|
North Aegean Islands
The North Aegean islands are a number of scattered islands in the North Aegean Sea, also known as the Northeastern Aegean islands, belonging mostly to Greece and a few of them to Turkey. The islands do not form a physical chain or group, but are frequently grouped together for tourist or administrative purposes. To the south are the Dodecanese islands, and to the west are the Cyclades and Sporades islands. Within this group, the main islands in the northeastern Aegean Sea and along the Turkish coast are the Greek islands of Samos, Ikaria, Chios, Lesbos, Lemnos, Agios Efstratios, Psara, Fournoi Korseon, Oinousses and the Turkish islands of Imbros, Tenedos and the Rabbit or ''Tavşan'' Islands. The main islands in the Thracian Sea in the far north are the Greek islands of Samothrace and Thasos. Most are in the North Aegean administrative region. History From the Mesolithic Age, the North Aegean, as indeed the entire Aegean, ceased to be an obstacle and became a bridge j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aegean Sea With Island Groups Labeled
Aegean may refer to: *Aegean Sea *Aegean Islands *Aegean Region (geographical), Turkey *Aegean Region (statistical), Turkey *Aegean civilizations *Aegean languages, a group of ancient languages and proposed language family *Aegean Sea (theme), a naval theme of the Byzantine Empire *Aegean Airlines *Aegean Macedonia, an irredentist term for the Greek region of Macedonia *Aegean Records, independent record label founded by singer and songwriter George Michael *University of the Aegean, a university based in Mytilene, Greece *Ege University, a university based in İzmir, Turkey *Aegean (stage), part of the Triassic system in stratigraphy *Aegean cat, a cat breed from Greece *Aegean Contagion, an alternate name to the euro area crisis with reference to its point of origin and a general term for an epidemic * Aegean (album), ''Aegean'' (album) See also * North Aegean * South Aegean * Archipelago {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imbros
Imbros (; ; ), officially Gökçeada () since 29 July 1970,Alexis Alexandris, "The Identity Issue of The Minorities in Greece And Turkey", in Hirschon, Renée (ed.), ''Crossing the Aegean: An Appraisal of the 1923 Compulsory Population Exchange Between Greece and Turkey'', Berghahn Books, 2003p. 120/ref> is the largest island of Turkey, located in Çanakkale Province. It is located in the north-northeastern Aegean Sea, at the entrance of Saros Bay, and has the westernmost point of Turkey ( Cape İncirburnu). Imbros has an area of , and has some wooded areas."Gökçeada" from Britannica Concise Encyclopedia As of 2023, the island-district of Gökçeada has a population of 10,721. The main industries of Imbros are fishing and tourism. By the end of the 20th century, the island was predominantly inhabited by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Polis, Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed Tyrant#Historical forms, tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, embarked on an Siege of Naxos (499 BC), expedition to conquer the island of Naxos Island, Naxos, with Persian support; however, the expedition was a debacle and, preempting his dismissal, Aristagoras incited all of Hellenic Asia Minor into rebellion against the Persians. This was the beginning of the Ionian Revolt, which would last unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaeans (Homer)
The Achaeans or Akhaians (; , "the Achaeans" or "of Achaea") is one of the names in Homer which is used to refer to the Greeks collectively. The term "Achaean" is believed to be related to the Hittite term Ahhiyawa and the Egyptian term Ekwesh which appear in texts from the Late Bronze Age and are believed to refer to the Mycenaean civilization or some part of it. In the historical period, the term fell into disuse as a general term for Greek people, and was generally reserved for inhabitants of the region of Achaea, a region in the north-central part of the Peloponnese. The city-states of this region later formed a confederation known as the Achaean League, which was influential during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC. Etymology According to Margalit Finkelberg the name Ἀχαιοί ( earlier Ἀχαιϝοί) is possibly derived, via an intermediate form *Ἀχαϝyοί, from a hypothetical older Greek form reflected in the Hittite form ''Aḫḫiyawā''; the latter is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraion Of Samos
The Heraion of Samos was a large sanctuary to the goddess Hera, on the island of Samos, Greece, 6 km southwest of the ancient city of Samos (modern Pythagoreion). It was located in the low, marshy basin of the Imbrasos river, near where it enters the sea. The late Archaic temple in the sanctuary was the first of the gigantic free-standing Ionic temples, but its predecessors at this site reached back to the Geometric Period of the 8th century BC, or earlier, and there is evidence of cult activities on the site from c. 1700 BC onwards. The ruins of the temple, along with the nearby archeological site of Pythagoreion, were designated UNESCO World Heritage Sites in 1992, as a testimony to their exceptional architecture and to the mercantile and naval power of Samos during the Archaic Period. History The core myth at the heart of the cult of Hera at Samos is that of her birth. According to the local tradition, the goddess was born under a ''lygos'' tree ('' Vitex agnus-castu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emporiou
Emporio is a prehistoric settlement in the southeastern part of the island of Chios in the Mastichochoria municipality of Greece. Pyrgi is the largest village nearby. It was inhabited since the early Neolithic times, around 6000 BC. The fertile valley with drinking water, a natural harbor nearby and the associated access to the sea were favorable conditions for settlement. The modern village nearby is called Emborios. It is a coastal town with 47 inhabitants (2011). Archaeology Sinclair Hood started his work on Chios for the British School at Athens in 1952. He noted the ruins of Emporio in the same year, and his excavations continued to 1955. A fortified settlement was founded on the peninsula south of Emborios Bay at the end of the Chalcolithic. At the same time, another settlement developed near the beach outside the fortress, which lasted until the final phase of the Mycenaean culture (ca. 1100 BC). The settlement flourished during the Copper and Bronze Age in the 3rd and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poliochnis
Poliochne, often cited under its modern name Poliochni (), was an ancient settlement on the east coast of the island of Lemnos. It was settled in the Late Chalcolithic and earliest Aegean Bronze Age and is believed to be one of the most ancient towns in Europe, preceding Troy I. Anatolian features of the earliest layers were affected by cultural influences from Helladic Greece, about the start of Early Helladic II, ca. 2500 BC. The site, with houses huddled together sharing party walls, was unearthed by excavations of the Italian School of Archaeology at Athens (''Scuola archeologica Italiana di Athene''), beginning in 1930. It is believed that Troy was its main rival commercially; a rivalry that led to the decline of Poliochne circa 2000 BC. Archaeology Following initial soundings, regular campaigns at Poliochne were undertaken under A. Della Seta ( it) in 1931-36, when they were suspended. Following Della Seta's death, excavations were resumed in 1951-53, 1956 and 1960. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic Age
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in the Middle East (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, but it is associated with a decline in the group hunting of large animals in favour of a broader hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
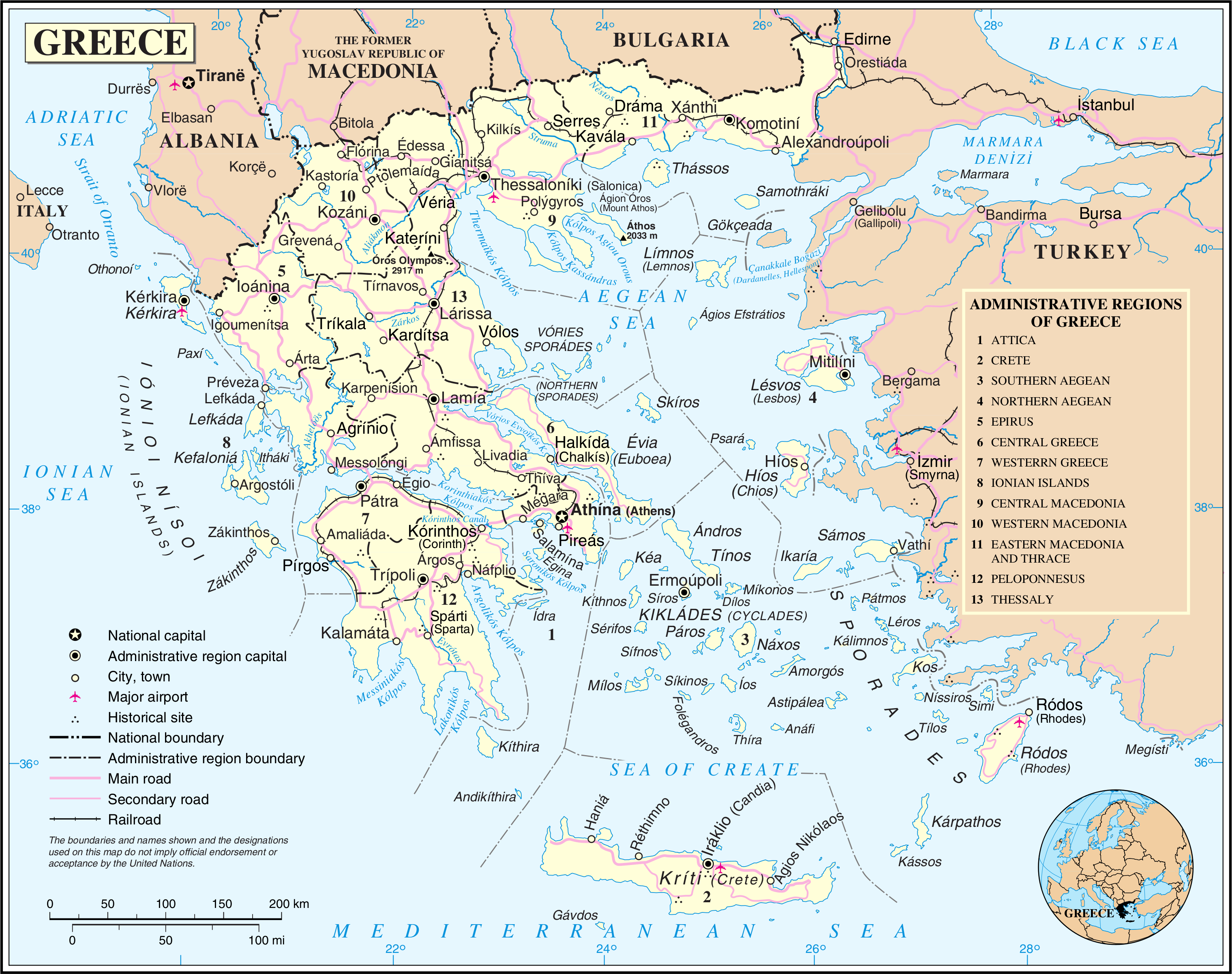
Regions Of Greece
The regions of Greece () are the country's thirteen second-level administrative divisions of Greece, administrative entities, counting decentralized administrations of Greece as first-level. Regions are divided into regional units of Greece, regional units, known as prefectures of Greece, prefectures until 2011. History The current regions were established in July 1986 (the presidential decree officially establishing them was signed in 1987), by decision of the interior minister, Menios Koutsogiorgas, as second-level administrative entities, complementing the Prefectures of Greece, prefectures (Law 1622/1986). Ν.1622/86 "Τοπική Αυτοδιοίκηση - Περιφερειακή Ανάπτυξη - Δημοκρατικός Προγραμματισμός", (ΦΕΚ 92/τ.Α΄/14-7-1986) Before 1986, there was a traditional division into broad geographic regions of Greece, historical–geographical regions (γεωγραφικά διαμερίσματα), which, however, was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Aegean
The North Aegean Region (, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece, and the smallest of the thirteen by population. It comprises the islands of the north-eastern Aegean Sea, called the North Aegean islands, except for Thasos and Samothrace, which belong to the Greek region of Eastern Macedonia and Thrace, and Imbros and Tenedos, which belong to Turkey. Administration The North Aegean region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with the Southern Aegean region, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of the Aegean based at Piraeus. The capital of the region is situated in Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Until the Kallikratis reform, the region consisted of the three prefectures of Samos, Chios and Lesbos. Since 1 January 2011, it has been divided into five regional units: Chios, Ikaria, Lemnos, Lesbos, and Samos. The total number of isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thasos
Thasos or Thassos (, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area. The island has an area of 380 km2 and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate regional unit within the East Macedonia and Thrace region. Before the local administration reform of 2011, it was part of the Kavala Prefecture. The largest town and the capital is Thasos, officially known as ''Limenas Thasou'', "Port of Thasos", situated on the northern side. It is connected with the mainland by regular ferry lines between Keramoti and Thasos town, and between the regional centre of Kavala and Skala Prinou. The most important economic activity on the island is tourism. The main agricultural products are honey, almonds, walnuts, olives (such as the local Throumba variety which has a protected designation of origin), olive oil, and wine. The inhabitants also engage in fishing, and in the herding of sheep and goats. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki; , ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long, in size and has a population of 2,596 (2021 census). Its main industries are fishing and tourism. Resources on the island include granite and basalt. Samothrace is one of the most rugged Greek islands, with Mt Saos and its highest peak, Fengari, rising to . The ''Winged Victory of Samothrace'' statue, which is now displayed at the Louvre in Paris, was found on the island. History Antiquity Samothrace never became a state of any political significance in ancient Greece, since it lacks natural harbours and most of the island is too mountainous for cultivation: Mount Fengari (literally 'Mt Moon') rises to . It was, however, the home of the Sanctuary of the Great Gods, site of important Hellenic and pre-Hellenic religious ceremonies. Those who visited this shrine to be initiated into the island cult inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |