|
Modernist Architecture
Modern architecture, also called modernist architecture, or the modern movement, is an architectural architectural movement, movement and architectural style, style that was prominent in the 20th century, between the earlier Art Deco Architecture, Art Deco and later Postmodern architecture, postmodern movements. Modern architecture was based upon new and innovative technologies of construction (particularly the use of glass, steel, and concrete); the principle Functionalism (architecture), functionalism (i.e. that Form follows function, form should follow function); an embrace of minimalism; and a rejection of Ornament (art), ornament. According to Le Corbusier, the roots of the movement were to be found in the works of Eugène Viollet-le-Duc, while Mies van der Rohe was heavily inspired by Karl Friedrich Schinkel. The movement emerged in the first half of the 20th century and became dominant after World War II until the 1980s, when it was gradually replaced as the principal sty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villa Savoye
Villa Savoye () is a Modern architecture, modernist villa and gatelodge in Poissy, on the outskirts of Paris, France. It was designed by the Swiss-French architect Le Corbusier and his cousin Pierre Jeanneret, and built between 1928 and 1931 using reinforced concrete.Courland, Robert. ''Concrete Planet''. Prometheus Books, Amherst, NY. (2012) page 326. As an exemplar of Le Corbusier's "Le Corbusier's Five Points of Architecture, five points" for new constructions, the villa is representative of the origins of modern architecture and is one of the most easily recognizable and renowned examples of the International style (architecture), International style. The house was originally built as a country retreat for the Savoye family. After being purchased by the neighbouring school, it became the property of the Republic of France, French state in 1958. Due to many different problems it was rarely inhabited. After surviving several proposals to demolish it, it was designated as an of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architectural Style
An architectural style is a classification of buildings (and nonbuilding structures) based on a set of characteristics and features, including overall appearance, arrangement of the components, method of construction, building materials used, form (architecture), form, size, structural design, and regional character. Architectural styles are frequently associated with a historical epoch (Renaissance style), geographical location (Italian Villa style), or an earlier architectural style (Neo-Gothic style), and are influenced by the corresponding broader Style (visual arts), artistic style and the "general human condition". Heinrich Wölfflin even declared an analogy between a building and a costume: an "architectural style reflects the ''attitude and the movement of people'' in the period concerned". The 21st century construction uses a multitude of styles that are sometimes lumped together as a "contemporary architecture" based on the common trait of extreme reliance on computer-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Friedrich Schinkel
Karl Friedrich Schinkel (13 March 1781 – 9 October 1841) was a Prussian architect, urban planning, city planner and painter who also designed furniture and stage sets. Schinkel was one of the most prominent architects of Germany and designed both Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical and Gothic revival architecture, neo-Gothic buildings. His most famous buildings are found in and around Berlin. Schinkel's Bauakademie is considered one of the forerunners of modern architecture. Biography Schinkel was born in Neuruppin, Margraviate of Brandenburg. When he was six, his father died in the disastrous Neuruppin fire of 1787. He became a student of architect Friedrich Gilly (1772–1800) (the two became close friends) and his father, David Gilly, in Berlin. At that time, the architectural taste in Prussia was shaped in Neoclassical style, mainly by Carl Gotthard Langhans, the architect of the Brandenburg Gate in Berlin. After returning to Berlin from his first trip to Italy in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mies Van Der Rohe
Ludwig Mies van der Rohe ( ; ; born Maria Ludwig Michael Mies; March 27, 1886August 17, 1969) was a German-American architect, academic, and interior designer. He was commonly referred to as Mies, his surname. He is regarded as one of the pioneers of modern architecture. In the 1930s, Mies was the last director of the Bauhaus, a ground-breaking school of modernist art, design and architecture. After Nazism's rise to power, with its strong opposition to modernism, Mies emigrated to the United States. He accepted the position to head the architecture school at what is today the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT). Mies sought to establish his own particular architectural style that could represent modern times. His buildings made use of modern materials such as industrial steel and plate glass to define interior spaces. He is often associated with his fondness for the aphorisms " less is more" and " God is in the details". Early career Mies was born March 27, 1886, in Aache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc (; 27 January 181417 September 1879) was a French architect and author, famous for his restoration of the most prominent medieval landmarks in France. His major restoration projects included Notre-Dame de Paris, the Basilica of Saint Denis, Mont Saint-Michel, Sainte-Chapelle, the medieval walls of the city of Carcassonne, and Roquetaillade castle in the Bordeaux region. His writings on decoration and on the relationship between form and function in architecture had a fundamental influence on a whole new generation of architects, including all the major Art Nouveau artists: Antoni Gaudí, Victor Horta, Hector Guimard, Henry van de Velde, Henri Sauvage and the École de Nancy, Paul Hankar, Otto Wagner, Eugène Grasset, Émile Gallé, and Hendrik Petrus Berlage. He also influenced the first modern architects, Frank Lloyd Wright, Ludwig Mies van der Rohe, Mies van der Rohe, Auguste Perret, Louis Sullivan, and Le Corbusier, who considered Viollet-le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornament (art)
In architecture and decorative art, ornament is decoration used to embellish parts of a building or object. Large figurative elements such as monumental sculpture and their equivalents in decorative art are excluded from the term; most ornaments do not include human figures, and if present they are small compared to the overall scale. Architectural ornament can be carved from stone, wood or precious metals, formed with plaster or clay, or painted or impressed onto a surface as applied ornament; in other applied arts the main material of the object, or a different one such as paint or vitreous enamel may be used. A wide variety of decorative styles and Motif (visual arts), motifs have been developed for architecture and the applied arts, including pottery, furniture, metalwork. In textiles, wallpaper and other objects where the decoration may be the main justification for its existence, the terms pattern or design are more likely to be used. The vast range of motifs used in orna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimalism
In visual arts, music, and other media, minimalism is an art movement that began in the post-war era in western art. The movement is often interpreted as a reaction to abstract expressionism and modernism; it anticipated contemporary post-minimal art practices, which extend or reflect on minimalism's original objectives. Minimalism's key objectives were to strip away conventional characterizations of art by bringing the importance of the object or the experience a viewer has for the object with minimal mediation from the artist. Prominent artists associated with minimalism include Donald Judd, Agnes Martin, Dan Flavin, Carl Andre, Robert Morris, Anne Truitt, and Frank Stella. Minimalism in music often features repetition and gradual variation, such as the works of La Monte Young, Terry Riley, Steve Reich, Philip Glass, Julius Eastman, and John Adams. The term has also been used to describe the plays and novels of Samuel Beckett, the films of Robert Bresson, the stori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Follows Function
Form follows function is a principle of design associated with late 19th- and early 20th-century architecture and industrial design in general, which states that the appearance and structure of a building or object ( architectural form) should primarily relate to its intended function or purpose. Origins of the phrase The architect Louis Sullivan coined the maxim, which encapsulates Viollet-le-Duc's theories: "a rationally designed structure may not necessarily be beautiful but no building can be beautiful that does not have a rationally designed structure". Sullivan also credited his friend and mentor, John H. Edelmann, who theorized the concept of "suppressed function" with inspiration for this maxim. The maxim is often incorrectly attributed to the sculptor Horatio Greenough (1805–1852), whose thinking mostly predates the later functionalist approach to architecture. Greenough's writings were for a long time largely forgotten, and were rediscovered only in the 1930s. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functionalism (architecture)
In architecture, functionalism is the principle that buildings should be designed based solely on their purpose and function. An international functionalist architecture movement emerged in the wake of World War I, as part of the wave of Modernism. Its ideas were largely inspired by a desire to build a new and better world for the people, as broadly and strongly expressed by the social and political movements of Europe after the extremely devastating world war. In this respect, functionalist architecture is often linked with the ideas of socialism and modern humanism. A new slight addition to this new wave of architecture was that not only should buildings and houses be designed around the purpose of functionality, architecture should also be used as a means to physically create a better world and a better life for people in the broadest sense. This new functionalist architecture had the strongest impact in Czechoslovakia, Germany, Poland, the USSR and the Netherlands, and from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
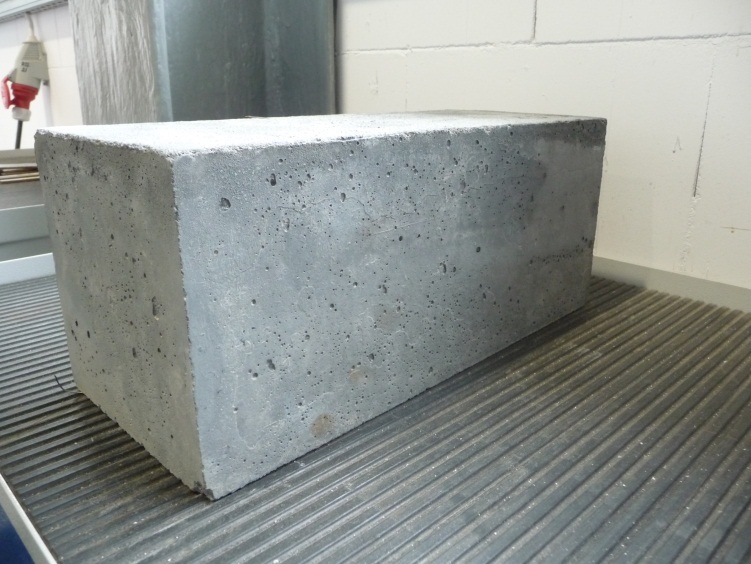
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactured material in the world. When aggregate is mixed with dry Portland cement and water, the mixture forms a fluid slurry that can be poured and molded into shape. The cement reacts with the water through a process called hydration, which hardens it after several hours to form a solid matrix that binds the materials together into a durable stone-like material with various uses. This time allows concrete to not only be cast in forms, but also to have a variety of tooled processes performed. The hydration process is exothermic, which means that ambient temperature plays a significant role in how long it takes concrete to set. Often, additives (such as pozzolans or superplasticizers) are included in the mixture to improve the physical prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength and low raw material cost, steel is one of the most commonly manufactured materials in the world. Steel is used in structures (as concrete Rebar, reinforcing rods), in Bridge, bridges, infrastructure, Tool, tools, Ship, ships, Train, trains, Car, cars, Bicycle, bicycles, Machine, machines, Home appliance, electrical appliances, furniture, and Weapon, weapons. Iron is always the main element in steel, but other elements are used to produce various grades of steel demonstrating altered material, mechanical, and microstructural properties. Stainless steels, for example, typically contain 18% chromium and exhibit improved corrosion and Redox, oxidation resistance versus its carbon steel counterpart. Under atmospheric pressures, steels generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |