|
Modern Synthesis (20th Century)
The modern synthesis was the early 20th-century synthesis of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution and Gregor Mendel's ideas on Mendelian inheritance, heredity into a joint mathematical framework. Julian Huxley coined the term in his 1942 book, ''Evolution: The Modern Synthesis''. The synthesis combined the ideas of natural selection, Mendelian inheritance, Mendelian genetics, and population genetics. It also related the broad-scale macroevolution seen by paleontology, palaeontologists to the small-scale microevolution of local population, populations. The synthesis was defined differently by its founders, with Ernst Mayr in 1959, G. Ledyard Stebbins in 1966, and Theodosius Dobzhansky in 1974 offering differing basic postulates, though they all include natural selection, working on heritable variation supplied by mutation. Other major figures in the synthesis included E. B. Ford, Bernhard Rensch, Ivan Schmalhausen, and George Gaylord Simpson. An early event in the modern synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modern Synthesis , the term coined by George John Romanes in 1895 to refer to a revision of Charles Darwin's theory first formulated in 1859.
{{SIA ...
Modern synthesis or modern evolutionary synthesis refers to several perspectives on evolutionary biology, namely: * Modern synthesis (20th century), the term coined by Julian Huxley in 1942 to denote the synthesis between Mendelian genetics and selection theory. * Neo-Darwinism Neo-Darwinism is generally used to describe any integration of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection with Gregor Mendel's theory of genetics. It mostly refers to evolutionary theory from either 1895 (for the combinations of D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gaylord Simpson
George Gaylord Simpson (June 16, 1902 – October 6, 1984) was an American paleontologist. Simpson was perhaps the most influential paleontologist of the twentieth century, and a major participant in the modern synthesis, contributing '' Tempo and Mode in Evolution'' (1944), ''The Meaning of Evolution'' (1949) and ''The Major Features of Evolution'' (1953). He was an expert on extinct mammals and their intercontinental migrations. Simpson was extraordinarily knowledgeable about Mesozoic fossil mammals and fossil mammals of North and South America. He anticipated such concepts as punctuated equilibrium (in ''Tempo and Mode'') and dispelled the myth that the evolution of the horse was a linear process culminating in the modern '' Equus caballus''. He coined the word '' hypodigm'' in 1940, and published extensively on the taxonomy of fossil and extant mammals. Simpson was influentially, and incorrectly, opposed to Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift, but accepted the th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tree Of Life (biology)
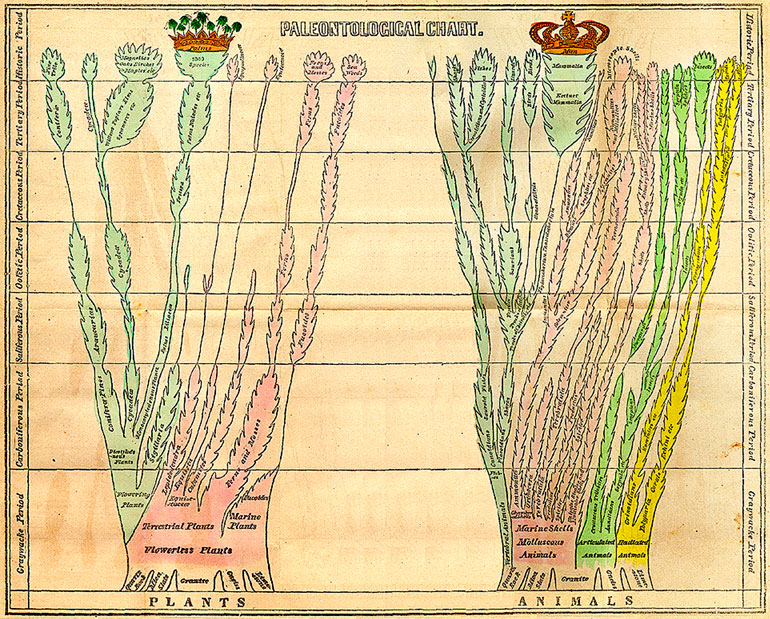
The tree of life or universal tree of life is a metaphor, conceptual model, and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct, as described in a famous passage in Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Tree diagrams originated in the Middle Ages, medieval era to represent family tree, genealogical relationships. Phylogenetic tree diagrams in the evolutionary sense date back to the mid-nineteenth century. The term phylogeny for the evolutionary relationships of species through time was coined by Ernst Haeckel, who went further than Charles Darwin, Darwin in proposing Phylogenetics, phylogenic histories of life. In contemporary usage, ''tree of life'' refers to the compilation of comprehensive phylogenetic databases rooted at the last universal common ancestor of life on Earth. Two public databases for the tree of life are ''TimeTree'', for phylogeny and divergence times, and the ''Ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryote
A prokaryote (; less commonly spelled procaryote) is a unicellular organism, single-celled organism whose cell (biology), cell lacks a cell nucleus, nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'before', and (), meaning 'nut' or 'kernel'. In the earlier two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. However, in the three-domain system, based upon molecular phylogenetics, prokaryotes are divided into two domain (biology), domains: Bacteria and Archaea. A third domain, Eukaryote, Eukaryota, consists of organisms with nuclei. Prokaryotes evolution, evolved before eukaryotes, and lack nuclei, mitochondria, and most of the other distinct organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. Some unicellular prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, form colony (biology), colonies held together by biofilms, and large colonies can create multilayered microbial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is a branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecule, molecular basis of biological activity in and between Cell (biology), cells, including biomolecule, biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. Though cells and other microscopic structures had been observed in living organisms as early as the 18th century, a detailed understanding of the mechanisms and interactions governing their behavior did not emerge until the 20th century, when technologies used in physics and chemistry had advanced sufficiently to permit their application in the biological sciences. The term 'molecular biology' was first used in 1945 by the English physicist William Astbury, who described it as an approach focused on discerning the underpinnings of biological phenomena—i.e. uncovering the physical and chemical structures and properties of biological molecules, as well as their interactions with other molecules and how these interactions explain observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Koonin
Eugene Viktorovich Koonin (Russian: Евге́ний Ви́кторович Ку́нин; born October 26, 1956) is a Russian-American biologist and Senior Investigator at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). He is a recognised expert in the field of evolutionary and computational biology. Education Koonin gained a Master of Science in 1978 and a PhD in 1983 in molecular biology, both from the Department of Biology at Moscow State University. His PhD thesis, titled "Multienzyme organization of encephalomyocarditis virus replication complexes", was supervised by Vadim I. Agol. Research From 1985 until 1991, Koonin worked as a research scientist in computational biology in the Institutes of Poliomyelitis and Microbiology at the USSR Academy of Medical Sciences, studying virus biochemistry and bacterial genetics. In 1991, Koonin moved to the NCBI, where he has held a Senior Investigator position since 1996. Koonin's principal research goals include the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Evolutionary Synthesis
The Extended Evolutionary Synthesis (EES) consists of a set of theoretical concepts argued to be more comprehensive than the earlier modern synthesis of evolutionary biology that took place between 1918 and 1942. The extended evolutionary synthesis was called for in the 1950s by C. H. Waddington, argued for on the basis of punctuated equilibrium by Stephen Jay Gould and Niles Eldredge in the 1980s, and was reconceptualized in 2007 by Massimo Pigliucci and Gerd B. Müller. The extended evolutionary synthesis revisits the relative importance of different factors at play, examining several assumptions of the earlier synthesis, and augmenting it with additional causative factors. It includes multilevel selection, transgenerational epigenetic inheritance, niche construction, evolvability, and several concepts from evolutionary developmental biology. Not all biologists have agreed on the need for, or the scope of, an extended synthesis. Many have collaborated on another synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerd B
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper gastrointestinal disease in which stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia, heartburn, odynophagia, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma. In the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus may arise. Risk factors include obesity, pregnancy, smoking, hiatal hernia, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepines, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, and certain asthma medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter, which is at the junction between the stomach and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massimo Pigliucci
Massimo Pigliucci (; born January 16, 1964) is an American philosopher and biologist who is professor of philosophy at the City College of New York, former co-host of the '' Rationally Speaking Podcast'', and former editor in chief for the online magazine ''Scientia Salon''. He is a critic of pseudoscience (including creationism), and an advocate for secularism and science education. His recent work has focused on stoicism. Biography Pigliucci was born in Monrovia, Liberia and raised in Rome. He has a doctorate in genetics from the University of Ferrara, a PhD in biology from the University of Connecticut, and a PhD in philosophy of science from the University of Tennessee. He is a fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science and of the Committee for Skeptical Inquiry. Pigliucci was formerly a professor of ecology and evolution at Stony Brook University. He explored phenotypic plasticity, genotype–environment interactions, natural selection, and the constra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryology
Embryology (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logy, -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the Prenatal development (biology), prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses. Additionally, embryology encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth, known as teratology. Early embryology was proposed by Marcello Malpighi, and known as preformationism, the theory that organisms develop from pre-existing miniature versions of themselves. Aristotle proposed the theory that is now accepted, Epigenesis (biology), epigenesis. Epigenesis (biology), Epigenesis is the idea that organisms develop from seed or egg in a sequence of steps. Modern embryology developed from the work of Karl Ernst von Baer, though accurate observations had been made in Italy by anatomists such as Aldrovandi and Leonardo da Vinci in the Renaissance. Comparative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Developmental Biology
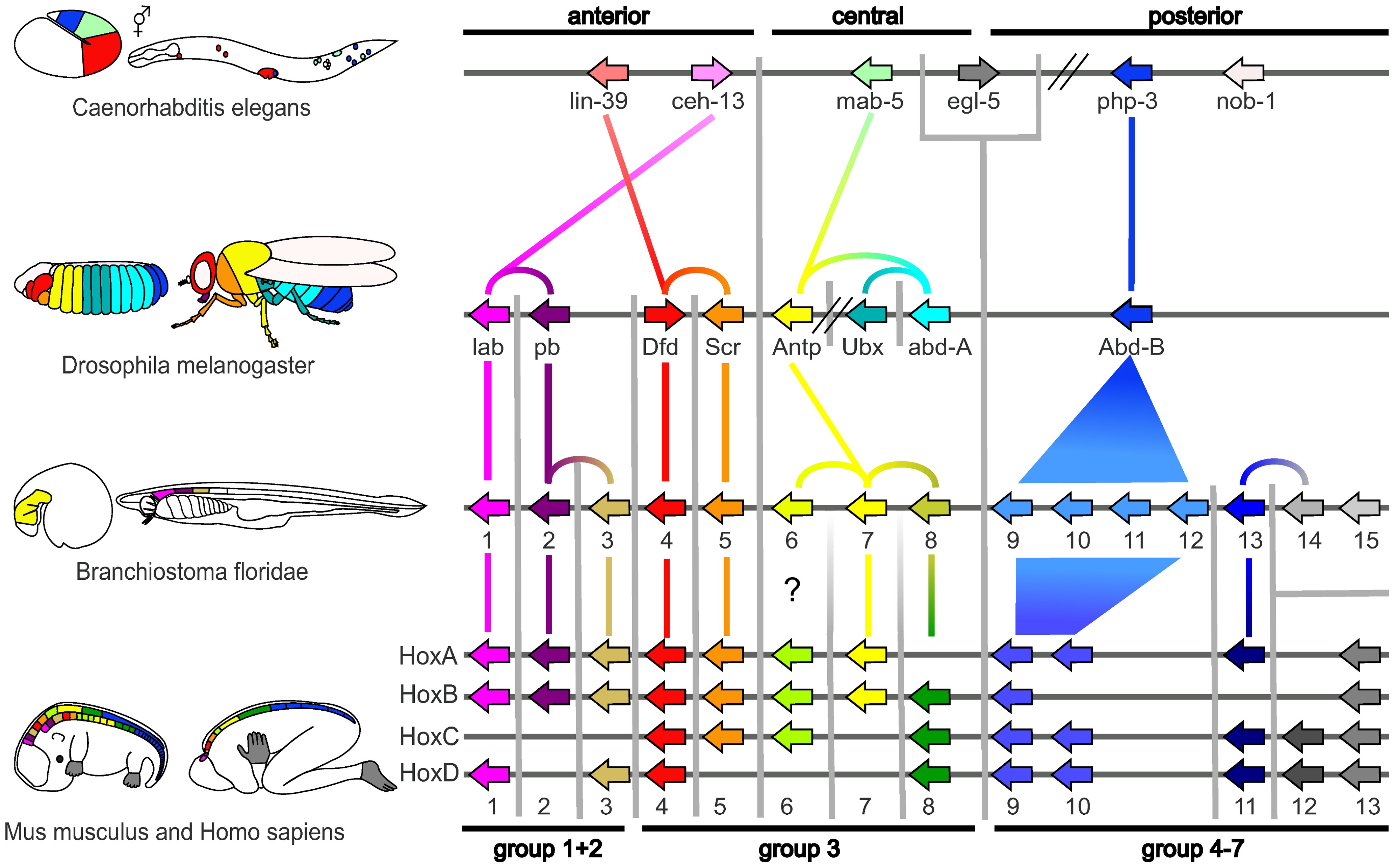
Evolutionary developmental biology, informally known as evo-devo, is a field of biological research that compares the developmental biology, developmental processes of different organisms to infer how developmental processes evolution, evolved. The field grew from 19th-century beginnings, where embryology faced a mystery: zoology, zoologists did not know how embryogenesis, embryonic development was controlled at the molecular level. Charles Darwin noted that having similar embryos implied common ancestry, but little progress was made until the 1970s. Then, recombinant DNA technology at last brought embryology together with molecular genetics. A key early discovery was that of homeotic genes that regulate development in a wide range of eukaryotes. The field is composed of multiple core evolutionary concepts. One is deep homology, the finding that dissimilar organs such as the eyes of insects, vertebrates and cephalopod molluscs, long thought to have evolved separately, are contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sociobiology
Sociobiology is a field of biology that aims to explain social behavior in terms of evolution. It draws from disciplines including psychology, ethology, anthropology, evolution, zoology, archaeology, and population genetics. Within the study of human society , societies, sociobiology is closely allied to evolutionary anthropology, human behavioral ecology, evolutionary psychology, and sociology. Sociobiology investigates social behaviors such as mating system , mating patterns, territoriality , territorial fights, pack hunter , pack hunting, and the hive society of social insects. It argues that just as selection pressure led to animals evolving useful ways of interacting with the natural environment, so also it led to the genetic evolution of advantageous social behavior. While the term "sociobiology" originated at least as early as the 1940s; the concept did not gain major recognition until the publication of E. O. Wilson's book ''Sociobiology: The New Synthesis'' in 1975. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |