|
Ngari Prefecture
Ngari Prefecture () or Ali Prefecture ( zh, s=阿里地区 , t=阿里地區 , p=Ālǐ Dìqū) is a prefecture of China's Tibet Autonomous Region covering Western Tibet, whose traditional name is Ngari Khorsum. Its administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Shiquanhe. It is one of the least densely populated areas in the world, with 0.4 people per square kilometer (1.0 per square mile). History In ancient times, Ngari was known as Zhangzhung. The Zhangzhung kingdom extended over much of western Tibet, until its conquest by the Tibetan Empire under Songtsen Gampo. Zhangzhung sites, such as its capital Khyung-lung dngul-mkhar, are traditionally believed to be closely associated with the development of Bon, the indigenous Tibetan religion. According to Bon tradition, the religion first spread to Zhangzhung from the semi-mythical lands of Olmo Lungring and Tagzig. Thereafter, Bon doctrines were transmitted to central Tibet. Archaeological evidence demonstrated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefecture (China)
zh, p=Dìqū, labels=no , alt_name = , map = , category = Second level administrative division of a unitary state , territory = China , start_date = , current_number = 7 prefectures , number_date = , population_range = 95,465 ( Ngari) – 3,979,362 ( Kaxgar) , area_range = ( Daxing'anling) – ( Ngari) , government = Various, Central Government , subdivision = Counties Prefectures are one of four types of prefecture-level divisions in China, the second-level administrative division in the country. While at one time prefectures were the most common prefecture-level division, they are in the process of being abolished and only seven formally-designated prefectures remain. The term "prefecture" is also used as a translation of three unrelated types of administrative divisions that were historically in use in China: the ''xian'', the ''zhou'', and the ''fu''. Modern prefecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Empire
The Tibetan Empire (,) was an empire centered on the Tibetan Plateau, formed as a result of expansion under the Yarlung dynasty heralded by its 33rd king, Songtsen Gampo, in the 7th century. It expanded further under the 38th king, Trisong Detsen, and reached its greatest extent under the 40th king, Ralpacan, Ralpachen, stretching east to Chang'an, west beyond modern Afghanistan, south into modern India and the Bay of Bengal. The Yarlung dynasty was founded in 127 BC in the Yarlung Valley along the Yarlung River, south of Lhasa. The Yarlung capital was moved in the 7th century from the palace Yumbulingka to Lhasa by the 33rd king Songtsen Gampo, and into the Red Fort during the imperial period which continued to the 9th century. The beginning of the imperial period is marked in the reign of the 33rd king of the Yarlung dynasty, Songtsen Gampo. The power of Tibet's military empire gradually increased over a diverse terrain. During the reign of Trisong Detsen, the empire became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholing Monastery
Tholing Monastery (or Toling, mtho lding dgon pa མཐོ་ལྡིང་དགོན་པ) (Tuolin si 托林寺) is the oldest monastery (or gompa) in the Ngari Prefecture of western Tibet. It is situated in Tholing (Zanda), Zanda County, near the border with India. It was built in 997 AD by Yeshe-Ö, the second King of the Guge Kingdom. In Tibetan language 'Tholing' means "hovering in the sky forever" and is reflected by the location of the monastery at an elevation of . The complex includes three temples, the Yeshe-O Temple, the Lhakhang Karpo and the Dukhang. There are many ancient, precious, and well-preserved frescoes. Geography The monastery is located in remote badlands of far western Tibet in Zanda County. It perches on an escarpment in the Grand Canyon along the Langchen Tsangpo (designated as Sutlej River, meaning "elephant river", in Tibet). It has a well laid out street, post office and telecommunication facilities. The isolated military installation of Zand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeshe-Ö
Yeshe-Ö ( 959–1040; Tibetan script, Tibetan: ཡེ་ཤེས་འོད་, Wylie transliteration, Wylie: ye shes 'od; spiritual names Lha bLama Yeshes 'Od, Byang Chub Ye Shes 'Od, Lha Bla Ma, Lalama Yixiwo, also Dharmaraja – 'Noble King') was the first notable lama-king in Tibet. Born as Khor-re, he is better known as Lhachen Yeshe-Ö, his spiritual name. Yeshe-Ö was the second king in the succession of the kingdom of Guge in the southwestern Tibetan Plateau. Yeshe-Ö abdicated the throne in 975 to become a lama. In classical Tibetan historiography, the restoration of an organized and monastic tradition of Tibetan Buddhism is attributed to him. He built Tholing Monastery in 997 when Tholing was the capital of Guge. Yeshe-Ö' sponsored novitiates, including the great translator Rinchen Zangpo. Early life and rule From a young age, Yeshe-Ö was interested in religious matters. He was the son of king Tashi-gon (bKra-shis-mgon), and ruled the merged kingdoms of Tashig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zanskar
Zanskar, Zahar (locally) or Zangskar, is the southwestern region of Kargil district in the Indian union territory of Ladakh. The administrative centre of Zanskar is Padum. Zanskar, together with the rest of Ladakh, was briefly a part of the kingdom of Geography of Tibet, Western Tibet called Ngari Khorsum. Zanskar lies 250 km south of Kargil, Kargil City on National Highway 301 (India), NH301. In August 2024, the Ministry of Home Affairs (India), Ministry of Home Affairs announced that Zanskar will become a district (India), district in Ladakh by 2028. Etymology Zanskar ( ''zangs dkar'') appears as ''“Zangskar”'' mostly in academic studies in social sciences (anthropology, gender studies), reflecting the Ladakhi pronunciation, although the Zanskari pronunciation is Zãhar. Older geographical accounts and maps may use the alternate spelling "Zaskar". An etymological study (Snellgrove and Skorupsky, 1980) of the name reveals that its origin might refer to the natural occ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
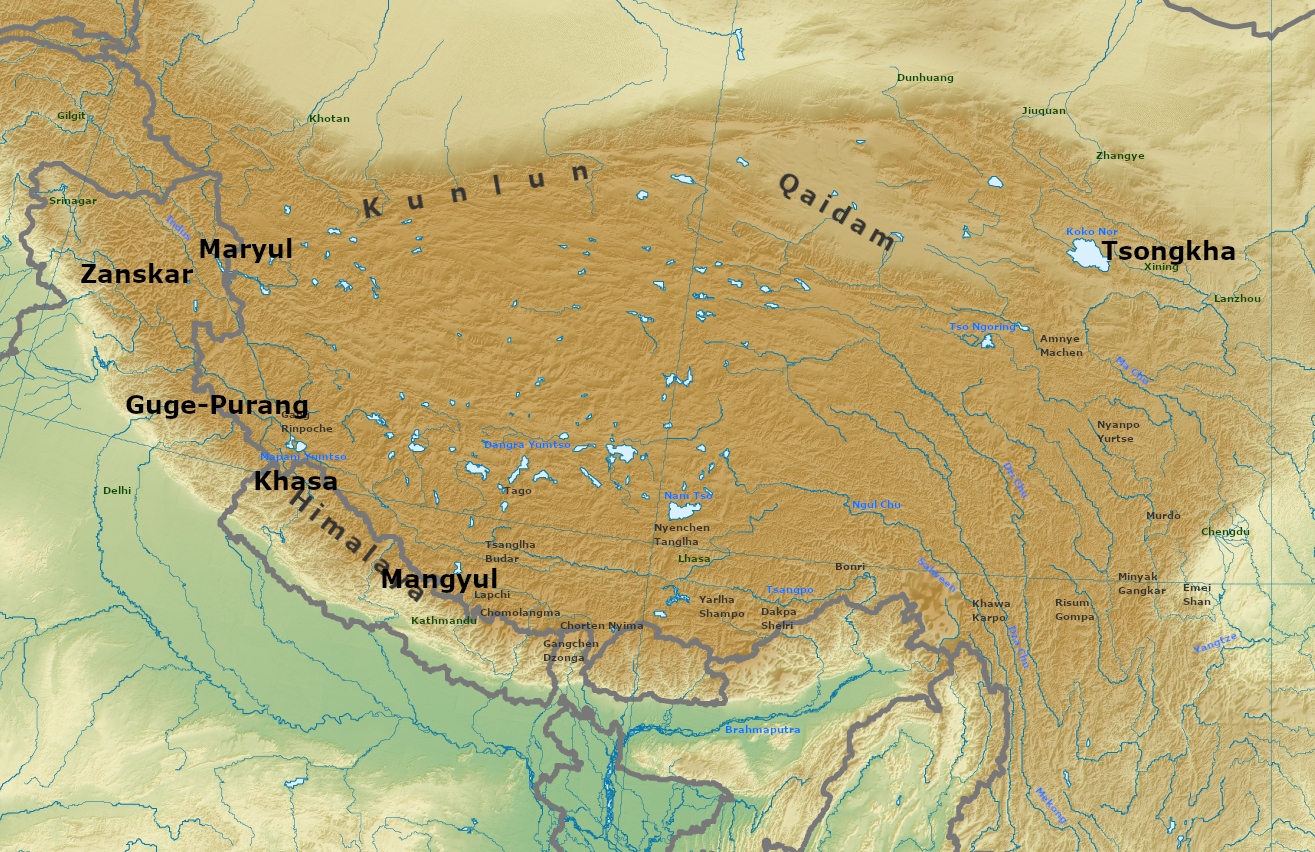
Maryul
Maryul (), also called ''mar-yul'' of ''mnga'-ris'', was the western-most Tibetan kingdom based in modern-day Ladakh and some parts of Tibet. The kingdom had its capital at Shey. The kingdom was founded by Lhachen Palgyigon, during the rule of his father Kyide Nyimagon, in .: "it seems that his father bequeathed him a theoretical right of sovereignty, but the actual conquest was effected by dPal-gyi-mgon himself." It stretched from the Zoji La at the border of Kashmir to Demchok in the southeast, and included Rudok and other areas presently in Tibet. The kingdom came under the control of the Namgyal dynasty in 1460, eventually acquiring the name "Ladakh", and lasted until 1842. In that year, the Dogra general Zorawar Singh, having conquered it, made it part of the would-be princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. Etymology ''Mar-yul'' has been interpreted in Tibetan sources as lowland (of Ngari),. Scholars suspect that it was a proper name that was in use earlier, even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purang-Guge Kingdom
Purang-Guge kingdom () was a small Western Himalayan kingdom which was founded and flourished in the 10th century in western Tibet. The original capital was at Purang Town, Purang () but was moved to Tholing in the Sutlej canyon southwest of Mount Kailash. It was divided into smaller kingdoms around the year 1100 CE. Tholing, at , the last town before Tsaparang in the kingdom of Guge was then its capital, (163 miles from Darchen). It was founded by the great-grandson of Langdarma, who was assassinated, leading to the collapse of the Tibetan Empire. Buddhist monuments at both Tsaparang and Tholing are now mostly in ruins except for a few statues and scores of murals in good condition, painted in the western Tibetan style. While Langdarma persecuted Buddhism in Tibet, his descendant, King Yeshe-Ö, who ruled the Guge Kingdom in the 10th century with Tholing as its capital, was responsible for the second revival or "second diffusion" of Buddhism in Tibet; the reign of the Guge Kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India and China since 1959.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kashmir dispute is supported by the WP:TERTIARY, tertiary sources (a) through (e), reflecting WP:DUE, due weight in the coverage. Although "controlled" and "held" are also applied neutrally to the names of the disputants or to the regions administered by them, as evidenced in sources (h) through (i) below, "held" is also considered politicised usage, as is the term "occupied", (see (j) below). (a) (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent ... has been the subject of dispute between India and Pakistan since the partition of the Indian subcontinent in 1947. The northern and wester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyide Nyimagon
Kyide Nyimagon (), whose original name was Khri-skyid-lding, was a member of the Yarlung dynasty of Tibet and a descendant of emperor Langdarma. He migrated to Western Tibet and founded the kingdom of Ngari Khorsum ("the three divisions of Ngari") around 912 CE. After his death in 930 CE, his large kingdom was divided among his three sons, giving rise to the three kingdoms of Maryul (Ladakh), Guge-Purang and Zanskar- Spiti. Family After the assassination of the emperor Langdarma, the Tibetan empire entered a period of civil war over succession by Langdarma's two sons (Yum-brtan) and ('Odsrung), which divided the empire into two parts. Ösung's son Depal Khortsen (–) is believed to have controlled most or part of Central Tibet. Nyimagon was one of the sons of Depal Khortsen, the other being Trashi Tsentsän (''bKraśis-brtsegs-brtsan''). Both the sons fled Ü-Tsang (Central Tibet) in 910 when their father was murdered, at the end of the 3rd , which is taken to mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarlung Dynasty
The Yarlung dynasty (;, is a Tibet, Tibetan dynasty of List of emperors of Tibet, 42 kings, dating from 127 BCE to 842 CE. This dynasty gave rise to the Tibetan Empire period from 614 CE to 848 CE, credited to the 33rd king Songtsen Gampo, and lasting through to the 40th king Ralpacan, Rapalchen. Rapalchen was murdered in 838 by his brother, the future 41st king Langdarma, Ü Dum Tsen, who in turn ruled for only one year (841-842) until his own murder. The dissolution of the empire occurred by 848. The early Yarlung dynasty chiefs and kings lived before the Tibetan language was created, and their reigns and lives were documented through the lineage of verbal history until c. 650 when in the reign of the 33rd king of the Yarlung Dynasty Songtsen Gampo, the Tibetan alphabet and grammar were created and the royal record keeping of people and events called the Testament of Ba, Chronicle of Ba began. While some scholars feel unsure of the definitive existence due to the lack of written ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
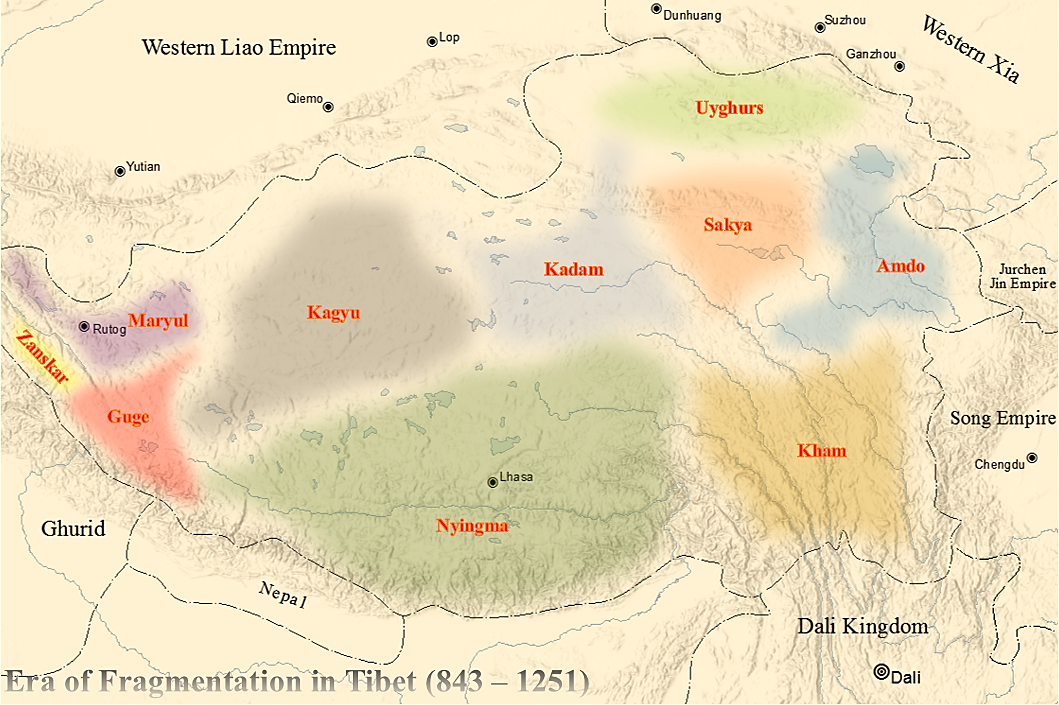
Era Of Fragmentation
The Era of Fragmentation () was an era of disunity in history of Tibet, Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three regions of Tibet in 1253, following the Mongol invasions of Tibet, Mongol conquest in the 1240s. During this period, the political unity of the Tibetan Empire collapsed following a civil war between Yumtän (''Yum brtan'') and Ösung (''’Od-srung''), after which followed numerous rebellions against the remnants of imperial Tibet and the rise of regional warlords. Civil war and the decline of imperial Tibet The last king of the unified Tibetan Empire, Langdarma, was assassinated in 842 possibly by a Buddhist hermit monk named Pelgyi Dorje of Lhalung, or other sources state he died from fright. The death left two possible heirs, the two princes Yumtän and Ösung, that fought for the throne and initiated a civil war. This civil war weakene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Tibetan
Classical Tibetan refers to the language of any text written in Tibetic after the Old Tibetan period. Though it extends from the 7th century until the modern day (along with Arabic, Ge'ez, and New Persian, it is one of the handful of 'living' classical languages), it particularly refers to the language of early canonical texts translated from other languages, especially Sanskrit. The phonology implied by Classical Tibetan orthography is very similar to the phonology of Old Tibetan, but the grammar varies greatly depending on period and geographic origin of the author. Such variation is an under-researched topic. In 816 AD, during the reign of King Sadnalegs, literary Tibetan underwent a thorough reform aimed at standardizing the language and vocabulary of the translations being made from Sanskrit, which was one of the main influences for literary standards in what is now called Classical Tibetan. Nouns Structure of the noun phrase Nominalizing suffixes — or and — ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |