|
Nervii
The Nervii or Nervians were one of the most powerful Belgae, Belgic tribes of northern Gaul at the time of its conquest by Rome. Their territory corresponds to the central part of modern Belgium, including Brussels, and stretched southwards to Cambrai in French Hainaut. During their first century BC Roman military campaign, Julius Caesar's contacts among the Remi stated that the Nervii were the most warlike of the Belgae. In times of war, they were known to trek long distances to take part in battles. Being one of the northerly Belgic tribes, with the Menapii to the west, and the Eburones to their east, they were considered by Caesar to be relatively uncorrupted by civilization. According to Tacitus they claimed List of early Germanic peoples, Germanic descent. According to Strabo they were of Germanic origin. Name They are mentioned as ''Nervii'' by Julius Caesar, Caesar (mid-1st c. BC) and Orosius (early fifth c. AD), ''Neroúioi'' (Νερούιοι) by Strabo (early first c. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menapii
The Menapii were a Belgic tribe dwelling near the North Sea, around present-day Cassel, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. History The Menapii were persistent opponents of Julius Caesar's conquest of Gaul, resisting until 54 BC. They were part of the Belgic confederacy defeated by Caesar in 57 BC, contributing 9,000 men. The following year they sided with the Veneti against Caesar. Caesar was again victorious, but the Menapii and the Morini refused to make peace and continued to fight against him. They withdrew into the forests and swamps and conducted a hit-and-run campaign. Caesar responded by cutting down the forests, seizing their cattle and burning their settlements, but this was interrupted by heavy rain and the onset of winter, and the Menapii and Morini withdrew further into the forests. In 55 BC the Menapii tried to resist a Germanic incursion across the Rhine, but were defeated. Later that year, while Caesar made his first expedition to Britain, he sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eburones
The Eburones ( Greek: ) were a Gaulish- Germanic tribe dwelling in the northeast of Gaul, who lived north of the Ardennes in the region near what is now the southern Netherlands, eastern Belgium and the German Rhineland, in the period immediately preceding the Roman conquest of the region. Though living in Gaul, they were also described as being both Belgae and Germani (for a discussion of these terms, see below). The Eburones played a major role in Julius Caesar's account of his "Gallic Wars", as the most important tribe within the ''Germani cisrhenani'' group of tribes — ''Germani'' living west of the Rhine amongst the Belgae. Caesar claimed that the name of the Eburones was wiped out after their failed revolt against his forces during the Gallic Wars, and that the tribe was largely annihilated. Whether any significant part of the population lived on in the area as Tungri, the tribal name found here later, is uncertain but considered likely. Name Attestations They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
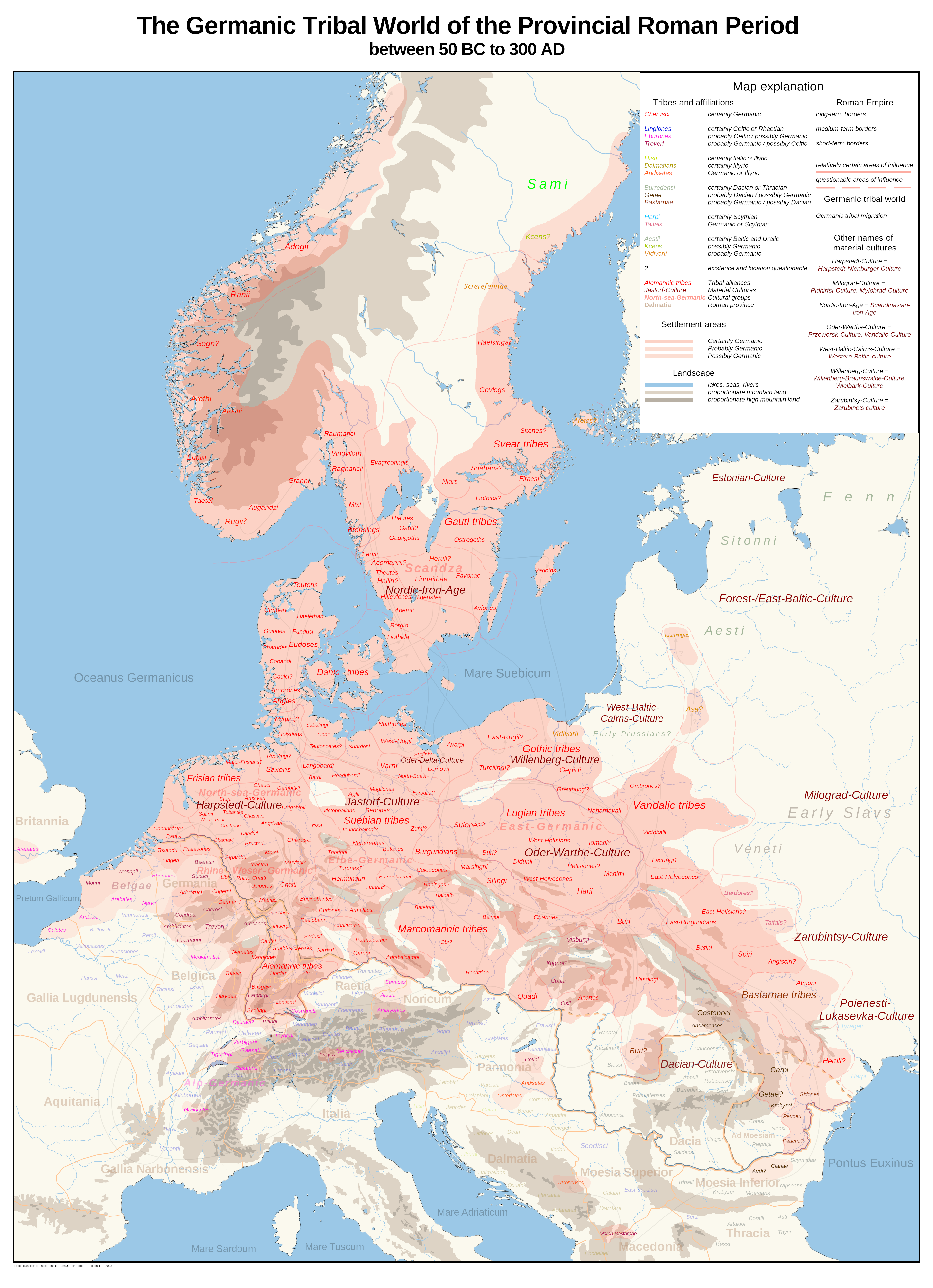
Belgae
The Belgae ( , ) were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Julius Caesar in his Commentarii de Bello Gallico, account of his wars in Gaul. Some peoples in southern Roman Britain, Britain were also called Belgae and had apparently moved from the continent. T. F. O'Rahilly believed that some had moved further west and he equated them with the Fir Bolg in Ireland. The Roman province of Gallia Belgica was named after the continental Belgae. The term continued to be used in the region until the present day and is reflected in the name of the modern country of Belgium. Etymology The consensus among linguists is that the ethnic name ''Belgae'' probably comes from the Proto-Celtic root ''*belg-'' or ''*bolg-'' meaning "to swell (particularly with anger/battle fury/etc.)", cognate with the Dutch language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Early Germanic Peoples
The list of early Germanic peoples is a catalog of ancient Germanic cultures, tribal groups, and other alliances of Germanic tribes and civilizations from antiquity. This information is derived from various ancient historical sources, beginning in the 2nd century BC and extending into late antiquity. By the Early Middle Ages, early forms of kingship had started to shape historical developments across Europe, with the exception of Northern Europe. In Northern Europe, influences from the Vendel Period (c.AD 550- 800) and the subsequent Viking Age (c. AD 800- 1050) played a significant role in the germanic historical context. The associations and locations of the numerous peoples and groups in ancient sources are often subject to heavy uncertainty and speculation, and classifications of ethnicity regarding a common culture or a temporary alliance of heterogeneous groups are disputed. It is uncertain whether certain groups are Germanic in the broader linguistic sense or whether they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; ; ), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,501 inhabitants in 2018. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai with 46,772 inhabitants. Its functional area, a more extensive range, included 94,576 inhabitants in 2018.Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Cambrai (108), Unité urbaine 2020 de Cambrai (59403), Commune de Cambrai (59122) INSEE With |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (, ''Geōgraphiká''; or , "Strabo's 17 Books on Geographical Topics") or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek in the late 1st century BC, or early 1st century AD, and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen of the Roman Empire of Greek descent. There is a fragmentary palimpsest dating to the fifth century. The earliest manuscripts of books 1–9 date to the tenth century, with a 13th-century manuscript containing the entire text. Title of the work Strabo refers to his ''Geography'' within it by several names: * geōgraphia, "description of the earth" * chōrographia, "description of the land" * periēgēsis, "an outline" * periodos gēs, "circuit of the earth" * periodeia tēs chōrās, "circuit of the land" Apart from the "outline", two words recur, "earth" and "country." Something of a theorist, Strabo explains what he means by Geography and Chorography:It is the sea more than anythin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognate
In historical linguistics, cognates or lexical cognates are sets of words that have been inherited in direct descent from an etymological ancestor in a common parent language. Because language change can have radical effects on both the sound and the meaning of a word, cognates may not be obvious, and it often takes rigorous study of historical sources and the application of the comparative method to establish whether lexemes are cognate. Cognates are distinguished from loanwords, where a word has been borrowed from another language. Name The English term ''cognate'' derives from Latin , meaning "blood relative". Examples An example of cognates from the same Indo-European root are: ''night'' ( English), ''Nacht'' ( German), ''nacht'' ( Dutch, Frisian), ''nag'' (Afrikaans), ''Naach'' ( Colognian), ''natt'' ( Swedish, Norwegian), ''nat'' ( Danish), ''nátt'' ( Faroese), ''nótt'' ( Icelandic), ''noc'' ( Czech, Slovak, Polish), ночь, ''noch'' ( Russian), но� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognomen
A ''cognomen'' (; : ''cognomina''; from ''co-'' "together with" and ''(g)nomen'' "name") was the third name of a citizen of ancient Rome, under Roman naming conventions. Initially, it was a nickname, but lost that purpose when it became hereditary. Hereditary ''cognomina'' were used to augment the second name, the ''nomen gentilicium'' (the Surname, family name, or clan name), in order to identify a particular branch within a family or family within a clan. The term has also taken on other contemporary meanings. Roman names Because of the limited nature of the Latin ''praenomen'', the ''cognomen'' developed to distinguish branches of the family from one another, and occasionally, to highlight an individual's achievement, typically in warfare. One example of this is Pompey, Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, whose cognomen ''Magnus'' was earned after his military victories under Sulla's dictatorship. The ''cognomen'' was a form of distinguishing people who accomplished important feats, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerva (other)
Nerva (30–98) was a Roman emperor, reigning 96–98. Nerva may also refer to: Other Roman cognomina * ''Nerva Traianus'', or Trajan (53–117), Roman emperor (reigning 98–117) * Cocceii Nervae, a family of the gens ''Cocceia'' ** Marcus Cocceius Nerva (other), politicians and relatives of emperor Nerva * Licinii Nervae, a family of the gens ''Licinia''. * Quintus Acutius Nerva, Roman consul in AD 100, from the gens '' Acutia'' * Publius Licinius Nerva, Propraetor (Governor) of Sicily whose fecklessness led to the Second Servile War Other uses * Nerva, Huelva, municipality in Huelva province, Spain * Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application (NERVA), part of a NASA project to produce a nuclear thermal rocket engine * Nerva, a character in the American science fiction action film ''Ultraviolet'' (2006) * Space Station Nerva, a fictional space station from the ''Doctor Who'' serial episode arcs "The Ark in Space" (1975; S12E05-08) and "Revenge of the Cybermen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagi Of The Nervians , a type ...
Pagi may refer to: People * Antoine Pagi (1624–1699), French ecclesiastical historian * François Pagi (1654–1721), French Franciscan historian of the Catholic Church * Mickaël Pagis (born 1973), French footballer * Ranchordas Pagi (1901–2013), Indian Army scout Other uses * ''pagi'', plural of ''pagus'', a Roman administrative term designating a rural subdivision of a tribal territory * Pagi language, spoken in Papua New Guinea * Pagi (title), a title used by the Koli caste in Gujarat * , a 1940s Israeli ideological and political movement See also * Pagoi, a village in Corfu * Buntot Pagi, or stingray tail, a type of Filipino whiplike weapon * '' Nuansa Pagi'', an Indonesian TV newscast * Pasar pagi ''Pasar pagi'' (Malay language, Malay/Indonesian language, Indonesian, lit.: 'morning market') is a type of traditional Market (place), market found in Indonesia and Malaysia, sometimes classified as a wet market. Operating hours ''Pasar pagi'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |