|
Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii state in the east (Capital: Cirta) and the Masaesyli state in the west (Capital: Siga). During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into the first unified Berbers, Berber state for Numidians in present-day Algeria. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and an ally of Roman Empire, Rome and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its foundation, was bordered by the Moulouya River to the west, Africa (Roman province), Africa Proconsularis and Cyrenaica to the east. the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south so that Numidia entirely surrounded Carthage except towards the sea. befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidian Language
Numidian was a language spoken in ancient Numidia. The script in which it was written, the Libyco-Berber alphabet (from which Tifinagh descended), has been almost fully deciphered and most characters (apart from a few exceptions restricted to specific areas) have known values. Despite this, the language has barely been transcribed and only a few words are known. Libyco-Berber inscriptions are attested from the 3rd century BC to the 3rd century AD. The language is scarcely attested and can be confidently identified only as belonging to the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic family, although it was most likely part of the Berber languages, spoken at the start of the breakup of the Proto-Berber language. Dialects and relation to other ancient languages Dialects and foreign influences It is known that there was an orthographical difference between the western and eastern Numidian language. Starting at Kabylia, which was a kind of mixed region, the regions to the east all the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidians
The Numidians were the Berber population of Numidia (present-day Algeria). The Numidians were originally a semi-nomadic people, they migrated frequently as nomads usually do, but during certain seasons of the year, they would return to the same camp. The Numidians soon became more than pastoralists and started to engage in more urban professions. The Numidians were one of the earliest Berber tribes to trade with Carthaginian settlers. As Carthage grew, the relationship with the Numidians blossomed. Carthage's military used the Numidian cavalry as mercenaries. Numidia provided some of the highest quality cavalry of the Second Punic War, and the Numidian cavalry played a key role in several battles, both early on in support of Hannibal and later in the war after switching allegiance to the Roman Republic. Numidian culture flourished between the end of the Second Punic War and around the Roman conquest, with Masinissa as the first king of a unified Numidia. History Reign of Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masinissa
Masinissa (''c.'' 238 BC – 148 BC), also spelled Massinissa, Massena and Massan, was an ancient Numidian king best known for leading a federation of Massylii Berber tribes during the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), ultimately uniting them into a kingdom that became a major regional power in North Africa. Much of what is known about Masinissa comes from Livy's '' History of Rome,'' and to a lesser extent Cicero's '' Scipio's Dream''. As the son of a Numidian chieftain allied to Carthage, he fought against the Romans in the Second Punic War, but later switched sides upon concluding that Rome would prevail. With the support of his erstwhile enemy, he united the eastern and western Numidian tribes and founded the Kingdom of Numidia. As a Roman ally, Masinissa took part in the decisive Battle of Zama in 202 BC that effectively ended the war in Carthage's defeat; he also allowed his wife Sophonisba, a famed Carthaginian noblewoman who had influenced Numidian affairs to Cartha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massinissa
Masinissa (''c.'' 238 BC – 148 BC), also spelled Massinissa, Massena and Massan, was an ancient Numidian king best known for leading a federation of Massylii Berber tribes during the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), ultimately uniting them into a kingdom that became a major regional power in North Africa. Much of what is known about Masinissa comes from Livy's '' History of Rome,'' and to a lesser extent Cicero's '' Scipio's Dream''. As the son of a Numidian chieftain allied to Carthage, he fought against the Romans in the Second Punic War, but later switched sides upon concluding that Rome would prevail. With the support of his erstwhile enemy, he united the eastern and western Numidian tribes and founded the Kingdom of Numidia. As a Roman ally, Masinissa took part in the decisive Battle of Zama in 202 BC that effectively ended the war in Carthage's defeat; he also allowed his wife Sophonisba, a famed Carthaginian noblewoman who had influenced Numidian affairs to Cart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia, the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Micipsa's two sons, Hiempsal and Adherbal, and their adopted brother Jugurtha succeeded him. Jugurtha arranged to have Hiempsal killed in 117 BC and, after a civil war, defeated and killed Adherbal in 112 BC. The death of Adherbal, which was against the wishes of Rome, along with the growing popular anger in Rome at Jugurtha's success in bribing Roman senators and thus avoiding retribution for his crimes, led to the Jugurthine War between Rome and Numidia. After a number of battles in Numidia between Roman and Numidian forces, Jugurtha was captured in 105 BC and paraded through Rome as part of Gaius Marius' Roman triumph. He was thrown into the Tullianum prison, where he was executed by strangulation in 104 BC. Etymology The Numidian name Jugurtha matches the ancient nami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
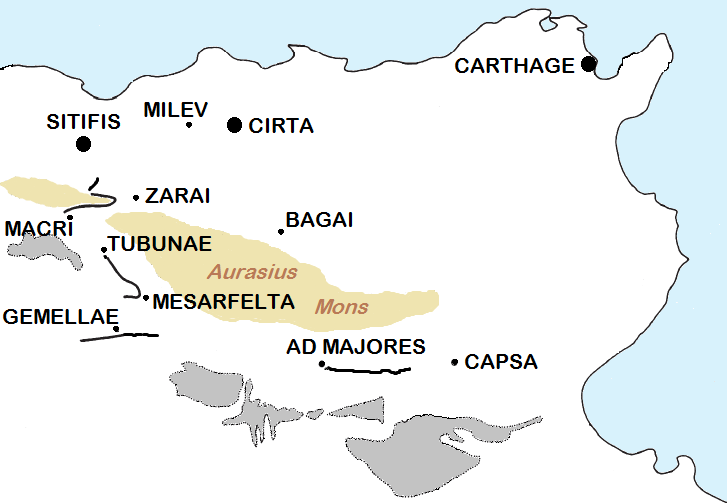
Cirta
Cirta, also known by #Names, various other names in classical antiquity, antiquity, was the ancient Berbers, Berber, Punic people, Punic and Roman Empire, Roman settlement which later became Constantine, Algeria, Constantine, Algeria. Cirta was the capital city of the Berbers, Berber kingdom of Numidia; its strategically important port city was Russicada. Although Numidia was a key ally of the ancient Roman Republic during the Punic Wars (264–146BC), Cirta was subject to Roman invasions during the 2nd and 1st centuriesBC. Eventually it fell under Roman dominion during the time of Julius Caesar. Cirta was then repopulated with Roman colonists by Caesar and Augustus and was surrounded by the autonomous territory of a "Confederation of Four Free Roman cities" (with Collo, Chullu, Russicada, and Milevum), ruled initially by Publius Sittius. The city was destroyed in the beginning of the 4thcentury and was rebuilt by the Roman emperor Constantine the Great, who gave his name to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulussa
Gulussa was the second legitimate son of Masinissa. Gulussa became the King of Numidia along with his two brothers around 148 BC and reigned as part of a triumvirate for about three years. Biography In 148 BC, Masinissa, feeling that he was near death, consulted with Scipio Aemilianus regarding the settlement of his state. Resuscitating, perhaps, a Libyan custom which shared the authority between three persons, Scipio Aemilianus established the three legitimate surviving sons as kings: Micipsa, Gulussa and Mastanabal. The royal power was divided among the three princes. Micipsa, the eldest, was in charge of the administration; it was to him that Masinissa had given his ring which, judging from the stelae of the Abizar style, was a sign of power. Gulussa was given the command of the armies. As for Mastanabal, who was said to have been instructed in Greek, he was charged with justice, and relations with vassal tribal leaders. War with Carthaginians Gulussa already had a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabion
Arabio (or Arabion) was the last independent Numidian king, ruling the western region between 44 and 40 BC. According to Appian, he was a son of Masinissa II and probable grandson of Gauda, who had divided Numidia between his sons in 88 BC. He was of Massylian origin. Etymology The etymology of the name Arabio is unknown, but it is undoubtedly of Semitic origin. It might be the same as that of "Arab" or else derive from the Punic word ''rab'', meaning "leader". The same word existed in biblical Hebrew (chief) and in Aramaic (governor, head of a professional class). The initial ''A-'' likely represents a berberisation of the Punic root. This root is the equivalent of the Numidian root ''mess'', "leader", which is in turn the root of the name of Arabio's father, Masinissa. It was first proposed by the numismatist Jean Mazard in 1955 that Arabio's given name was the same as that of his father and that Roman authors referred to him merely by the Punic form with whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massinissa II
Masinissa II (or Massinissa II) was the petty king of western Numidia with his capital at Cirta (81–46 BC). He was named after, or took his name after, his famous ancestor Masinissa I, the unifier and founder of the kingdom of Numidia. Masinissa was probably the son of Masteabar, an obscure king who is known from a single fragmentary inscription. Masteabar was a son of King Gauda (died 88 BC), who divided the kingdom of Numidia between his sons, Masteabar and his brother Hiempsal II. Masinissa's ally and contemporary, Juba I of eastern Numidia, was most likely his first cousin. The western Numidian kingdom was smaller and weaker than the eastern. In 81 BC, the Roman general Pompey invaded Numidia, which, under the rule of a certain Hiarbas, was assisting the Roman rebel Domitius. Pompey subdued Numidia in a forty-day campaign and restored Hiempsal II to his throne and established Masinissa on his. This constituted formal Roman recognition of the two Numidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juba I
Juba I of Numidia (, ; –46BC) was a king of Numidia (present-day Algeria) who reigned from 60 to 46 BC. He was the son and successor to Hiempsal II. Biography In 81 BC, Hiempsal had been driven from his throne; soon afterwards, Pompey was sent to Africa by Sulla to reinstate him as king in Numidia, and because of this Hiempsal and later Juba became Pompey's allies. This alliance was strengthened during a visit by Juba to Rome when Julius Caesar insulted him by pulling on his beard during a trial wherein Caesar was defending his client against Juba's father and still further in 50 BC when the tribune Gaius Scribonius Curio openly proposed that Numidia should be sold privately. In August 49 BC, Caesar sent Curio to take Africa from the Republicans. Curio was overconfident and held Publius Attius Varus (Varus), the governor of Africa, in low esteem. Curio took fewer legions than he had been given. In the Battle of the Bagradas the same year, Curio led his army in a bold, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastanabal
Mastanabal (Numidian: MSTNB; , ) was one of three legitimate sons of Masinissa, the King of Numidia, a Berber kingdom in, present day Algeria, North Africa. The three brothers were appointed by Scipio Aemilianus Africanus to rule Numidia after Masinissa's death. His name in Numidian was written as "MSTNB" which Salem Chaker gave its possible reconstruction as "Amastan (a)B(a)", which could mean "defender/protector (a)b(a)". Biography Well versed in Greek literature, he learned law. Mastanbal is a great sportsman and Athlete since his youth, the prince took part in chariot races and the Panathenaic Games. He was a sportsman who was passionate about horseback riding. He owned a stud farm of purebred horses. Around 168 BC or 164 BC, he won a gold medal at the Athens Hippodrome at the Panathenaic Games in the prestigious horse-drawn chariot racing event. According to the Roman general Scipio Aemilianus, after the death of his father in 148 BC, Mastanabal was given authority ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Berber Religion
The traditional Berber religion is the sum of ancient and native set of beliefs and deities adhered to by the Berbers. Originally, the Berbers seem to have believed in worship of the sun and moon, animism and in the afterlife, but interactions with the Phoenicians, Greeks and Romans influenced religious practice and merged traditional faiths with new ones. By the seventh century, apart from some Berber tribes, most of North Africa's population was Christian and after the Arab conquest of the Maghreb the traditional Berber religion gradually disappeared. Some of the ancient Berber beliefs still exist today subtly within the Berber popular culture and tradition, such as the idea of holy men (marabouts). Syncretic influences from the traditional Berber religion can also be found in many other faiths around the Mediterranean. Pantheon Worship of sun and the moon According to Herodotus, all ancient Berbers worshipped the moon and sun (''Tafukt'' in Tamazight) and sacrificed sole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |