 |
Network Science
Network science is an academic field which studies complex networks such as telecommunication networks, computer networks, biological networks, Cognitive network, cognitive and semantic networks, and social networks, considering distinct elements or actors represented by ''nodes'' (or ''vertices'') and the connections between the elements or actors as ''links'' (or ''edges''). The field draws on theories and methods including graph theory from mathematics, statistical mechanics from physics, data mining and information visualization from computer science, inferential statistics, inferential modeling from statistics, and social structure from sociology. The United States National Research Council defines network science as "the study of network representations of physical, biological, and social phenomena leading to predictive models of these phenomena." Background and history The study of networks has emerged in diverse disciplines as a means of analyzing complex relational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
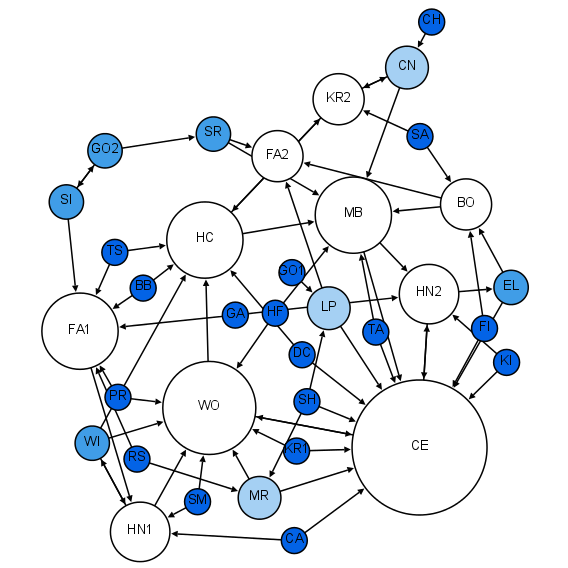
Moreno Sociogram 1st Grade
Moreno may refer to: Places Argentina * Moreno (Buenos Aires Metro), a station on Line C of the Buenos Aires Metro *Moreno, Buenos Aires, a city in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina * Moreno Department, a depatnent of Santiago del Estero Province, Argentina * Moreno Partido, a division of the Buenos Aires Province, Argentina Elsewhere * Moreno, California (other) * Moreno, Pernambuco, Brazil, a city * Moreno Rock, a rock in Antarctica * Point Moreno, a promontory on Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands People with the name Lists of people with the name * Moreno (given name) * Moreno (surname) People with the nickname or professional name * Moreno (footballer, born 1948), Daniel Euclides Moreno, Brazilian football forward * Moreno (Portuguese footballer) (born 1981), Portuguese football defensive midfielder * Moreno (footballerc, born 1983), Moreno Aoas Vidal, Brazilian football leftback * Moreno (Spanish footballer) (born 1986), Spanish football defender * Moreno (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Reka Albert
Reka may refer to: Places * Řeka, a village in the Czech Republic * Reka, Cerkno, a village near Cerkno, Slovenia * Reka, Laško, a village near Laško, Slovenia * Reka (Kladovo), a village near Kladovo, Serbia * Reka, Koprivnica, a village near Koprivnica, Croatia * Slovene name for Rijeka, a city in northwestern Croatia * Reka (region), a region in Macedonia, North Macedonia ** Upper Reka, a subregion in Macedonia, North Macedonia ** , a subregion in Macedonia, North Macedonia * Reka (Metohija), a region in Metohija, Kosovo * Pusta Reka (region), earlier only ''Reka'', a region in Leskovac Valley, Serbia Other uses * Réka, a given name in Hungary * REKA or Reka One, names for Australian street artist James Reka * Reka (river), a river in Slovenia and Italy * Reka dialect, of Macedonian * Reka Devnia hoard, a hoard of Roman silver * The River (1933 film) (Czech: ''Řeka''), a 1933 Czechoslovak film * Upper Reka dialect The Upper Reka Albanian dialect is a member o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Albert-László Barabási
Albert-László Barabási (born March 30, 1967) is a Romanian-born Hungarian-American physicist, renowned for his pioneering discoveries in network science and network medicine. He is a distinguished university professor and Robert Gray Professor of Network Science at Northeastern University, holding additional appointments at the Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School and the Department of Network and Data Science at Central European University. Barabási previously served as the former Emil T. Hofmann Professor of Physics at the University of Notre Dame and was an associate member of the Center of Cancer Systems Biology (CCSB) at the Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard University. In 1999 Barabási discovered the concept of scale-free networks and proposed the Barabási–Albert model, which explains the widespread emergence of such networks in natural, technological and social systems, including the World Wide Web and online communities. Barabási is the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Network Probability Matrix
The network probability matrix describes the probability structure of a network based on the historical presence or absence of edges in a network. For example, individuals in a social network are not connected to other individuals with uniform random probability. The probability structure is much more complex. Intuitively, there are some people whom a person will communicate with or be connected more closely than others. For this reason, real-world networks tend to have clusters or cliques of nodes that are more closely related than others (Albert and Barabasi, 2002, Carley ear In vertebrates, an ear is the organ that enables hearing and (in mammals) body balance using the vestibular system. In humans, the ear is described as having three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear co ... Newmann 2003). This can be simulated by varying the probabilities that certain nodes will communicate. The network probability matrix was originally pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Exponential Random Graph Model
Exponential family random graph models (ERGMs) are a set of statistical models used to study the structure and patterns within networks, such as those in social, organizational, or scientific contexts. They analyze how connections ( edges) form between individuals or entities ( nodes) by modeling the likelihood of network features, like clustering or centrality, across diverse examples including knowledge networks, organizational networks, colleague networks, social media networks, networks of scientific collaboration, and more. Part of the exponential family of distributions, ERGMs help researchers understand and predict network behavior in fields ranging from sociology to data science. Background Many metrics exist to describe the structural features of an observed network such as the density, centrality, or assortativity. However, these metrics describe the observed network which is only one instance of a large number of possible alternative networks. This set of alternative netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Social Networks
A social network is a social structure consisting of a set of social actors (such as individuals or organizations), networks of dyadic ties, and other social interactions between actors. The social network perspective provides a set of methods for analyzing the structure of whole social entities along with a variety of theories explaining the patterns observed in these structures. The study of these structures uses social network analysis to identify local and global patterns, locate influential entities, and examine dynamics of networks. For instance, social network analysis has been used in studying the spread of misinformation on social media platforms or analyzing the influence of key figures in social networks. Social networks and the analysis of them is an inherently interdisciplinary academic field which emerged from social psychology, sociology, statistics, and graph theory. Georg Simmel authored early structural theories in sociology emphasizing the dynamics of tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Random Graphs
In mathematics, random graph is the general term to refer to probability distributions over Graph (discrete mathematics), graphs. Random graphs may be described simply by a probability distribution, or by a random process which generates them. The theory of random graphs lies at the intersection between graph theory and probability theory. From a mathematical perspective, random graphs are used to answer questions about the properties of ''typical'' graphs. Its practical applications are found in all areas in which complex networks need to be modeled – many random graph models are thus known, mirroring the diverse types of complex networks encountered in different areas. In a mathematical context, ''random graph'' refers almost exclusively to the Erdős–Rényi model, Erdős–Rényi random graph model. In other contexts, any graph model may be referred to as a ''random graph''. Models A random graph is obtained by starting with a set of ''n'' isolated vertices and add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Alfréd Rényi
Alfréd Rényi (20 March 1921 – 1 February 1970) was a Hungarian mathematician known for his work in probability theory, though he also made contributions in combinatorics, graph theory, and number theory. Life Rényi was born in Budapest to Artúr Rényi and Borbála Alexander; his father was a mechanical engineer, while his mother was the daughter of philosopher and literary critic Bernhard Alexander; his uncle was Franz Alexander, a Hungarian-American psychoanalyst and physician. He was prevented from enrolling in university in 1939 due to the anti-Jewish laws then in force, but enrolled at the University of Budapest in 1940 and finished his studies in 1944. At this point, he was drafted to forced labour service, from which he managed to escape during transportation of his company. He was in hiding with false documents for six months. Biographers tell an incredible story about Rényi: after half of a year in hiding, he managed to get hold of a soldier's uniform and march ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Paul Erdős
Paul Erdős ( ; 26March 191320September 1996) was a Hungarian mathematician. He was one of the most prolific mathematicians and producers of mathematical conjectures of the 20th century. pursued and proposed problems in discrete mathematics, graph theory, number theory, mathematical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory. Much of his work centered on discrete mathematics, cracking many previously unsolved problems in the field. He championed and contributed to Ramsey theory, which studies the conditions in which order necessarily appears. Overall, his work leaned towards solving previously open problems, rather than developing or exploring new areas of mathematics. Erdős published around 1,500 mathematical papers during his lifetime, a figure that remains unsurpassed. He was known both for his social practice of mathematics, working with more than 500 collaborators, and for his eccentric lifestyle; ''Time'' magazine called him "The Oddball's Oddba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
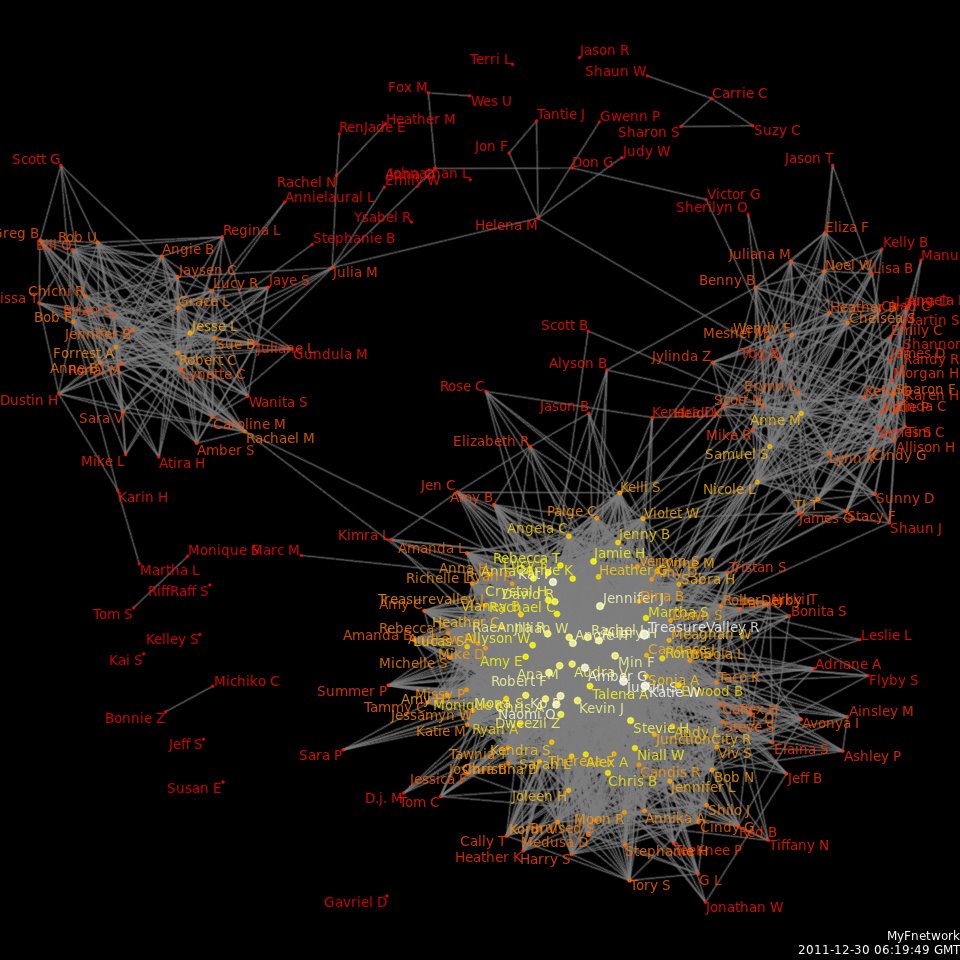 |
Social Network Analysis
Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of ''nodes'' (individual actors, people, or things within the network) and the ''ties'', ''edges'', or ''links'' (relationships or interactions) that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, meme proliferation, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through '' sociograms'' in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of the longest-running newspapers in the United States, the ''Times'' serves as one of the country's Newspaper of record, newspapers of record. , ''The New York Times'' had 9.13 million total and 8.83 million online subscribers, both by significant margins the List of newspapers in the United States, highest numbers for any newspaper in the United States; the total also included 296,330 print subscribers, making the ''Times'' the second-largest newspaper by print circulation in the United States, following ''The Wall Street Journal'', also based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' is published by the New York Times Company; since 1896, the company has been chaired by the Ochs-Sulzberger family, whose current chairman and the paper's publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |