|
Nineveh Plains
Nineveh Plains (, Modern ; ; ) is a region in Nineveh Governorate in Iraq. Located to the north and east of the city Mosul, it is the only Christian-majority region in Iraq and have been a gathering point for Iraqi Christians since 2003. Control over the region is contested between Iraqi security forces, Peshmerga, KRG security forces, Nineveh Plain Protection Units, Assyrian security forces, Babylon Brigade and the Shabak Militia. The plains have a heterogenous population of Aramaic-speaking Assyrian Christians belonging to different churches: the Assyrian Church of the East, the Chaldean Catholic, the Syriac Orthodox church, and the Syriac Catholic church. Arabs, Kurds, Yazidis, Shabaks and Iraqi Turkmen, Turkmens, and includes ruins of ancient Assyrian cities and religious sites, such as Nimrud, Dur-Sharrukin, Mar Mattai Monastery, Rabban Hormizd Monastery and the Tomb of Nahum. History The Middle Bronze Age Andarig, Kingdom of Andarig used to be located in the north. Tabula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineveh Governorate
Nineveh Governorate (; , ) is a governorate in northern Iraq. It has an area of and an estimated population of 2,453,000 people as of 2003. Its largest city and provincial capital is Mosul, which lies across the Tigris river from the ruins of ancient Nineveh. Before 1976, it was called ''Mosul Province'' and included the present-day Dohuk Governorate. The second largest city is Tal Afar, which has an almost exclusively Turkmen population. An ethnically, religiously and culturally diverse region, it was partly conquered by ISIS in 2014. Iraqi government forces retook the city of Mosul in 2017. Recent history and administration Its two cities endured the 2003 U.S.-led invasion of Iraq and emerged unscathed. In 2004, however, Mosul and Tal Afar were the scenes of fierce battles between US-led troops and Iraqi insurgents. The insurgents moved to Nineveh after the Battle of Fallujah in 2004. After the invasion, the military of the province was led by (then Major Genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Church Of The East
The Assyrian Church of the East (ACOE), sometimes called the Church of the East and officially known as the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East, is an Eastern Christianity, Eastern Syriac Christianity, Syriac Christian denomination that follows the traditional Christology and ecclesiology of the historical Church of the East. It belongs to the eastern branch of Syriac Christianity, and employs the Liturgy of Addai and Mari, Divine Liturgy of Saints Addai and Mari belonging to the East Syriac Rite. Its main Sacred language, liturgical language is Syriac language, Classical Syriac, a dialect of Eastern Aramaic languages, Eastern Aramaic. Officially known as the Church of the East until 1976, it was then renamed the Assyrian Church of the East, with its patriarchate remaining hereditary until the death of Shimun XXIII Eshai, Shimun XXI Eshai in 1975. The Assyrian Church of the East is officially headquartered in the city of Erbil, in northern Iraq; its original a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabban Hormizd Monastery
Rabban Hormizd Monastery () is an important convent to the Assyrian Church of the East, and the Chaldean Catholic Church, founded about 640 AD by the Church of the East, carved out in the mountains about 2 miles from Alqosh, Iraq, 28 miles north of Mosul. It was the official residence of the patriarchs of the ''Eliya'' line of the Assyrian Church of the East from 1551 to the 18th century, and after the union with Rome in the early 19th century, passed to becoming a prominent monastery of the Chaldean Catholic Church. The convent is named after Rabban Hormizd (''rabban'' is the Syriac for "monk") of the Church of the East, who founded it in the seventh century. History of the monastery Because of the fame of Rabban Hormizd, the monastery he founded became extremely important for the Church of the East. It flourished until the 10th century. Already, before the end of the 15th century, the Rabban Hormizd Monastery served as the patriarchal burial site. Yohannan Sulaqa was monk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mar Mattai Monastery
Dayro d-Mor Mattai (; ; ''The Monastery of St. Matthew'' or ''Dayro d-Mor Mattai'') is a Syriac Orthodox Church monastery on Mount Alfaf in northern Iraq. Located 20 kilometers northeast of the city of Mosul, it is recognized as one of the oldest Christian monasteries in existence and the oldest Syriac Orthodox monastery in the world. The monastery was famous for the number of monks and scholars it housed, and for its large library and considerable collection of Syriac Christian manuscripts. Today, it is an archbishopric; the current archbishop is Mor Timothius Mousa Alshamany. History Founding The monastery was founded in 363 AD by Mar (title), Mor Matthew the Hermit, Mattai the Hermit who fled persecution in Amida (Mesopotamia), Amid under the Roman Emperor Julian the Apostate with 25 other monks and took residence in Mount Alfaf. According to Syriac tradition, he converted Behnam, Sarah, and the Forty Martyrs, Mor Behnam to Christianity and healed his sister, Sarah, whom he c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dur-Sharrukin
Dur-Sharrukin (, "Fortress of Sargon"; , Syriac Language, Syriac: ܕܘܪ ܫܪܘ ܘܟܢ), present day Khorsabad, was the Assyrian capital in the time of Sargon II of Assyria. Khorsabad is a village in northern Iraq, 15 km northeast of Mosul. The great city was entirely built in the decade preceding 706 BC. After the unexpected death of Sargon in battle, the capital was shifted 20 km south to Nineveh. History Sargon II ruled from 722 to 705 BC. The demands for timber and other materials and craftsmen, who came from as far as coastal Phoenicia, are documented in contemporary Assyrian letters. The debts of construction workers were nullified in order to attract a sufficient labour force. The land in the environs of the town was taken under cultivation, and olive groves were planted to increase Assyria's deficient oil-production. The great city was entirely built in the decade preceding 706 BC, when the court moved to Dur-Sharrukin, although it was not compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
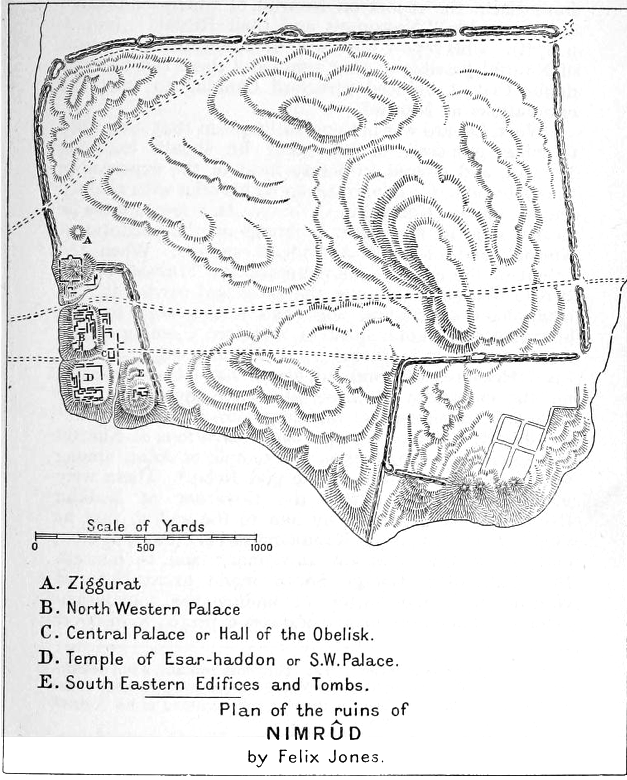
Nimrud
Nimrud (; ) is an ancient Assyrian people, Assyrian city (original Assyrian name Kalḫu, biblical name Calah) located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah (), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a major Assyrian city between approximately 1350 BC and 610 BC. The city is located in a strategic position north of the point that the river Tigris meets its tributary the Great Zab.Brill's Encyclopedia of Islam 1913-36 p.923 The city covered an area of . The ruins of the city were found within of the modern-day Assyrian people, Assyrian village of Numaniyah, Al-Hamdaniya, Noomanea in Nineveh Governorate, Iraq. The name Nimrud was recorded as the local name by Carsten Niebuhr in the mid-18th century.N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC to the 7th century BC. Spanning from the early Bronze Age to the late Iron Age, modern historians typically divide ancient Assyrian history into the Early Assyrian period, Early Assyrian ( 2600–2025 BC), Old Assyrian period, Old Assyrian ( 2025–1364 BC), Middle Assyrian Empire, Middle Assyrian ( 1363–912 BC), Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Assyrian (911–609 BC), and Post-imperial Assyria, post-imperial (609 BC– AD 240) periods, based on political events and gradual changes in language. Assur, the first Assyrian capital, was founded 2600 BC, but there is no evidence that the city was independent until the collapse of the Third Dynasty of Ur, in the 21st century BC, when a line of independent kings starting with Puzur-Ashur I began rulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iraqi Turkmen
The Iraqi Turkmen (, عراق تورکمنلری; Arabic: تركمان العراق), also referred to as Iraqi Turks, (, عراق توركلری; ) are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq. They make up to 10%–13% of the Iraqi population. Iraqi Turkmens are descendants of Turkish people, Turkish settlers from the time of Ottoman Iraq, and are closely related to Syrian Turkmen, Syrian Turkmens and Azerbaijanis, Azerbaijani people. Turkmen in Iraq do not closely identify with the traditionally-nomadic Turkmens of Central Asia and Iran.: "Turkmen, Iraqi citizens of Turkmen seljukh origin, are the third largest ethnic group in Iraq after Arabs and Kurds and they are said to number about 3 million of Iraq's 34.7 million citizens according to the Iraqi Ministry of Planning." Ethnonyms According to Iraqi Turkmen scholar Professor Suphi Saatçi, prior to the mid-20th century the Turkmens in Iraq were known simply as "Turks". It was not until after the military coup of 14 July 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shabaks
Shabaks (, ) are a group native to the Nineveh Plains in Iraq. Their origin is uncertain, although they are largely considered Kurds by scholars. They speak Shabaki, a branch of the Zaza–Gorani languages, one of the main Kurdish variants alongside common Kurdish. Shabaks largely follow Shia Islam. Origins The origins of the word ''Shabak'' are not clear. One theory is that ''Shabak'' is an Arabic word that means ''intertwine'', indicating that the Shabak people originated as a confederation of many tribes of different ethnicities. Others claim that the word Shabak came from the Persian "shah" and Turkish " bek", meaning "master of kings", eventually being Arabized to "Shabak". Austin Henry Layard considered Shabaks to be descendants of Kurds who originated in Iran, and believed that they possibly had affinities with the Ali-Ilahis. Anastase-Marie al-Karmali also argued that Shabaks were ethnic Kurds. Another theory claimed that Shabaks were local ethnic Kurds who were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yazidis
Yazidis, also spelled Yezidis (; ), are a Kurdish languages, Kurdish-speaking Endogamy, endogamous religious group indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey, and Iran. The majority of Yazidis remaining in the Middle East today live in Iraq, primarily in the Governorates of Iraq, governorates of Nineveh Governorate, Nineveh and Duhok Governorate, Duhok. There is a disagreement among scholars and in Yazidi circles on whether the Yazidi people are a distinct ethnoreligious group or a religious sub-group of the Kurds, an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group. Yazidism is the ethnic religion of the Yazidi people and is Monotheism, monotheistic in nature, having roots in a Ancient Iranian religion, pre-Zoroastrian Iranic faith. Since the spread of Islam began with the early Muslim conquests of the 7th–8th centuries, Persecution of Yazidis, Yazidis have faced persecution by Arabs and later by Turkish people, Turks, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurds
Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peoples, Iranic ethnic group from West Asia. They are indigenous to Kurdistan, which is a geographic region spanning southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Iraq, and northeastern Syria. Consisting of 30–45 million people, the global Kurdish population is largely concentrated in Kurdistan, but significant communities of the Kurdish diaspora exist in parts of West Asia beyond Kurdistan and in parts of Europe, most notably including: Turkey's Central Anatolian Kurds, as well as Kurds in Istanbul, Istanbul Kurds; Iran's Khorasani Kurds; the Caucasian Kurds, primarily in Kurds in Azerbaijan, Azerbaijan and Kurds in Armenia, Armenia; and the Kurdish populations in various European countries, namely Kurds in Germany, Germany, Kurds in France, France, Kurds in Sweden, Sweden, and the Kurds in the Netherlands, Netherlands. The Kurdish language, Kurdish languages and the Zaza–Gorani languages, both of which belong to the Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |