|
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Nanotechnology
Because of the ongoing controversy on the implications of nanotechnology, there is significant debate concerning whether nanotechnology or nanotechnology-based List of nanotechnology applications, products merit special government regulation. This mainly relates to when to assess new substances prior to their release into the market, community and environment. Nanotechnology refers to an increasing number of commercially available products – from socks and trousers to tennis racquets and cleaning cloths. Such nanotechnologies and their accompanying industries have triggered calls for increased community participation and effective regulatory arrangements. However, these calls have presently not led to such comprehensive regulation to oversee research and the commercial application of nanotechnologies, or any comprehensive labeling for products that contain nanoparticles or are derived from nano-processes. Regulatory bodies such as the United States Environmental Protection Age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Nanotechnology
Molecular nanotechnology (MNT) is a technology based on the ability to build structures to complex, atomic specifications by means of mechanosynthesis. This is distinct from nanoscale materials. Based on Richard Feynman's vision of miniature factories using nanomachines to build complex products ( including additional nanomachines), this advanced form of nanotechnology (or ''molecular manufacturing'') would make use of positionally-controlled mechanosynthesis guided by molecular machine systems. MNT would involve combining physical principles demonstrated by biophysics, chemistry, other nanotechnologies, and the molecular machinery of life, with the systems engineering principles found in modern macroscale factories. Introduction While conventional chemistry uses inexact processes obtaining inexact results, and biology exploits inexact processes to obtain definitive results, molecular nanotechnology would employ original definitive processes to obtain definitive resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomedicine
Nanomedicine is the medical application of nanotechnology, translating historic nanoscience insights and inventions into practical application. Nanomedicine ranges from the medical applications of nanomaterials and biological devices, to nanoelectronic biosensors, and even possible future applications of molecular nanotechnology such as biological machines. Current problems for nanomedicine involve understanding the issues related to toxicity and environmental impact of nanoscale materials (materials whose structure is on the scale of nanometers, i.e. billionths of a meter). Functionalities can be added to nanomaterials by interfacing them with biological molecules or structures. The size of nanomaterials is similar to that of most biological molecules and structures; therefore, nanomaterials can be useful for both in vivo and in vitro biomedical research and applications. Thus far, the integration of nanomaterials with biology has led to the development of diagnostic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology In Agriculture
Research has shown nanoparticles to be a groundbreaking tool for tackling many arising global issues, the agricultural industry being no exception. In general, a nanoparticle is defined as any particle where one characteristic dimension is 100 nm or less. Because of their unique size, these particles begin to exhibit properties that their larger counterparts may not. Due to their scale, quantum mechanical interactions become more important than classic mechanical forces, allowing for the prevalence of unique physical and chemical properties due to their extremely high surface-to-body ratio. Properties such as cation exchange capacity, enhanced diffusion, ion adsorption, and complexation are enhanced when operating at nanoscale.Currall SC, King EB, Lane N, Madera J, Turner S. What drives public acceptance of nanotechnology? Nat Nanotechnol. 2006;1:153–155. This is primarily the consequence of a high proportion of atoms being present on the surface, with an increased proportion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nanotechnology Applications
The applications of nanotechnology, commonly incorporate industrial, medicinal, and energy uses. These include more durable construction materials, therapeutic drug delivery, and higher density hydrogen fuel cells that are environmentally friendly. Being that nanoparticles and nanodevices are highly versatile through modification of their physiochemical properties, they have found uses in nanoscale electronics, cancer treatments, vaccines, hydrogen fuel cells, and nanographene batteries. Nanotechnology's use of smaller sized materials allows for adjustment of molecules and substances at the nanoscale level, which can further enhance the mechanical properties of materials or grant access to less physically accessible areas of the body. Health applications Nanobiotechnology The terms nanobiotechnology and bionanotechnology refer to the combination of ideas, techniques, and sciences of biology and nanotechnology. More specifically, nanobiotechnology refers to the application of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
There's Plenty Of Room At The Bottom
"There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom: An Invitation to Enter a New Field of Physics" was a lecture given by physicist Richard Feynman at the annual American Physical Society meeting at Caltech on December 29, 1959. Feynman considered the possibility of direct manipulation of individual atoms as a more robust form of synthetic chemistry than those used at the time. Versions of the talk were reprinted in a few popular magazines, but it went largely unnoticed until the 1980s. The title references the popular quote ''"There is always room at the top."'' attributed to Daniel Webster (who is thought to have said this phrase in response to warnings against becoming a lawyer, which was seen as an oversaturated field in the 19th century). Conception Feynman considered some ramifications of a general ability to manipulate matter on an atomic scale. He was particularly interested in the possibilities of denser computer circuitry and microscopes that could see things much smaller than is po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grey Goo
Gray goo (also spelled as grey goo) is a hypothetical global catastrophic scenario involving molecular nanotechnology in which out-of-control self-replicating machines consume all biomass (and perhaps also everything else) on Earth while building many more of themselves, a scenario that has been called '' ecophagy'' . The original idea assumed machines were designed to have this capability, while popularizations have assumed that machines might somehow gain this capability by accident. Self-replicating machines of the macroscopic variety were originally described by mathematician John von Neumann, and are sometimes referred to as von Neumann machines or clanking replicators. The term ''gray goo'' was coined by nanotechnology pioneer K. Eric Drexler in his 1986 book '' Engines of Creation''. In 2004, he stated "I wish I had never used the term 'gray goo'." ''Engines of Creation'' mentions "gray goo" as a thought experiment in two paragraphs and a note, while the popularized i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
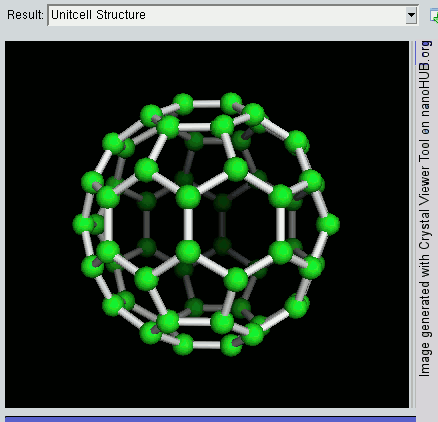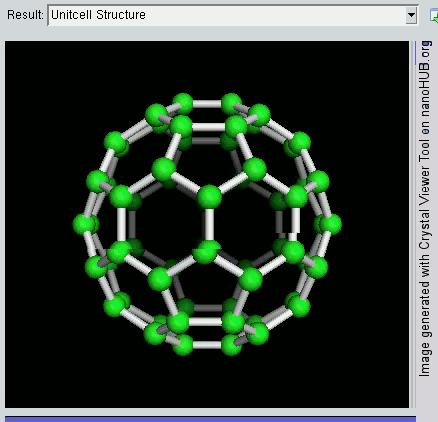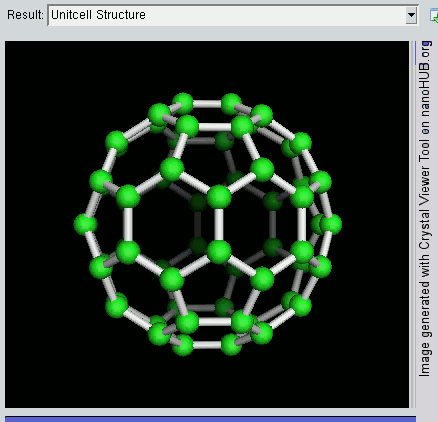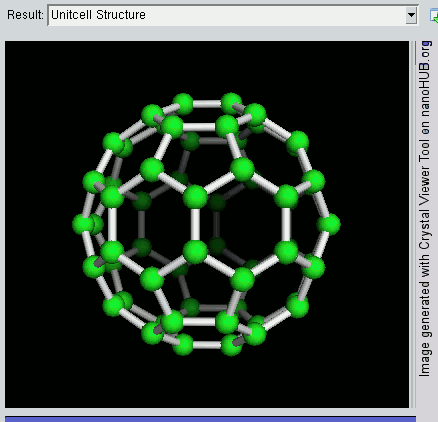
Nanomaterial
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale). Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology, leveraging advances in materials metrology and synthesis which have been developed in support of microfabrication research. Materials with structure at the nanoscale often have unique optical, electronic, thermo-physical or mechanical properties. Nanomaterials are slowly becoming commercialized and beginning to emerge as commodities. Definition In ISO/TS 80004, ''nanomaterial'' is defined as the "material with any external dimension in the nanoscale or having internal structure or surface structure in the nanoscale", with ''nanoscale'' defined as the "length range approximately from 1 nm to 100 nm". This includes both ''nano-objects'', which are discrete pieces of material, and ''nanostructur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotoxicology
Nanotoxicology is the study of the toxicity of nanomaterials. Because of quantum size effects and large surface area to volume ratio, nanomaterials have unique properties compared with their larger counterparts that affect their toxicity. Of the possible hazards, inhalation exposure appears to present the most concern, with animal studies showing pulmonary effects such as inflammation, fibrosis, and carcinogenicity for some nanomaterials. Skin contact and ingestion exposure are also a concern. Background Nanomaterials have at least one primary dimension of less than 100 nanometers, and often have properties different from those of their bulk components that are technologically useful. Because nanotechnology is a recent development, the health and safety effects of exposures to nanomaterials, and what levels of exposure may be acceptable, is not yet fully understood. Nanoparticles can be divided into combustion-derived nanoparticles (like diesel soot), manufactured nanopa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Self-assembly
In chemistry and materials science, molecular self-assembly is the process by which molecules adopt a defined arrangement without guidance or management from an outside source. There are two types of self-assembly: intermolecular and intramolecular. Commonly, the term ''molecular self-assembly'' refers to the former, while the latter is more commonly called '' folding''. Supramolecular systems Molecular self-assembly is a key concept in supramolecular chemistry. This is because assembly of molecules in such systems is directed through non-covalent interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonding, metal coordination, hydrophobic forces, van der Waals forces, pi-stacking interactions, and/or electrostatic) as well as electromagnetic interactions. Common examples include the formation of colloids, biomolecular condensates, micelles, vesicles, liquid crystal phases, and Langmuir monolayers by surfactant molecules. Further examples of supramolecular assemblies demonstrate that a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Feynman
Richard Phillips Feynman (; May 11, 1918 – February 15, 1988) was an American theoretical physicist. He is best known for his work in the path integral formulation of quantum mechanics, the theory of quantum electrodynamics, the physics of the superfluidity of supercooled liquid helium, and in particle physics, for which he proposed the parton model. For his contributions to the development of quantum electrodynamics, Feynman received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1965 jointly with Julian Schwinger and Shin'ichirō Tomonaga. Feynman developed a pictorial representation scheme for the mathematical expressions describing the behavior of subatomic particles, which later became known as Feynman diagrams and is widely used. During his lifetime, Feynman became one of the best-known scientists in the world. In a 1999 poll of 130 leading physicists worldwide by the British journal ''Physics World'', he was ranked the seventh-greatest physicist of all time. He assisted in the Manhatt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |