of the traditional Hindu caste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four varnas of the Hindu class and social system in ancient India. Some sources translate it into English as a caste, or as a social class. Theoretically, Shudras constituted a class like workers. According to Richard Gombrich's study of Buddhist texts, particularly relating to castes in Sri Lankan Buddhist and Tamil Hindu society, The word ''Shudra'' appears in the ''Rigveda'' and it is found in other Hindu texts such as the ''Manusmriti'', ''Arthashastra'', dharmaśāstras and jyotiḥśāstras. In some cases, Shudras participated in the coronation of kings, or were amatya "ministers" and rajas "kings" according to early Indian texts. History Vedas The term ''śūdra'' appears only once in the ''Rigveda''. This mention is found in the mythical story of creation embodied in the '' Puruṣasuktam''. It describes the formation of the four varnas from the body of a primeval man. It states that the brahmin emerged from hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarala Das
Sarala Dasa (born as Siddheswara Parida) was a 15th-century poet and scholar of Odia literature. Best known for three Odia books — '' Sarala Mahabharata'', '' Vilanka Ramayana'' and ''Chandi Purana'' — he was the first scholar to write in Odia and his revered as the ''Adi Kabi'' (First Poet) of Odia literature. As an originator of Odia literature, his work has formed an enduring source of information for succeeding generations. Life The early life of Sarala Dasa is not accurately known. He was a contemporary of the Gajapati King Kapilendra Deva. Though the date of his birth cannot be accurately determined, he can safely be placed to the 15th century AD. He was born at a village called ''kanakavati patana'' known as Kanakapura at the Tentuliapada, Jagatsinghpur district. Sarala Dasa belonged to Chasa community. Sarala Dasa had no organized early education, and what he achieved through self-education was attributed to the grace of Sarala, goddess of devotion and inspiratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantra
Tantra (; ) is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the India, Indian subcontinent beginning in the middle of the 1st millennium CE, first within Shaivism and later in Buddhism. The term ''tantra'', in the Greater India, Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on Indian Tantras (Buddhism), Buddhist Tantras. They include Tibetan Buddhism, Indo-Tibetan Buddhism, Chinese Esoteric Buddhism, Japanese Shingon Buddhism and Nepalese Newar Buddhism. Although Southern Esoteric Buddhism does not directly reference the tantras, its practices and ideas parallel them. In Bud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Indo-Aryan languages, excluding Pali. The oldest stage of Middle Indo-Aryan language is attested in the inscriptions of Ashoka (ca. 260 BCE), as well as in the earliest forms of Pāli, the language of the Theravāda Buddhist canon. The most prominent form of Prakrit is Ardhamāgadhı̄, associated with the ancient kingdom of Magadha, in modern Bihar, and the subsequent Mauryan Empire. Mahāvı̄ra, the last tirthankar of 24 tirthankar of Jainism, was born in Magadha, and the earliest Jain texts were composed in Ardhamāgadhı̄. Etymology There are two major views concerning the way in which Sanskrit and Prakrit are related. One holds that the original matter in question is the speech of the common people, unadorned by grammar, and that p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanha (poet)
Kānhapā, Kanha or Kanhapada or Krishnacharya ( c 10th century AD) was one of the main poets of '' Charyapada'', the earliest known example of Assamese, Bengali, Maithili, Bhojpuri, and Odia literature. He was a tantric Buddhist and a disciplle of JalandhaPage21Kanhapada is also a prominent siddhacharya to Nath Sampradaya after Matsyendranatha Matsyendranātha, also known as Matsyendra, Macchindranāth, Mīnanātha and Minapa (early 10th century) was a saint and yogi in a number of Buddhism, Buddhist and Hinduism, Hindu traditions. He is considered the revivalist of hatha yoga as we ... and Gorakhnath. His poems in Charjyapad are written in a code, whereby every poem has a descriptive or narrative surface meaning but also encodes tantric Buddhist teachings. Some experts believe this was to conceal sacred knowledge from the uninitiated, while others hold that it was to avoid religious persecution. In one of his poems, Kanhupa wrote: The language of Kanhupa's poetr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luipa
Luipa or Luipada (c. 10th century) was a mahasiddha siddhacharya from Eastern India.Ayyappapanicker, K. & Akademi, Sahitya (1997). ''Medieval Indian literature: an anthology, Volume 3''. Sahitya Akademi. , . Source(accessed: Friday March 5, 2010) He was a Buddhist saint from the Kãivartā community. He was a writer of a number of Buddhist texts and one of the early poets of Charyapada, a late Apabhraṃśa collection of poems. Nomenclature and etymology Although the Tibetan translation for ''Lui'' is "the fish-gut eater" (), the root of the word is probably Sanskrit ''lohita'' which means "red" and the names like Luidhar, Luichandra and Luiya mentioned in the ''Dharmamangal''s of the late medieval period originated from the same root.Sen, Sukumar (2002). ''Charyageeti Padabali'' (in Bengali), Ananda Publishers, Kolkata, , pp.20-1 Ayyappapanicker & Akademi (1997: p. 599) amplify the view of prior scholarship in that the nomenclature "Luipa" is related to the Brahmaputra R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |