|
Obazoa
Obazoa is a proposed sister clade of Amoebozoa (which together form Amorphea). The term Obazoa is based on the OBA acronym for Opisthokonta, Breviatea, and Apusomonadidae, the group's three constituent clades. Determining the placement of Breviatea and Apusomonadida and their properties is of interest for the development of the opisthokonts in which the main lineages of animals and fungi A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ... emerged. The relationships among opisthokonts, breviates and apusomonads are not conclusively resolved (as of 2018), though Breviatea is usually inferred to be the most basal of the three lineages. The phylogeny of the Obazoa is shown in the cladogram. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q22087764 Amorphea taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
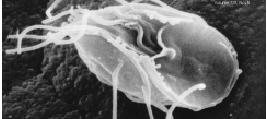
Breviatea
Breviatea, commonly known as breviate amoebae, are a group of free-living, amitochondriate protists with uncertain phylogenetic position. They are biflagellate, and can live in anaerobic (oxygen-free) environments. They are currently placed in the Obazoa clade. They likely do not possess vinculin proteins. Their metabolism relies on fermentative production of ATP as an adaptation to their low-oxygen environment. The lineage emerged roughly one billion years ago, at a time when the oxygen content of the Earth's oceans was low, and they thus developed anaerobic lifestyles. Together with Apusomonads, they are the closest relatives of the Opisthokonts, a group that includes animals and fungi. Characteristics Mitochondrion-related organelles Mitochondrion-related organelles (MROs) are organelles that evolved from a degradation of ancestral, fully functional mitochondria. Among Breviatea, MROs are present in '' Pygsuia'', '' Breviata'' and '' Subulatomonas''. In the cells of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apusomonadidae
The apusomonads (family Apusomonadidae) are a group of protozoan zooflagellates that glide on surfaces, and mostly consume prokaryotes. They are of particular evolutionary interest because they appear to be the sister group to the Opisthokonts, the clade that includes both animals and fungi. Together with the Breviatea, these form the Obazoa clade. Characteristics Apusomonads are small gliding heterotrophic biflagellates (i.e. with two flagella) that possess a proboscis, formed partly or entirely by the anterior flagellum surrounded by a membranous sleeve. There is a pellicle under the dorsal cell membrane that extends into the proboscis sleeve and into a skirt that covers the sides of the cell. Apusomonads present two different cell plans: *Derived cell plan, represented by '' Apusomonas'', with a round cell body and a mastigophore, a projection of the cell containing both basal bodies at its end. *"''Amastigomonas''-like" cell plan, with an oval or oblong cell that general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opisthokont
The opisthokonts () are a broad group of eukaryotes, including both the animal and fungus kingdoms. The opisthokonts, previously called the "Fungi/Metazoa group", are generally recognized as a clade. Opisthokonts together with Apusomonadida and Breviata comprise the larger clade Obazoa. Flagella and other characteristics A common characteristic of opisthokonts is that flagellate cells, such as the sperm of most animals and the spores of the chytrid fungi, propel themselves with a single ''posterior'' flagellum. It is this feature that gives the group its name. In contrast, flagellate cells in other eukaryote groups propel themselves with one or more ''anterior'' flagella. Flagellate cells however have been secondarily lost in some opisthokont groups, including most of the fungi. Opisthokont characteristics include synthesis of extracellular chitin in exoskeleton, cyst/spore wall, or cell wall of filamentous growth and hyphae; the extracellular digestion of substrates with os ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphea
Amorphea is a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the fungi, animals and the choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. The International Society of Protistologists, the recognised body for taxonomy of protozoa, recommended in 2012 that the term Unikont be changed to Amorphea because the name "Unikont" is based on a hypothesized synapomorphy that the ISOP authors and other scientists later rejected. It includes amoebozoa, opisthokonts, and apusomonads. Taxonomic revisions within this group Thomas Cavalier-Smith proposed two new phyla: Sulcozoa, which consists of the subphyla Apusozoa ( Apusomonadida and Breviatea), and Varisulca, which includes the subphyla Diphyllatea, Discocelida, Mantamonadidae, Planomonadida and Rigifilida. Further work by Cavalier-Smith showed that Sul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podiata
Podiates (Cavalier-Smith, 2012, excl. Ancyromonadida) are a proposed clade containing the Amorphea (incl. Opisthokonta, Amoebozoa, apusomonads and breviates) and the organisms now assigned to the clade CRuMs. Ancyromonadida does not appear to have emerged in this grouping. Sarcomastigota (Cavalier-Smith, 1983) is a proposed subkingdom (currently shown to be paraphyletic) that includes all the podiates that are ''not'' animals or fungi. Sulcozoa (Cavalier-Smith, 2012) is a proposed phylum (currently shown to be paraphyletic) within Sarcomastigota that does not include the phyla Amoebozoa (clade In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...) and Choanozoa (paraphyletic), i.e. it includes the proposed subphyla Apusozoa and Varisulca.. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
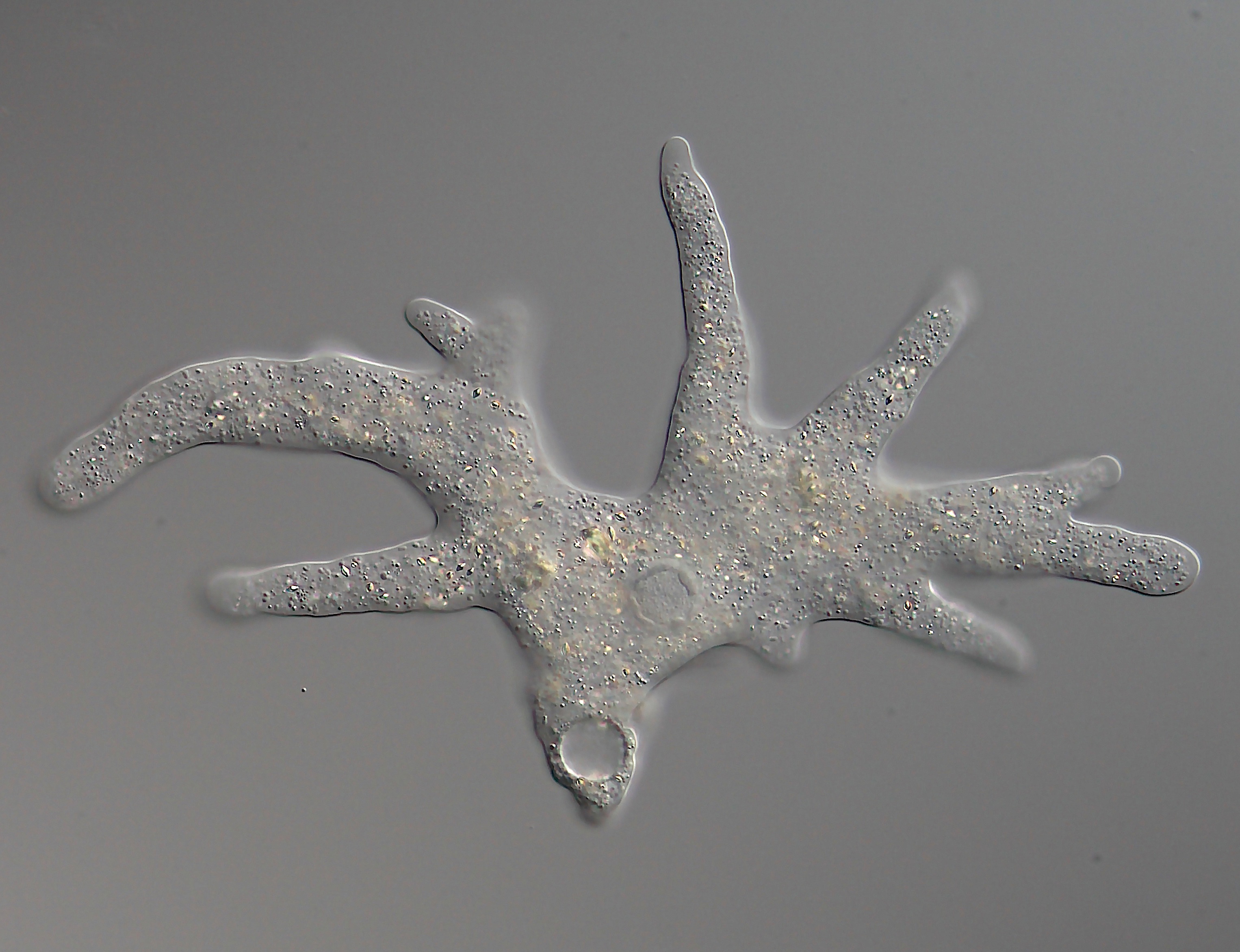
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of Amoeba, amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, Pseudopod#Morphology, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional classification schemes, Amoebozoa is usually ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom (biology), kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked "supergroup (biology), supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetics, Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, named Amorphea. Amoeboz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRuMs
CRuMs is a clade of microbial eukaryotes, whose name is an acronym of the following constituent groups: i) Diphylleids, ii) rigifilids and iii) mantamonads as sister of the Amorphea. A new CRuMs order Glissandrida was proposed in 2025 to place the yet unclassified genus Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ... '' Glissandra''. It more or less supersedes Varisulca, as Ancyromonadida are inferred not to be specifically related to the orders Diphylleida / Collodictyonida, Rigifilida and Mantamonadida. Phylogeny References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q134939335, from2=Q59153571 Eukaryote taxa Podiata Protist taxa CRuMs taxa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancyromonadida
Ancyromonadida or Planomonadida is a small group of biflagellated eukaryotes found in the soil and in aquatic habitats, where they feed on bacteria.Cavalier-Smith, T. (2013)Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla Loukozoa, Sulcozoa, and Choanozoa European journal of protistology, 49(2), 115-178. They are freshwater or marine organisms, benthic, dorsoventrally compressed and with two unequal flagellae, each emerging from a separate pocket. The apical anterior flagellum can be very thin or end in the cell membrane, while the posterior flagellum is long and is inserted ventrally or laterally. The cell membrane is supported by a thin single-layered theca and the mitochondrial crests are discoidal/flat. The group's placement is doubtful, as it seems to fall outside the five supergroups of eukaryotes. Cavalier-Smith considers that they constitute a basal group to Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta and places it togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of life forms alongside the two groups of prokaryotes: the Bacteria and the Archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but given their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is much larger than that of prokaryotes. The eukaryotes emerged within the archaeal kingdom Promethearchaeati and its sole phylum Promethearchaeota. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among the Archaea. Eukaryotes first emerged during the Paleoproterozoic, likely as flagellated cells. The leading evolutionary theory is they were created by symbiogenesis between an anaerobic Promethearchaeati archaean and an aerobic proteobacterium, which form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphoda
A bikont ("two flagella") is any of the eukaryotic organisms classified in the group Bikonta. Many single-celled and multi-celled organisms are members of the group, and these, as well as the presumed ancestor, have two flagella. Enzymes Another shared trait of bikonts is the fusion of two genes into a single unit: the genes for thymidylate synthase (TS) and dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) encode a single protein with two functions. The genes are separately translated in unikonts. Relationships Some research suggests that a unikont (a eukaryotic cell with a single flagellum) was the ancestor of opisthokonts (Animals, Fungi, and related forms) and Amoebozoa, and a bikont was the ancestor of Archaeplastida (Plants and relatives), Excavata, Rhizaria, and Chromalveolata. Cavalier-Smith has suggested that Apusozoa, which are typically considered ''incertae sedis'', are in fact bikonts. Relationships within the bikonts are not yet clear. Cavalier-Smith has grouped the Excavata a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discoba
Excavata is an obsolete, extensive and diverse Paraphyly, paraphyletic group of unicellular Eukaryote, Eukaryota. The group was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and the name latinized and assigned a rank by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic protists, and includes some important parasites of humans such as ''Giardia'' and ''Trichomonas''. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now- obsolete Protist, Protista kingdom. They were distinguished from other lineages based on electron-microscopic information about how the cells are arranged (they have a distinctive ultrastructural identity). They are considered to be a Basal_(phylogenetics), basal flagellate lineage. On the basis of phylogenomic analyses, the group was shown to contain three widely separated eukaryote groups, the discobids, metamonads, and malawimonads. A current view of the composition of the excavates is given below, indicating that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |