|
Namibian Savanna Woodlands
The Namibian savanna woodlands, also known as the Namib escarpment woodlands, are the deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Namibia and Angola. Geography They extend north and south from southwestern Angola to central Namibia, east of the coastal Namib Desert. The woodlands cover the Namib escarpment, which rises from the low-lying Namib coastal plain to the Southern African plateau on the east. Baynes (2038 m), Erongo (2319 m), Naukluft (1974 m), Spitzkoppe (1759 m), and Gamsberg (2347 m) mountains lie along the edge of the escarpment. Brandberg Mountain (2,573 m) lies west of the escarpment in the Namib Desert, and is included in the ecoregion.Burgess, Neil, Jennifer D'Amico Hales, Emma Underwood, et al. (2004). ''Terrestrial Ecoregions of Africa and Madagascar: A Conservation Assessment''. World Wildlife Fund. Island Press, 2004. To the northeast lie more humid woodland and savanna ecoregions – the Angolan miombo woodlands at the furthest northern end, and the Angolan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Erongo
Mount Erongo (21º37'S 15º40'E) is a mountain of 2,350 metres northeast of Swakopmund in Erongo Region, Namibia. Like the Brandberg Mountain it is a granitic intrusion. It is the only place on Earth that '' Versicorpus erongoensis'', a dung beetle species, occurs. References Geography of Erongo Region Erongo Erongo is one of the 14 regions of Namibia. The capital is Swakopmund. It is named after Mount Erongo, a well-known landmark in Namibia and in this area. Erongo contains the municipalities of Walvis Bay, Swakopmund, Henties Bay and Omaruru, as ... Namibian savanna woodlands {{Namibia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brandberg Mountain
The Brandberg ( Damara: ; ) is Namibia's highest mountain. Location and extent Brandberg Mountain is located in former Damaraland, now Erongo, in the northwestern Namib Desert, near the coast, and covers an area of approximately 650 km2.landsat.usgs.gov With its highest point, the Königstein ( for 'King's Stone'), standing at above and located on the flat gravel plains, on a clear day the Brandberg can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-faced Impala
The impala or rooibok (''Aepyceros melampus'', lit. 'black-footed high-horn' in Ancient Greek) is a medium-sized antelope found in eastern and southern Africa. The only extant member of the genus '' Aepyceros'', and tribe Aepycerotini, it was first described to Europeans by German zoologist Hinrich Lichtenstein in 1812. Two subspecies are recognised—the grassland-dwelling common impala (sometimes referred to as the Kenyan impala), and the larger and darker black-faced impala, which lives in slightly more arid, scrubland environments. The impala reaches at the shoulder and weighs . It features a glossy, reddish brown coat. The male's slender, lyre-shaped horns are long. Active mainly during the day, the impala may be gregarious or territorial depending upon the climate and geography. Three distinct social groups can be observed: the territorial males, bachelor herds and female herds. The impala is known for two characteristic leaps that constitute an anti-predator str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemsbok
The gemsbok (''Oryx gazella''), or South African oryx, is a large antelope in the genus '' Oryx''. It is endemic to the dry and barren regions of Botswana, Namibia, South Africa and (parts of) Zimbabwe, mainly inhabiting the Kalahari and Namib Deserts, areas in which it is supremely adapted for survival. Previously, some sources classified the related East African oryx, or beisa oryx (''Oryx beisa''), as a subspecies. Name The name ''gemsbok'' is from Afrikaans, which itself is from the Dutch word of the same spelling, meaning "male chamois", composed of (“chamois”) + (“buck, male goat”). The Dutch is further from German ("chamois"). Although some superficial similarities in appearance (especially in the facial pattern) are noticed, the chamois and the oryx are not closely related. The usual pronunciation in English is . Description Gemsbok are light taupe to tan in color, with lighter patches toward the bottom rear of the rump. Their tails are long and black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
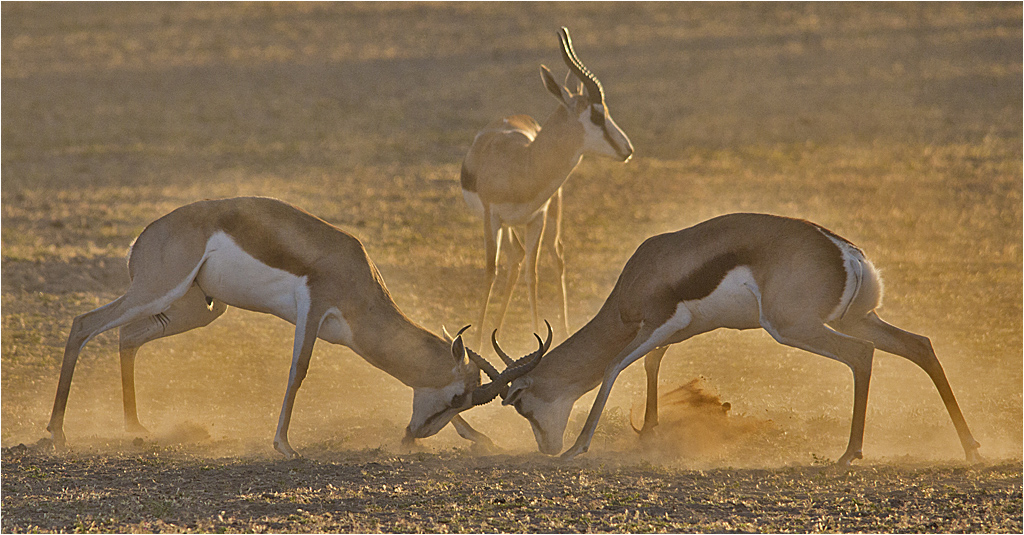
Springbok
The springbok or springbuck (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is an antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus (biology), genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first Species description, described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm von Zimmermann in 1780. Three subspecies are identified. A slender, long-legged antelope, the springbok reaches at the shoulder and weighs between . Both sexes have a pair of black, long horn (anatomy), horns that curve backwards. The springbok is characterised by a white face, a dark stripe running from the eyes to the mouth, a light brown coat (animal), coat marked by a reddish-brown stripe that runs from the upper foreleg to the buttocks across the flanks like the Thomson's gazelle, and a white Rump (animal), rump flap. Active mainly at dawn and dusk, springbok form harem (zoology), harems (mixed-sex herds). In earlier times, springbok of the Kalahari Desert and Karoo migrated in large numbers acros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Kudu
The greater kudu (''Tragelaphus strepsiceros'') is a large woodland antelope, found throughout East Africa, eastern and southern Africa. Despite occupying such widespread territory (animal), territory, they are sparsely populated in most areas due to declining habitat, deforestation, and poaching. The greater kudu is one of two species commonly known as kudu, the other being the lesser kudu, ''T. imberbis''. Etymology Kudu ( ), or koodoo, is the Khoikhoi name for this antelope. ''Trag-'' (Greek) denotes a goat and ''elaphos'' (Greek) a deer. ''Strepho'' (Greek) means 'twist', and ''strepsis'' is 'twisting'. ''Keras'' (Greek) refers to the horn of the animal. Physical characteristics Greater kudus have a narrow Anatomy, body with long legs, and their coat (animal), coats can range from brown/bluish grey to reddish brown. They possess between 4 and 12 vertical white stripes along their torso. The head tends to be darker in colour than the rest of the body, and exhibits a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
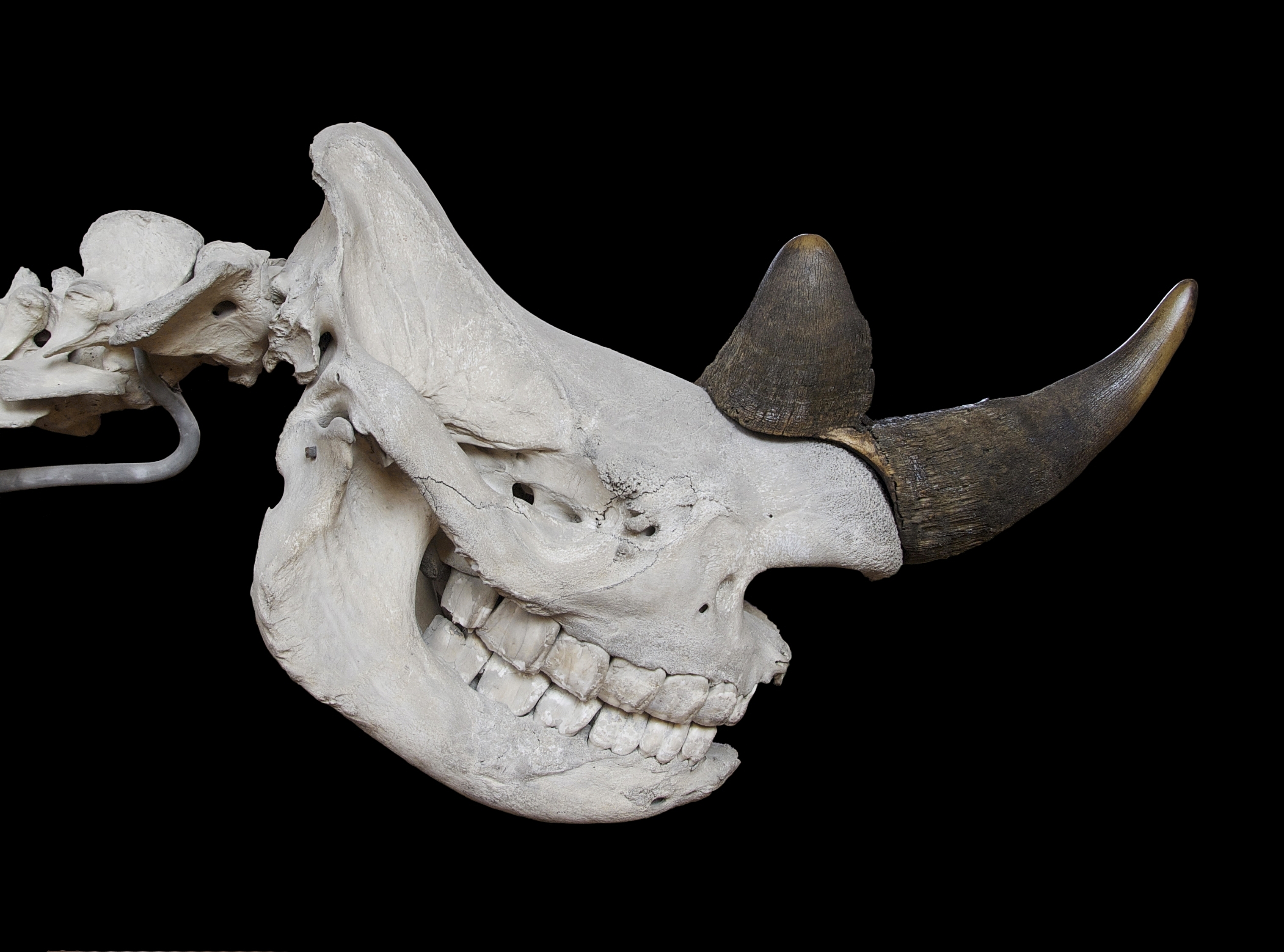
Black Rhinoceros
The black rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis''), also called the black rhino or the hooked-lip rhinoceros, is a species of rhinoceros native to East Africa, East and Southern Africa, including Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the species is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. It is the only extant species of the genus ''Diceros''. The other rhinoceros native to Africa is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' (Dutch language, Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Bush Elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), also known as the African savanna elephant, is a species of elephant native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of three extant elephant species and, along with the African forest elephant, one of two extant species of African elephant. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with fully grown bulls reaching an average shoulder height of and a body mass of ; the largest recorded specimen had a shoulder height of and an estimated body mass of . The African bush elephant is characterised by its long prehensile trunk with two finger-like processes; a convex back; large ears which help reduce body heat; and sturdy tusks that are noticeably curved. The skin is grey with scanty hairs, and bending cracks which support thermoregulation by retaining water. The African bush elephant inhabits a variety of habitats such as forests, grasslands, woodlands, wetlands and agricultural land. It is a mixed herbivore feeding mostly on grasse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesamothamnus Guerichii
''Sesamothamnus'' is a genus of plant in the family Pedaliaceae. The genus is found from Ethiopia to South Africa. Taxonomy ''Sesamothamnus'' was first named and described in 1869 by Friedrich Welwitsch. Species As of June 2024, Plants of the World Online Plants of the World Online (POWO) is an online taxonomic database published by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. History Following the Convention on Biological Diversity, the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew launched Plants of the World Online i ... accepts six species for this genus: *'' Sesamothamnus benguellensis'' Welw. *'' Sesamothamnus busseanus'' Engl. *'' Sesamothamnus guerichii'' (Engl.) E.A.Bruce *'' Sesamothamnus leistnari'' P.Craven ex Swanepoel & A.E.van Wyk *'' Sesamothamnus lugardii'' N.E.Br. *'' Sesamothamnus rivae'' Engl. References Lamiales genera Pedaliaceae Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Lamiales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |