|
Non-volatile Random-access Memory
Non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) is random-access memory that retains data without applied power. This is in contrast to dynamic random-access memory (DRAM) and static random-access memory (SRAM), which both maintain data only for as long as power is applied, or forms of Sequential access memory, sequential-access memory such as magnetic tape, which cannot be randomly accessed but which retains data indefinitely without electric power. Read-only memory devices can be used to store system firmware in embedded systems such as an automotive ignition system control or home appliance. They are also used to hold the initial processor instructions required to Bootstrapping, bootstrap a computer system. Read-write memory such as NVRAM can be used to store calibration constants, passwords, or setup information, and may be integrated into a microcontroller. If the main memory of a computer system were non-volatile, it would greatly reduce the time required to start a system afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
DS1225
DS1 or DS-1 may refer to: * BOSS DS-1, a guitar distortion pedal * Digital Signal 1, a T-carrier signaling scheme devised by Bell Labs * Deep Space 1, a mission to 9969 Braille & 19P/Borrelly * DS-1 (drug), a selective GABAA α4β3δ agonist drug * South African Class DS1, a diesel locomotive class * Datsun ''DS-1'', a car by Nissan, see Datsun DS Series * '' Dark Souls'', an action role-playing game * Dead Space (2008 video game), a survival horror game * VR Class Ds1, a Finnish railbus class * DS-1 Orbital Battle Station, the full name of the original Death Star space station in the ''Star Wars ''Star Wars'' is an American epic film, epic space opera media franchise created by George Lucas, which began with the Star Wars (film), eponymous 1977 film and Cultural impact of Star Wars, quickly became a worldwide popular culture, pop cu ...'' franchise See also * DS (other) * Canon EOS-1Ds series {{Letter-number combination disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, flip-flops and latches are electronic circuit, circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will output its state (often along with its logical complement too). It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements to store a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state (computer science), state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
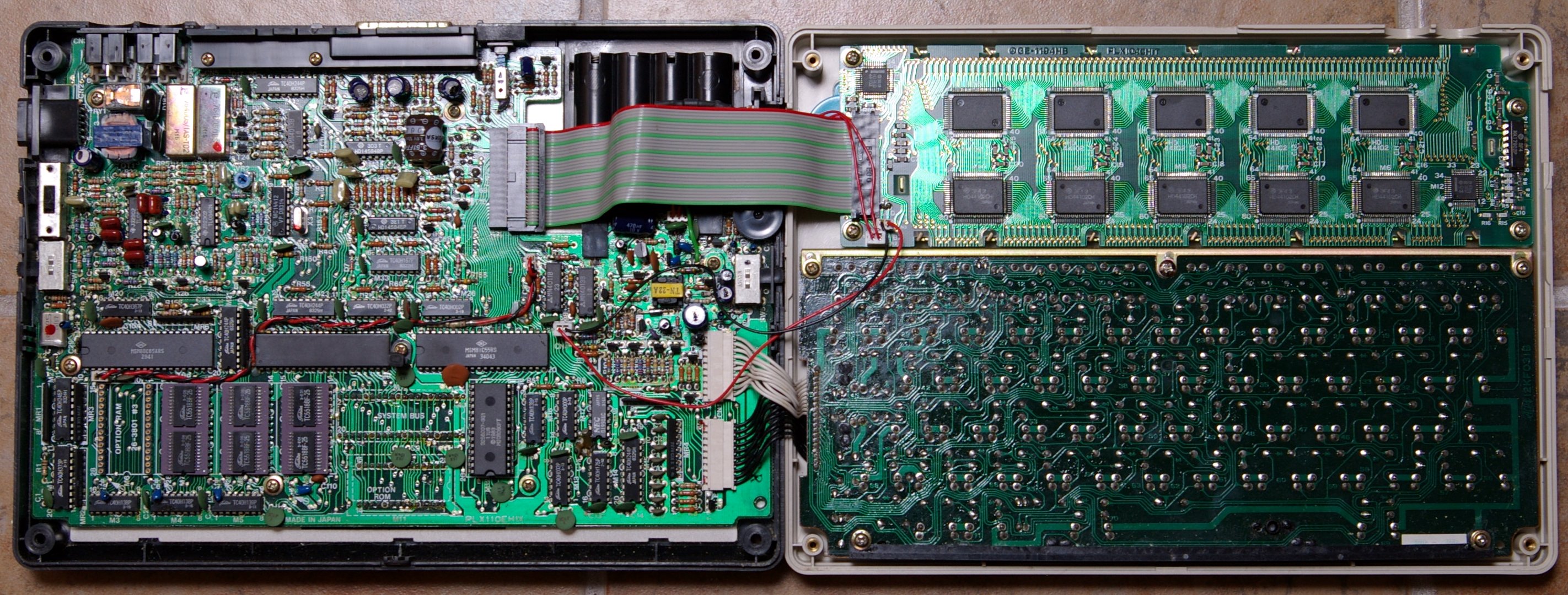 |
TRS-80 Model 100
The TRS-80 Model 100 is a Notebook form factor, notebook-sized portable computer introduced in April 1983. It was the first commercially successful notebook computer, as well as one of the first notebook computers ever released. It features a keyboard and liquid-crystal display, in a battery-powered package roughly the size and shape of a notepad or large book. The 224-page, spiral-bound User Manual is nearly the same size as the computer itself. It was made by Kyocera, and originally sold in Japan as the Kyotronic 85. Although a slow seller for Kyocera, the rights to the machine were purchased by Tandy Corporation. The computer was sold through Radio Shack stores in the United States and Canada and affiliated dealers in other countries. It became one of the company's most popular models, with over 6 million units sold worldwide. The Olivetti M-10 and the NEC PC-8201 and PC-8300 were also built on the same Kyocera platform, with some design and hardware differences. It was orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Apple Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup includes the MacBook Air and MacBook Pro laptops, and the iMac, Mac Mini, Mac Studio, and Mac Pro desktops. Macs are currently sold with Apple's UNIX-based macOS operating system, which is Proprietary software, not licensed to other manufacturers and exclusively Pre-installed software, bundled with Mac computers. This operating system replaced Apple's original Macintosh operating system, which has variously been named System, Mac OS, and Classic Mac OS. Jef Raskin conceived the Macintosh project in 1979, which was usurped and redefined by Apple co-founder Steve Jobs in 1981. The original Macintosh 128K, Macintosh was launched in January 1984, after Apple's 1984 (advertisement), "1984" advertisement during Super Bowl XVIII. A series of increment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Nonvolatile BIOS Memory
Nonvolatile BIOS memory refers to a small Memory (computers), memory on personal computer, PC motherboards that is used to store BIOS settings. It is traditionally called CMOS RAM because it uses a volatile memory, volatile, low-power CMOS, complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) Static random access memory, SRAM (such as the Motorola MC146818 or similar) powered by a small battery when system and standby power is off. It is referred to as non-volatile memory or Non-volatile random-access memory, NVRAM because, after the system loses power, it does retain state by virtue of the CMOS battery. When the battery fails, BIOS settings are reset to their defaults. The battery can also be used to power a real time clock (RTC) and the RTC, NVRAM and battery may be integrated into a single component. The name CMOS memory comes from the technology used to make the memory, which is easier to say than NVRAM. The CMOS RAM and the real-time clock have been integrated as a part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
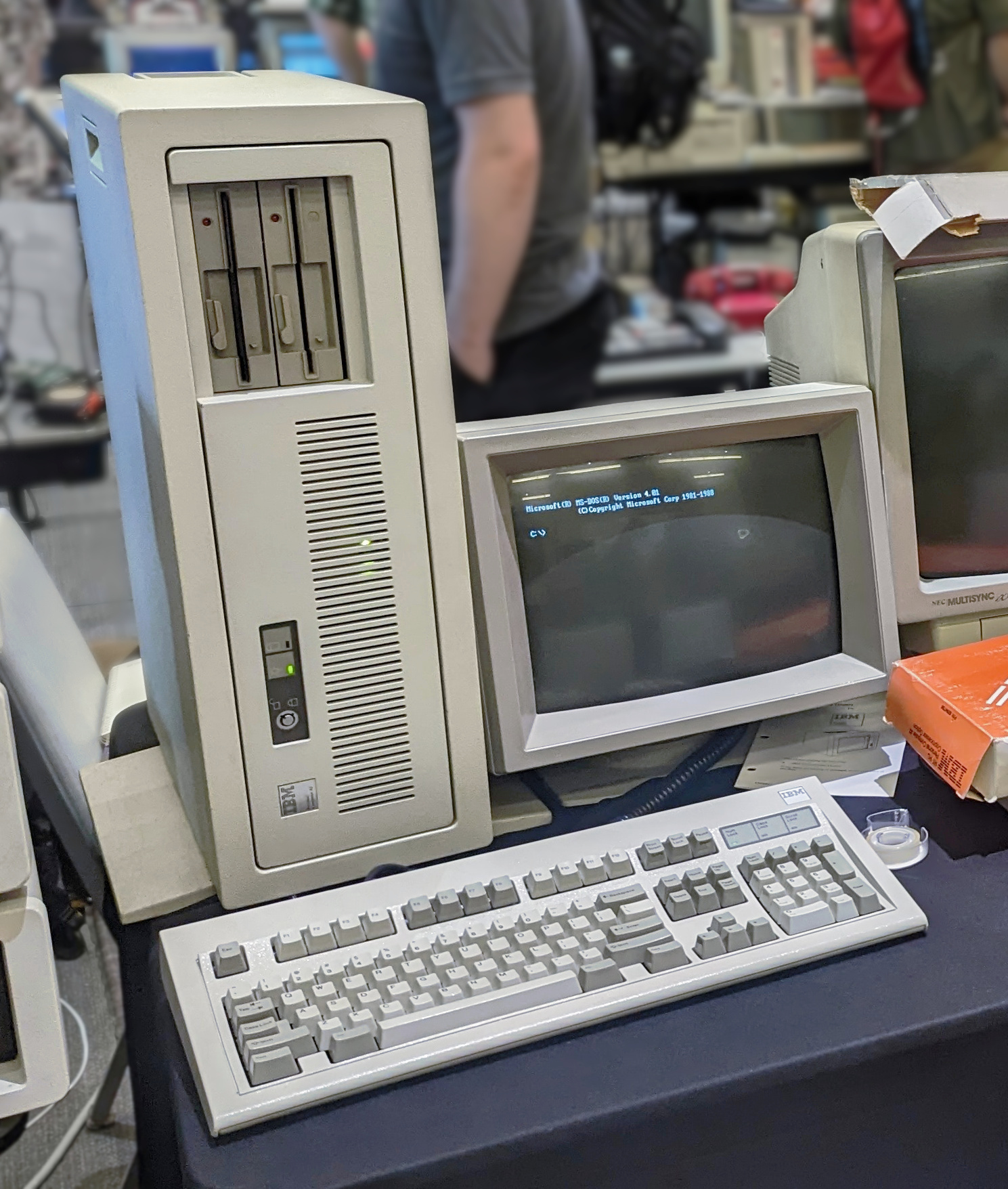 |
IBM PC AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 80286 microprocessor. Name IBM did not specify an expanded form of ''AT'' on the machine, press releases, brochures or documentation, but some sources expand the term as ''Advanced Technology'', including at least one internal IBM document. History IBM's 1984 introduction of the AT was seen as an unusual move for the company, which typically waited for competitors to release new products before producing its own models. At $4,000–6,000, it was only slightly more expensive than considerably slower IBM models. The announcement surprised rival executives, who admitted that matching IBM's prices would be difficult. No major competitor showed a comparable computer at COMDEX Las Vegas that year. Features The AT is IBM PC compatible, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Universal Memory
Universal memory refers to a computer data storage device combining the cost benefits of DRAM, the speed of SRAM, the non-volatility of flash memory along with infinite durability, and longevity. Such a device, if it ever becomes possible to develop, would have a far-reaching impact on the computer market. Some doubt that such a type of memory will ever be possible. Computers, for most of their recent history, have depended on several different data storage technologies simultaneously as part of their operation. Each one operates at a level in the memory hierarchy where another would be unsuitable. A personal computer might include a few megabytes of fast but volatile and expensive SRAM as the CPU cache, several gigabytes of slower DRAM for program memory, and Hundreds of GB to a few TB of slow but non-volatile flash memory or "spinning platter" hard disk drive for long-term storage. For example, a university recommended students entering in 2015–2016 to have a PC with: : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Flash Memory
Flash memory is an Integrated circuit, electronic Non-volatile memory, non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR gate, NOR and NAND gate, NAND logic gates. Both use the same cell design, consisting of floating-gate MOSFETs. They differ at the circuit level, depending on whether the state of the bit line or word lines is pulled high or low; in NAND flash, the relationship between the bit line and the word lines resembles a NAND gate; in NOR flash, it resembles a NOR gate. Flash memory, a type of floating-gate memory, was invented by Fujio Masuoka at Toshiba in 1980 and is based on EEPROM technology. Toshiba began marketing flash memory in 1987. EPROMs had to be erased completely before they could be rewritten. NAND flash memory, however, may be erased, written, and read in blocks (or pages), which generally are much smaller than the entire devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
EEPROM
EEPROM or E2PROM (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory) is a type of non-volatile memory. It is used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as a separate chip device, to store relatively small amounts of data by allowing individual bytes to be erased and reprogrammed. EEPROMs are organized as arrays of floating-gate transistors. EEPROMs can be programmed and erased in-circuit, by applying special programming signals. Originally, EEPROMs were limited to single-byte operations, which made them slower, but modern EEPROMs allow multi-byte page operations. An EEPROM has a limited life for erasing and reprogramming, reaching a million operations in modern EEPROMs. In an EEPROM that is frequently reprogrammed, the life of the EEPROM is an important design consideration. Flash memory is a type of EEPROM designed for high speed and high density, at the expense of large erase blocks (typically 512 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Fuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is an electrical safety device that operates to provide overcurrent protection of an electrical circuit. Its essential component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it, thereby stopping or interrupting the current. It is a sacrificial device; once a fuse has operated, it is an open circuit, and must be replaced or rewired, depending on its type. Fuses have been used as essential safety devices from the early days of electrical engineering. Today there are thousands of different fuse designs which have specific current and voltage ratings, breaking capacity, and response times, depending on the application. The time and current operating characteristics of fuses are chosen to provide adequate protection without needless interruption. Wiring regulations usually define a maximum fuse current rating for particular circuits. A fuse can be used to mitigate short circuits, overloading, mismatched loads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Programmable Read-only Memory
A programmable read-only memory (PROM) is a form of digital memory where the contents can be changed once after manufacture of the device. The data is then permanent and cannot be changed. It is one type of read-only memory (ROM). PROMs are used in digital electronic devices to store permanent data, usually low level programs such as firmware or microcode. The key difference from a standard Read-only memory, ROM is that the data is written into a ROM during manufacture, while with a PROM the data is programmed into them after manufacture. Thus, ROMs tend to be used only for large production runs with well-verified data. PROMs may be used where the volume required does not make a factory-programmed ROM economical, or during development of a system that may ultimately be converted to ROMs in a mass produced version. PROMs are manufactured blank and, depending on the technology, can be programmed at wafer, final test, or in system. Blank PROM chips are programmed by plugging them int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Main Memory
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers. The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer is what manipulates data by performing computations. In practice, almost all computers use a storage hierarchy, which puts fast but expensive and small storage options close to the CPU and slower but less expensive and larger options further away. Generally, the fast technologies are referred to as "memory", while slower persistent technologies are referred to as "storage". Even the first computer designs, Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine and Percy Ludgate's Analytical Machine, clearly distinguished between processing and memory (Babbage stored numbers as rotations of gears, while Ludgate stored numbers as displacements of rods in shuttles). This distinction was extended in the Von Neumann architecture, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |