|
Nipple
The nipple is a raised region of tissue on the surface of the breast from which, in lactating females, breast milk, milk from the mammary gland leaves the body through the lactiferous ducts to Breastfeeding, nurse an infant. The milk can flow through the nipple passively, or it can be ejected by smooth muscles, smooth muscular contraction, muscle contractions that occur along with the ductal system. The nipple is surrounded by the areola, which is often a darker colour than the surrounding skin. Male mammals also have nipples but without the same level of function or prominence. A nipple is often called a ''teat'' when referring to non-humans. "Nipple" or "teat" can also be used to describe the flexible mouthpiece of a baby bottle. In humans, the nipples of both males and females can be sexually stimulated as part of sexual arousal. In many cultures, female nipples are sexualized, or regarded as sex objects and evaluated in terms of their physical characteristics and sex appeal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
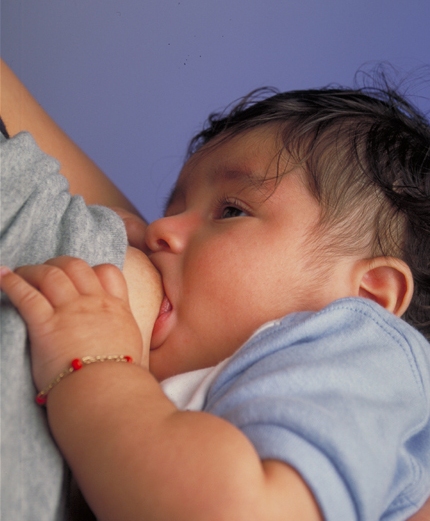
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's birth and continue as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
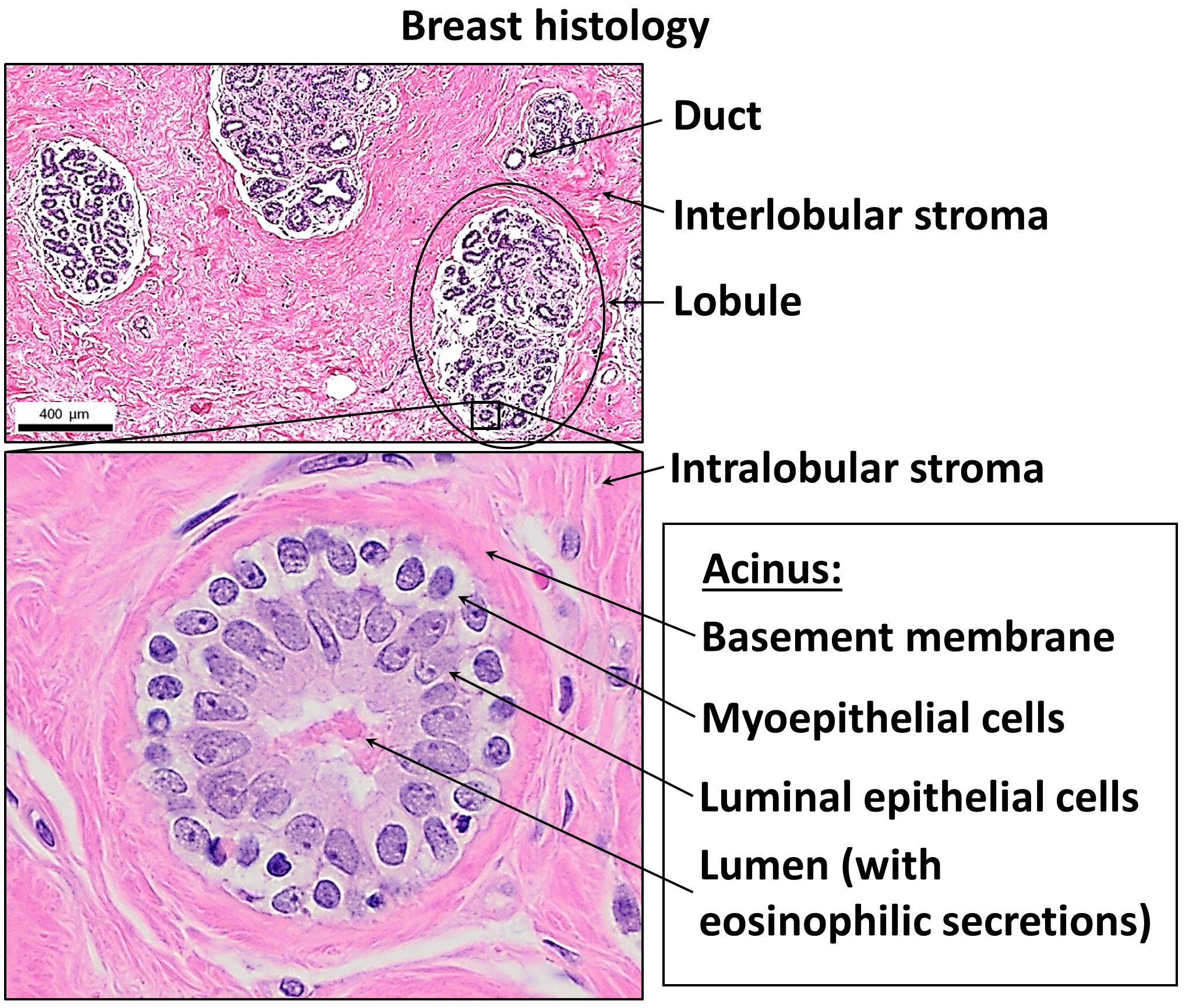
Breast
The breasts are two prominences located on the upper ventral region of the torso among humans and other primates. Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryology, embryological tissues. The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males. There is also considerable Bra size, variation in size between individuals. Permanent Breast development, breast growth during puberty is caused by estrogens in conjunction with the growth hormone. Female humans are the only mammals that permanently develop breasts at puberty; all other mammals develop their mammary tissue during the latter period of pregnancy. In females, the breast serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secretes milk to feed infants. Subcutaneous fat covers and envelops a network of lactiferous duct, ducts that converge on the nipple, and these tissue (biology), tissues give the breast its distinct size and globular shape. At the ends of the ducts are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
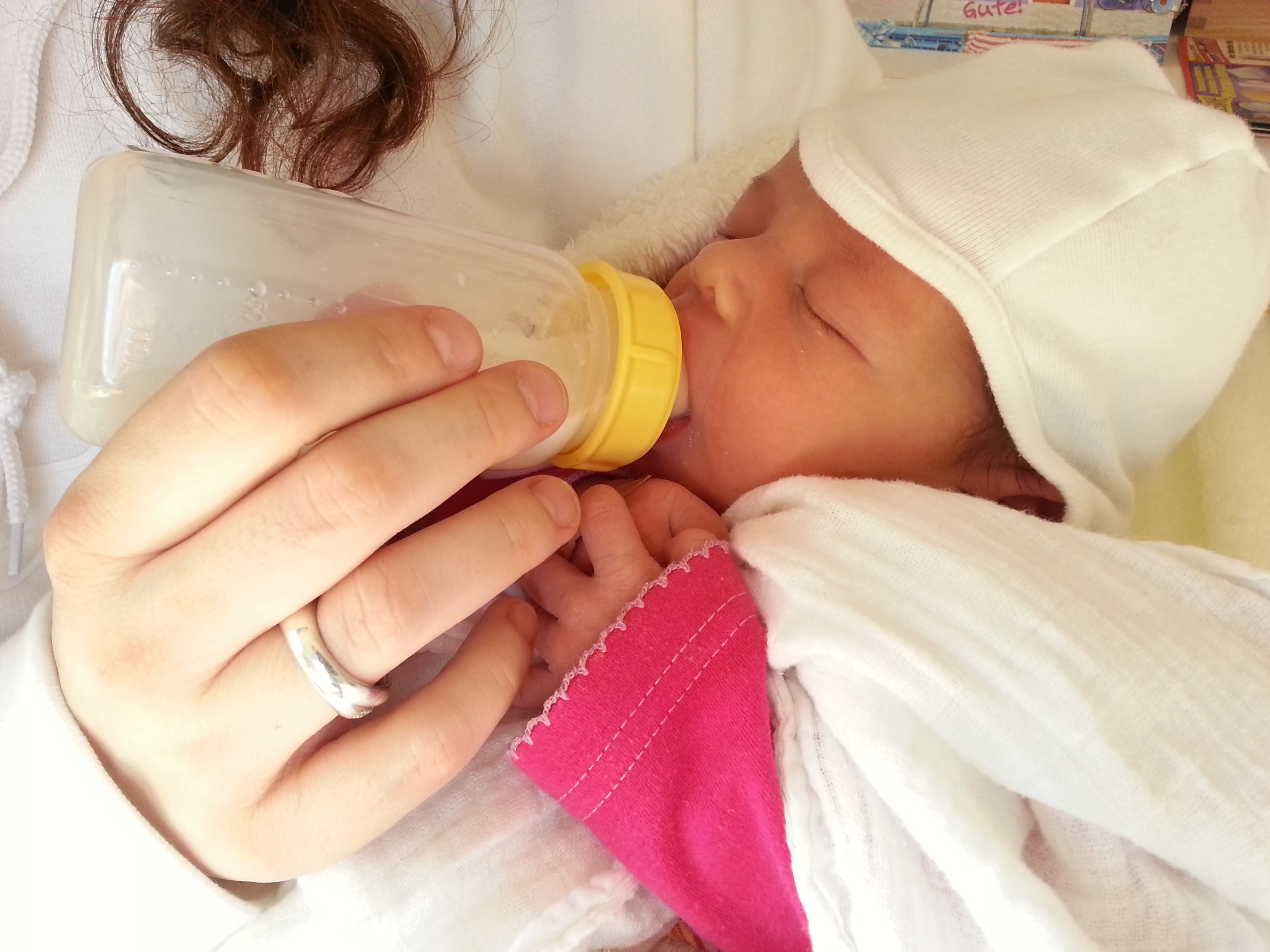
Baby Bottle
A baby bottle, nursing bottle, or feeding bottle is a bottle with a ''teat'' (also called a ''nipple'' in the US) attached to it, which creates the ability to drink via suckling. It is typically used by infants and young children, or if someone cannot (without difficulty) drink from a cup, for feeding oneself or being fed. It can also be used to feed non-human mammals, whose mother cannot feed their young or mammals which have no mother. Hard plastic is the most common material used, being transparent, light-weight, and resistant to breakage. Glass bottles have been recommended as being easier to clean, less likely to retain formula residues, and relatively chemically inert. Hybrid bottles using plastic on the outside and glass inside have also been developed. Other materials used for baby bottles include food-grade stainless steel and silicone rubber. Baby bottles can be used to feed expressed breast milk, infant formula, or pediatric electrolyte solution. A 2020 review re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammary Gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland that produces milk in humans and other mammals. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats) to feed young offspring. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: monotremes, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of monotremes, their mammary glands are modified seba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Areola
The human areola (''areola mammae'', or ) is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. More generally, an areola is a small circular area on the Human body, body with a different histology from the surrounding Tissue (biology), tissue, or other small circular areas such as an inflamed region of skin. The mature human female nipple has several small openings arranged radially around the tip of the lactiferous ducts, from which milk is released during lactation. The other small openings in the areola are sebaceous glands, also known as Areolar gland, areolar glands. Shade The areolae can range from pink to red to brown to dark brown or nearly black, but generally tend to be paler among people with lighter skin tones and darker among people with darker skin tones. A reason for the differing color may be to make the nipple area more visible to the infant. Hyperpigmentation occurs in most women during the second stage of pregnancy, leading to a temporarily darker shade. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Stimulated
Sexual stimulation is anything that leads to sexual arousal or orgasm. This thing can be physical or of other senses, and is known as a stimulus. Sexual stimulation is a broad term, usually understood to mean physical touching of the genitals or other body parts. The term can, however, include stimuli affecting the mind ( sexual fantasy), or senses other than touch (such as sight, smell, or hearing). Sufficient physical stimulation of the genitals usually results in an orgasm. Stimulation can be by oneself (masturbation or sexual fantasy) or by a sexual partner (sexual intercourse or other sexual activity), by use of objects or tools, or by some combination of these methods. Some people practice orgasm control, whereby a person or their partner controls the level of stimulation to prolong the experience leading up to orgasm. Physical sexual stimulation Physical sexual stimulation consists of touching the genitals or other erogenous zones. Genital Masturbation, ero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
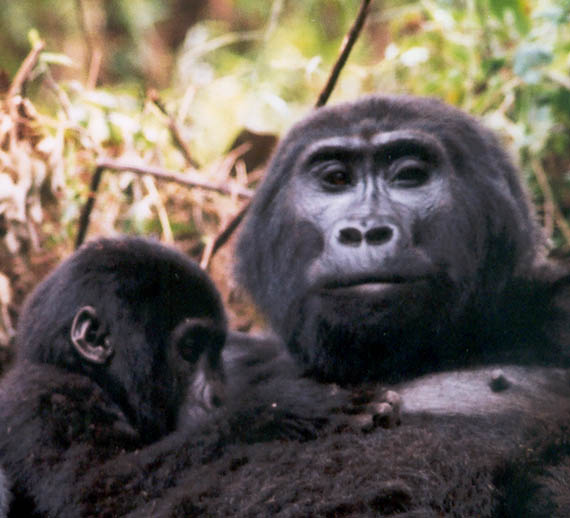
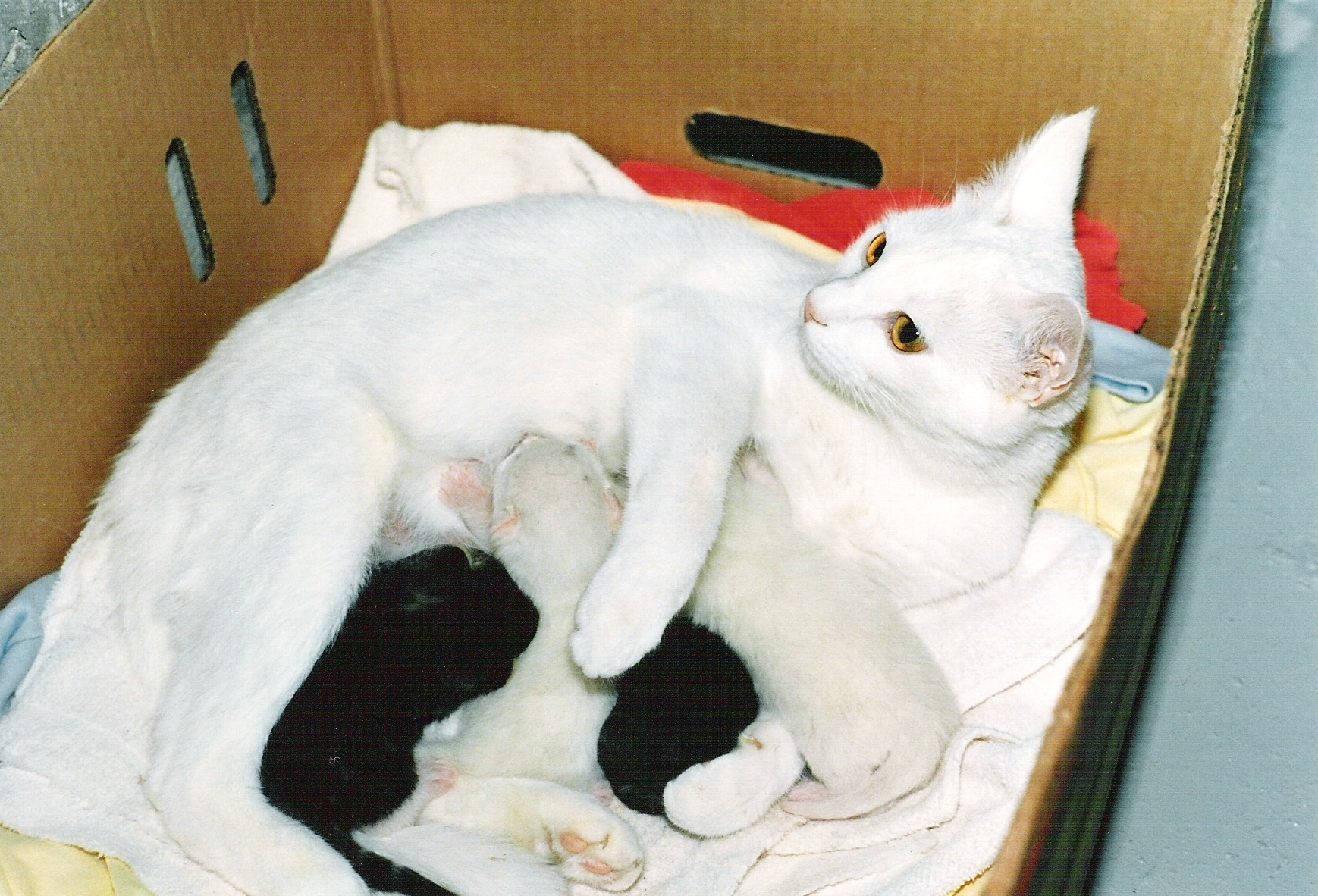
Lactating
Lactation describes the secretion of milk from the mammary glands and the period of time that a mother lactates to feed her young. The process naturally occurs with all sexually mature female mammals, although it may predate mammals. The process of feeding milk in all female creatures is called ''nursing'', and in humans it is also called ''breastfeeding''. Newborn infants often produce some milk from their own breast tissue, known colloquially as witch's milk. In most species, lactation is a sign that the female has been pregnant at some point in her life, although in humans and goats, it can happen without pregnancy. Nearly every species of mammal has teats; except for monotremes, egg-laying mammals, which instead release milk through ducts in the abdomen. In only a handful of species of mammals, certain bat species, is milk production a normal male function. ''Galactopoiesis'' is the maintenance of milk production. This stage requires prolactin. Oxytocin is critical for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Arousal
Sexual arousal (also known as sexual excitement) describes the Physiology, physiological and psychological responses in preparation for sexual intercourse or when exposed to Sexual stimulation, sexual stimuli. A number of physiological responses occur in the body and mind as preparation for sexual intercourse, and continue during intercourse. #Male physiological response, Male arousal will lead to an erection, and in #Female physiological response, female arousal, the body's response is engorged sexual tissues such as Erection of nipples, nipples, Clitoral erection, clitoris, Vagina#Microanatomy, vaginal walls, and vaginal lubrication. Stimulus (psychology), Mental stimuli and Stimulus (physiology), physical stimuli such as touch, and the internal fluctuation of hormones, can influence sexual arousal. Sexual arousal has several stages and may not lead to any actual sexual activity beyond a mental arousal and the physiological changes that accompany it. Given sufficient sexual st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactiferous Duct
Lactiferous ducts are ducts that converge and form a Morphogenesis#Branching morphogenesis, branched system connecting the nipple to the lobules of the mammary gland. When lactogenesis occurs, under the influence of hormones, the breast milk, milk is moved to the nipple by the action of smooth muscle contractions along the ductal system to the tip of the nipple. They are also referred to as ''galactophores'', ''galactophorous ducts'', ''mammary ducts'', ''mamillary ducts'' or ''milk ducts''. Structure Lactiferous ducts are lined by a columnar epithelium supported by myoepithelial cells. Prior to 2005, it was thought within the areola the lactiferous duct would dilate to form the lactiferous sinus in which milk accumulates between breastfeeding sessions. However past studies have shown that the lactiferous sinus does not exist. Function The columnar epithelium plays a key role in balancing milk production, milk stasis and reabsorption. The cells of the columnar epithelium form tig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by the mammary glands in the breasts of women. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborn infants, comprising fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and a varying composition of minerals and vitamins. Breast milk also contains substances that help protect an infant against infection and inflammation, such as Human milk microbiome, symbiotic bacteria and other microorganisms and immunoglobulin A, whilst also contributing to the healthy development of the infant's immune system and gut microbiome. Use and methods of consumption The World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF recommend Breastfeeding#Duration and exclusivity, exclusive breastfeeding with breast milk for the first six months of an infant’s life. This period is followed by the incorporation of nutritionally adequate and safe complementary solid foods at six months, a stage when an infant’s nutrient and energy requirements start ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |