|
Oates Land
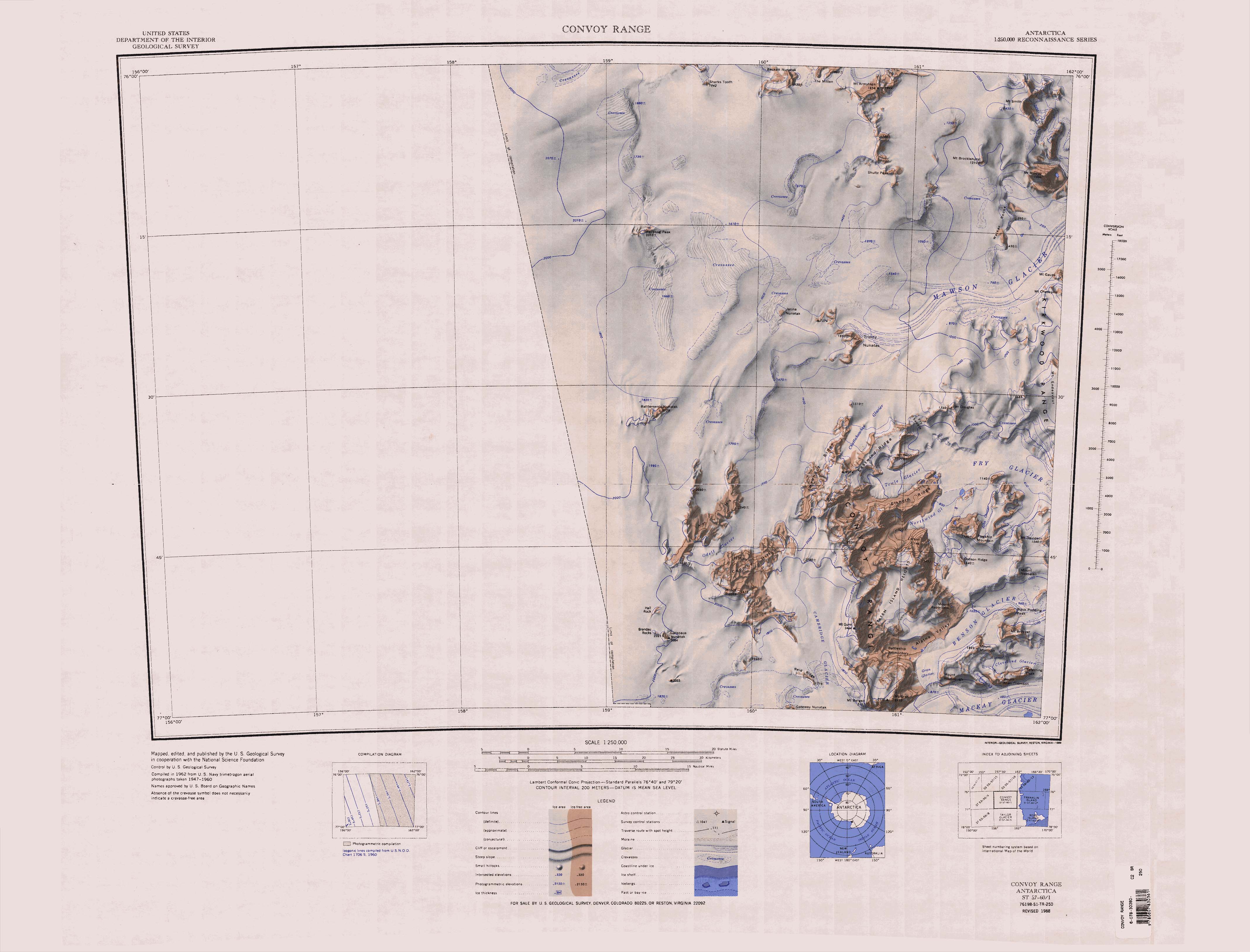
Oates Land is a region of Antarctica. It is variously defined as a portion of the East Antarctica near the coast stretching along and inland from the Oates Coast (see map) and as an officially delineated wedge-shaped segment of the Australian Antarctic Territory. The segment of the Australian claim extends between 153°45' E and 160° E, forming a wedge between Latitude 60° S and the South Pole. It is bounded in the east by the Ross Dependency and overlaps George V Land to the west. Exploration Oates Land was discovered in February 1911 by Lieutenant Harry Pennell of the Royal Navy, commander of the '' Terra Nova'', the expedition ship of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. It is named after Captain Lawrence Edward Grace "Titus" Oates of the 6th (Iniskilling) Dragoons, who, with Captain Robert Falcon Scott and three companions, lost his life on the return journey from the South Pole in 1912.Geographic Names Information System,Oates Land, United States Geological S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oates Land In Australian Antarctic Territory
Oates may refer to: __NOTOC__ People * Oates (surname) * Kate Micucci, half of the musical comedy duo Garfunkel and Oates Places * Oates, Missouri, an unincorporated community in the United States * Mount Oates, on the border between Alberta and British Columbia, Canada * Mount Oates (New Zealand), Southern Alps of New Zealand * Oates Land Oates Land is a region of Antarctica. It is variously defined as a portion of the East Antarctica near the coast stretching along and inland from the Oates Coast (see map) and as an officially delineated wedge-shaped segment of the Australian A ..., a region of Antarctica ** Oates Bank, a submarine bank off the coast of Oates Land ** Oates Coast, the coast of Oates Land * Oates Canyon, an undersea canyon in the Ross Sea off Antarctica Other uses * Oates Building, a historic building in Florida, United States See also * Oates's soft coral crab, the only species in the genus '' Hoplophrys'' * Oats (other) {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Oates
Lawrence Edward Grace "Titus" Oates (17 March 188017 March 1912) was a British army officer, and later an Antarctic explorer, who died from hypothermia“Oates, Lawrence Edward Grace - Captain (1880-1912) - Biographical notes” Cool Antarctica. during the ''Terra Nova'' Expedition when he walked from his tent into a blizzard. His death, which occurred on his 32nd birthday, is seen as an act of self-sacrifice when, aware that the and |
Todd Gully
The Allan Hills () are a group of hills, mainly ice free and about long, lying just north-west of the Coombs Hills near the heads of Mawson Glacier and Mackay Glacier in the Oates Land and Victoria Land regions of Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Allan Hills were mapped by the New Zealand party (1957–58) of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition and named for Professor R. S. Allan of the University of Canterbury, New Zealand. Allan Hills is referred to as the ''Allan Nunatak'', and mapped north of Carapace Nunatak, in the memoirs of the Scott Base Leader Adrian Hayter. Both names are in the USGS listing. Location Allan Hills lie to the north of Odell Glacier, facing Coombs Hills to the south of the glacier. They are west of the Convoy Range, south of Battlements Nunatak and east of the Antarctic Plateau. Allan Hills are in the shape of the letter "Y", with the open end pointing roughly northwards, and encompassing the Shimmering Icefield. The southern end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedalling Ice Field
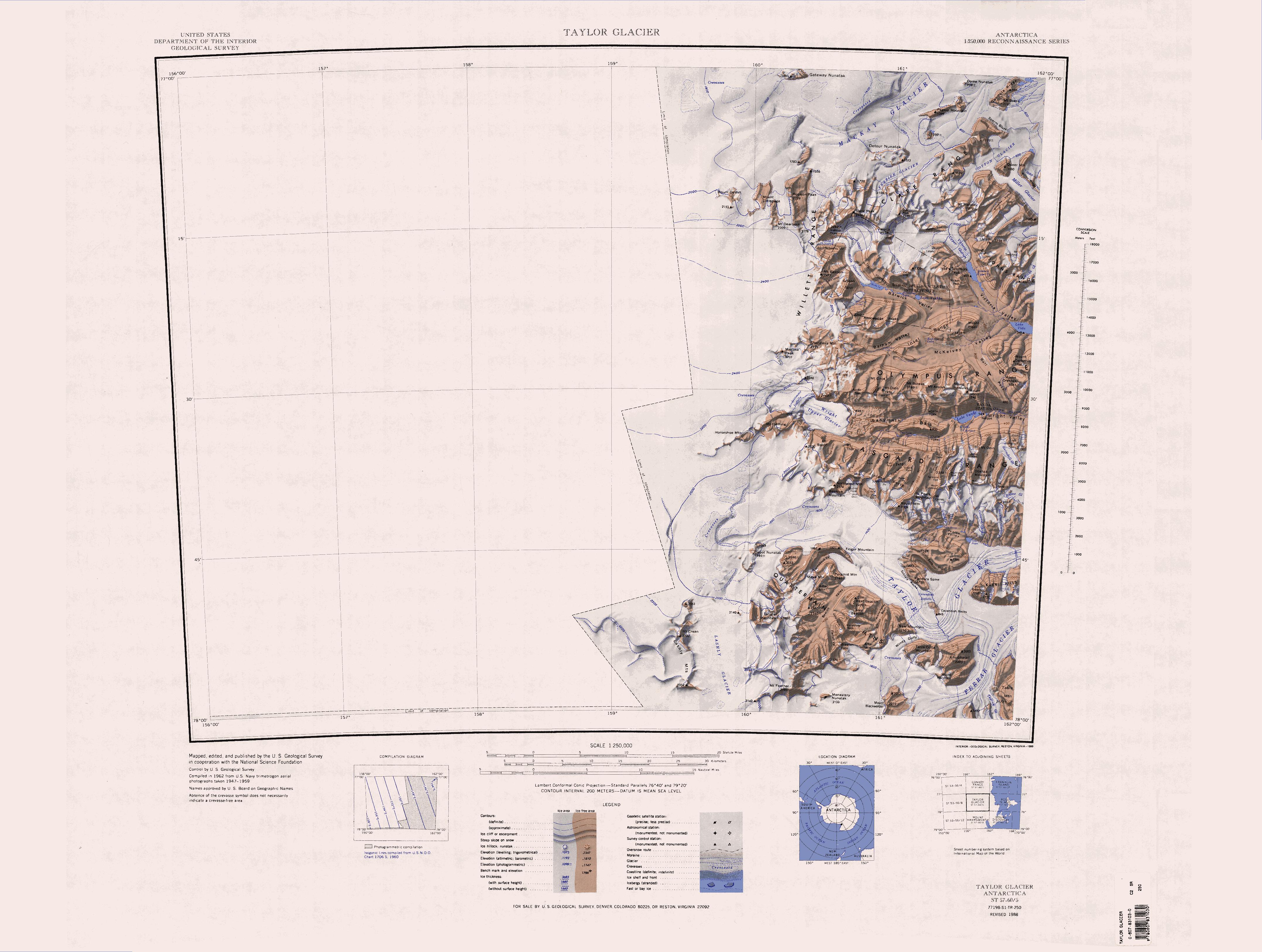
The Willett Range () is the range extending north from Mistake Peak and running for as a high shelf along the edge of the continental ice to the Mackay Glacier, in Victoria Land. The range is breached by several glaciers flowing east from the plateau. Name The Willett Range was named by the New Zealand Northern Survey Party of the Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition (CTAE; 1956–58) for R.W. Willett, Director of the New Zealand Geological Survey, who gave valuable assistance throughout the expedition and in the compilation stages after its return. Location The Willet Range runs from south to north along the eastern side of the Antarctic Plateau. It is north of Wright Upper Glacier and the Olympus Range, and west of Balham Valley, the Apocalypse Peaks, Barwick Valley, the Cruzen Range, and Clare Range. The head of the Mackay Glacier is to the north. Head Mountains . A group of mountains to the south of Gateway Nunatak and the head of Mackay Glacier near the interio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Public S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANARE
The Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE ) is the historical name for the Australia: Antarctic Program#Australian Antarctic program, Australian Antarctic Program (AAP) administered for Australia by the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD). History Australia has had a long involvement in South Pole, south polar regions since as early as Douglas Mawson's Australasian Antarctic Expedition in 1911. Further Australian exploration of the Antarctic continent was conducted during the British Australian and New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE), which was conducted over the years 1929–1931. The Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions were established in 1947 with expeditions to Macquarie Island and Heard Island. In 1948 the Australian Antarctic Division (AAD) was established to administer the expedition program. ANARE Name The name ANARE fell out of official use in the early 2000s. However current and former Australian Antarctic expedit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Antarctic Expedition
The Soviet Antarctic Expedition (SAE or SovAE) (, ''Sovetskaya antarkticheskaya ekspeditsiya'') was part of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute of the Soviet Committee on Antarctic Research of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR. It was succeeded by the Russian Antarctic Expedition. The Soviet Union's Ministry of Sea Transport was responsible for the administration, logistics and supply of the expeditions. The first Soviet contact with Antarctica was in January 1947 when the Slava whaling flotilla began whaling in Antarctic waters. Stations The first Soviet Antarctic station, '' Mirny'', was established near the coast on February 13, 1956. In December 1957 another station, '' Vostok,'' was built inland near the South geomagnetic pole. Year-round stations * Mirny (established February 13, 1956) * Vostok (established December 16, 1957) * Novolazarevskaya (established January 18, 1961) * Molodyozhnaya (established January 14, 1963) * Bellingshausen (established Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Highjump
Operation HIGHJUMP, officially titled The United States Navy Antarctic Developments Program, 1946–1947, (also called Task Force 68), was a United States Navy (USN) operation to establish the Antarctic research base Little America (exploration base), Little America IV. The operation was organized by Rear admiral (United States)#Rear admiral, Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd, Jr., USN, Officer in Charge, Task Force 68, and led by Rear Admiral Ethan Erik Larson, USN, Commanding Officer, Task Force 68. Operation HIGHJUMP commenced 26 August 1946 and ended in late February 1947. Task Force 68 included 4,700 men, 70 ships, and 33 aircraft. HIGHJUMP's objectives, according to the U.S. Navy report of the operation, were: # Training personnel and testing equipment in frigid conditions; # Consolidating and extending the United States' sovereignty over the largest practicable area of the Antarctic continent (publicly denied as a goal before the expedition ended); # Determining the feasibility ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with List of aircraft carriers in service, eleven in service, one undergoing trials, two new carriers under construction, and six other carriers planned as of 2024. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the U.S. Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 299 deployable combat vessels and about 4,012 operational aircraft as of 18 July 2023. The U.S. Navy is one of six United States Armed Forces, armed forces of the United States and one of eight uniformed services of the United States. The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Falcon Scott
Captain Robert Falcon Scott (6 June 1868 – ) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer who led two expeditions to the Antarctic regions: the Discovery Expedition, ''Discovery'' expedition of 1901–04 and the Terra Nova Expedition, ''Terra Nova'' expedition of 1910–13. On the first expedition, he set a new southern record by marching to latitude 82°S and discovered the Antarctic Plateau, on which the South Pole is located. On the second venture, Scott led a party of five which reached the South Pole on 17 January 1912, less than five weeks after Amundsen's South Pole expedition. On the return journey from the Pole, a planned meeting with supporting dog teams from the base camp failed, despite Scott's written instructions, and at a distance of from their base camp at Hut Point and approximately from the next depot, Scott and his companions died. When Scott and his party's bodies were discovered, they had in their possession the first Antarctic fossils discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th (Iniskilling) Dragoons
The 6th (Inniskilling) Dragoons was a cavalry regiment in the British Army, first raised in 1689 as Sir Albert Cunningham's Regiment of Dragoons. One of the regiment's most notable battles was the Battle of the Boyne in July 1690. It became the 6th (Inniskilling) Regiment of Dragoons in 1751. The regiment also fought with distinction in the Charge of the Union Brigade at the Battle of Waterloo and again as part of the successful Charge of the Heavy Brigade against superior numbers at the Battle of Balaclava during the Crimean War. The First World War sounded the death knell for mounted cavalry as it became apparent that technology had moved forward with greater destructive power and made horsed cavalry redundant on the modern battlefield. The British Army reorganised and reduced its cavalry corps by disbanding or amalgamating many of its famous cavalry regiments. The Inniskillings was one of those affected. It saw service for two centuries, including the First World War, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |