|
Misegian Languages
The Misegian, also known as Mikarew or Ruboni Range languages, are a small family of clearly related languages, : Giri, Sepen, and Mikarew (Aruamu). They are generally classified among the Ramu languages of northern Papua New Guinea. The Misegian languages are all spoken in Yawar Rural LLG, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n .... Phonemes Usher (2020) reconstructs the consonant inventory as follows: : : Pronouns Usher reconstructs the pronouns as: : As of 2020, these are tagged for revision. References External links * Timothy Usher, New Guinea WorldProto–Ruboni Range {{Ramu–Lower Sepik languages Lower Ramu languages Languages of Madang Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruboni Range
The Ruboni Range is a mountain range in Papua New Guinea. Ruboni Rangein Geonames.org (cc-by) post updated 2013-05-07; database downloaded 2015-06-22 Various Ramu languages The Ramu languages are a family of some thirty languages of Northern Papua New Guinea. They were identified as a family by John Z'graggen in 1971 and linked with the Sepik languages by Donald Laycock two years later. Malcolm Ross (2005) classi ... are spoken in the mountain range. See also * Ruboni languages References Mountain ranges of Papua New Guinea {{PapuaNewGuinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
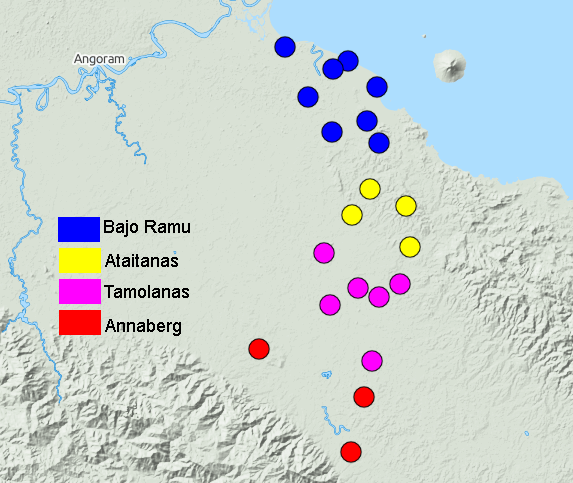
Yawar Rural LLG
Yawar Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Madang Province, Papua New Guinea. The Lower Ramu languages (Ottilien–Misegian) are all spoken in this LLG. Wards *01. Marangis ( Marangis language speakers) *02. Kaiyan ( Kaian language speakers) *03. Boroi ( Mbore language speakers) *04. Buliva *05. Daiden *06. Dongan ( Bosmun language speakers) *07. Awar ( Awar language speakers) *08. Nubia *09. Birap *10. Rugusak *11. Ambu *13. Sepa ( Sepen language speakers) *14. Rugasak *15. Banag *16. Giri Tung ( Giri language speakers) *17. Damangap *18. Kumnung *19. Minung *20. Kuarak *21. Mikarew ( Mikarew language speakers) *22. Abegini *23. Dinam Adui *24. Apengan *25. Ariangon *26. Amba Arep *27. Aringen Gun *28. Dimuk Sirin *29. Giar Wazamb *30. Andeamarup *31. Duapmung *32. Andarum *33. Ingamuk *34. Barit *35. Kayoma *36. Bang Wokam (Gorovu language Gorovu is a nearly extinct Ramu language of Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in the two villages of: *Bangapela village, Bang W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madang Province
Madang is a Provinces of Papua New Guinea, province of Papua New Guinea. The province is on the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea and has many of the country's highest peaks, active volcanoes and its biggest mix of languages. The capital is the town of Madang. Districts and LLGs and clans Each province in Papua New Guinea has one or more districts, and each district has one or more Local Level Government (LLG) areas. For census purposes, the LLG areas are subdivided into wards and those into census units. Education Tertiary educational institutions in Madang Province include: *Madang Technical College *Madang Marine Time College *Madang Teachers College *Divine Word University (DWU) is a national university and a leading tertiary institution in Papua New Guinea. Formerly Divine Word Institute, it was established by an Act of Parliament in 1980 and was established as a University in 1996. DWU It is ecumenical, coeducational and privately governed with government su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia. It has Indonesia–Papua New Guinea border, a land border with Indonesia to the west and neighbours Australia to the south and the Solomon Islands to the east. Its capital, on its southern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest list of island countries, island country, with an area of . The nation was split in the 1880s between German New Guinea in the North and the Territory of Papua, British Territory of Papua in the South, the latter of which was ceded to Australia in 1902. All of present-day Papua New Guinea came under Australian control following World War I, with the legally distinct Territory of New Guinea being established out of the former German colony as a League of Nations mandate. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramu Languages
The Ramu languages are a family of some thirty languages of Northern Papua New Guinea. They were identified as a family by John Z'graggen in 1971 and linked with the Sepik languages by Donald Laycock two years later. Malcolm Ross (2005) classifies them as one branch of a Ramu – Lower Sepik language family. Z'graggen had included the Yuat languages, but that now seems doubtful. With no comprehensive grammar yet available for any of the Ramu languages, the Ramu group remains one of the most poorly documented language groups in the Sepik-Ramu basin. Classification The small families listed below in boldface are clearly valid units. The first five, sometimes classified together as ''Lower Ramu,'' are relatable through lexical data, so their relationship is widely accepted. Languages of the Ottilien family share plural morphology with Nor–Pondo. Late 20th century Laycock (1973) included the Arafundi family, apparently impressionistically, but Arafundi is poorly known. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Ramu Languages
The Lower Ramu or Ottilien–Misegian languages consist of two branches in the Ramu language family. They are all spoken in Yawar Rural LLG, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea. Classification The Lower Ramu languages as classified by Usher and by Foley (2018) are:Timothy Usher, New Guinea WorldLower Ramu River/ref> ;Lower Ramu languages *Ottilien languages ** Watam, Kaian **Gamay ( Borei) ** Bosmun, Awar *Misegian languages (Ruboni languages) ** Mikarew ( Aruamu) ** Sepen, Kirei Lower Ramu as presented in Foley (2018) has been reduced in scope from the classification given in Foley (2005), which is as follows. ;Lower Ramu *Watam-Awar-Gamay (WAG) = Ottilien ** Watam, Kaian **Gamay ** Bosmun, Awar * Mikarew-Kire (MK) = Misegian (Ruboni) * Tangu, Igom The Ataitan languages The Ataitan languages, also known as the Tanggu or Moam River languages, are a small family of clearly related languages spoken in the region of the Moam River in Papua New Guinea. They are, * Andarum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language Family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term ''family'' is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics analogous to a family tree, or to phylogenetic trees of taxa used in evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists thus describe the ''daughter languages'' within a language family as being ''genetically related''. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with different regional dialects of the proto-language undergoing different language changes and thus becoming distinct languages over time. One well-known example of a language family is the Romance languages, including Spanish, French, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian, Catalan, and many others, all of which are descended from Vulgar Latin.Lewis, M. Paul, Gary F. Simons, and Charles D. Fennig (eds.)''Ethnologue: Languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giri Language
Kire (Giri) is a Ramu language of Giri village () in Yawar Rural LLG, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea. Phonology Out of all the Ramu languages The Ramu languages are a family of some thirty languages of Northern Papua New Guinea. They were identified as a family by John Z'graggen in 1971 and linked with the Sepik languages by Donald Laycock two years later. Malcolm Ross (2005) classi ..., Kire has the most complex consonant phonemic inventory. * Aspirated plosives only occur word-initially. * /w/ has only been found word-initially. Additionally, the following diphthongs and triphthongs are found: /ia/, /ĩã/, /ei/, /ẽĩ/, /ai/, /aːi/, /oi/, /ui/, /uiː/, /ũĩ/, /ue/, /ũẽː/, /ua/, /ũã/, /ũãː/, /uei/, /uai/, /ũãĩ/, /ũĩã/, /ũẽĩ/. Orthography Kire orthography: References {{Ramu–Lower Sepik languages Misegian languages Languages of Madang Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepen Language
Sepen is a Ramu language of Yawar Rural LLG, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n .... Speakers prefer the name Akukem. References Misegian languages Languages of Madang Province {{papuan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikarew Language
Aruamu a.k.a. Mikarew (Mikarup, Makarup, Makarub), also ''Ariawiai (Mikarew-Ariaw),'' is a Ramu language spoken in Mikarew village () of Yawar Rural LLG, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n .... References Misegian languages Languages of Madang Province {{papuan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951 and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Parachurch organization, Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL Global (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistics, linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' is not ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and Exo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIL International
SIL Global (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics International) is an evangelical Christian nonprofit organization whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages, and aid minority language development. Based on its language documentation work, SIL publishes a database, '' Ethnologue'', of its research into the world's languages, and develops and publishes software programs for language documentation, such as FieldWorks Language Explorer (FLEx) and Lexique Pro. Its main offices in the United States are located at the International Linguistics Center in Dallas, Texas. History Early History William Cameron Townsend, a Presbyterian minister, founded the organization in 1934, after undertaking a Christian mission with the Disciples of Christ among the Kaqchikel Maya people in Guatemala in the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |