|
Microdigital Eletrônica
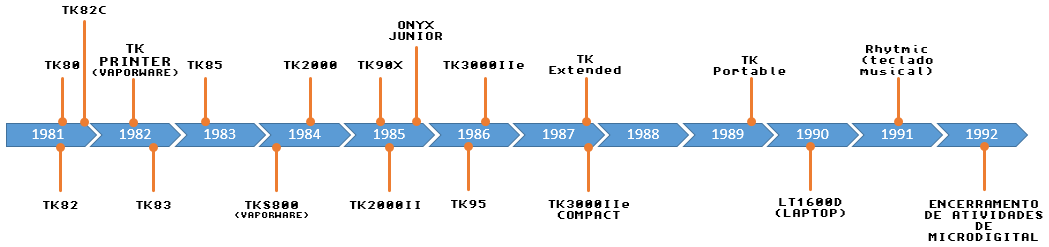
Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda. was a Brazilian computer company in the 1980s, based in São Paulo. History Established in 1981 by the brothers George and Tomas Kovari (whose initials were the TK of the domestic computers line made by the company), its first product was the TK80, a clone of the British microcomputer Sinclair ZX80. The company reached its height around 1985, with the launching of the TK90X (clone of the ZX Spectrum) and the TK 2000/II'''', a personal computer partially compatible (at Applesoft BASIC level) with the Apple II+. At this time, it had approximately 400 employees in three plants (two in São Paulo (state), São Paulo and one in the Zona Franca de Manaus) and more than 700 peddlers spread for all Brazil. Although the logo of the company is identical to the earlier Microdigital Ltd of the United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northweste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Paulo
São Paulo (; ; Portuguese for 'Paul the Apostle, Saint Paul') is the capital of the São Paulo (state), state of São Paulo, as well as the List of cities in Brazil by population, most populous city in Brazil, the List of largest cities in the Americas, Americas, and both the Western Hemisphere, Western and Southern Hemispheres. Listed by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network (GaWC) as an global city, alpha global city, it exerts substantial international influence in commerce, finance, arts, and entertainment. It is the List of largest cities#List, largest urban area by population outside Asia and the most populous Geographical distribution of Portuguese speakers, Portuguese-speaking city in the world. The city's name honors Paul the Apostle and people from the city are known as ''paulistanos''. The city's Latin motto is ''Non ducor, duco'', which translates as "I am not led, I lead." Founded in 1554 by Jesuit priests, the city was the center of the ''bandeirant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II+
The Apple II Plus (stylized as Apple ] or apple plus) is the second model of the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Inc., Apple Computer. It was sold from June 1979 to December 1982. Approximately 380,000 II Pluses were sold during its four years in production before being replaced by the Apple IIe in January 1983. Features Memory The Apple II Plus shipped with 16 KB, 32 KB or 48 KB of main RAM, expandable to 64 KB by means of the Language Card, an expansion card that could be installed in the computer's slot 0. The Apple's 6502 microprocessor could support a maximum of 64 KB of address space, and a machine with 48 KB RAM reached this limit because of the additional 12 KB of read-only memory and 4 KB of I/O addresses. For this reason, the extra RAM in the language card was bank-switched over the machine's built-in ROM, allowing code loaded into the additional memory to be used as if it actually were ROM. Users could th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics Companies Of Brazil
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signals to digital signals. Electronic devices have significantly influenced the development of many aspects of modern society, such as telecommunications, entertainment, education, health care, industry, and security. The main driving force behind the advancement of electronics is the semiconductor industry, which continually produces ever-more sophisticated electronic devices and circuits in response to global demand. The semiconductor industry is one of the global e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK-3000 IIe
The TK 3000 IIe is a personal microcomputer model manufactured by the Brazilian company Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda., compatible with the Apple IIe Enhanced. It was presented to the public at the V International Computing Fair in September 1985, and entered the market in April 1986 with a retail price of Cz$ 12,500.00 (approximately R$ 13,000.00 in updated values as of September 2023). In 1987 an updated version, the TK 3000 IIe COMPACT was released. Details Due to Apple using dedicated integrated circuits (ASICs, called ''MMU'' (''Memory Management Unit'' and ''IOU'' ''Input / Output Unit'') in the Apple IIe, copying these became more complicated compared to the Apple II and Apple II Plus, which were based on off-the-shelf integrated circuits. For this reason, Microdigital had to Reverse engineering, reverse engineer these components to achieve compatibility with the Apple model. Microdigital designed two dedicated integrated circuits used in the TK 3000 IIe, the MC168300 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK95
The TK 95 microcomputer was a 1986 ZX Spectrum clone by Microdigital Eletrônica, a company located at São Paulo, Brazil. It was an evolution of the TK90X introduced the previous year. The case was redesigned (copied from the Commodore Plus/4) and the keyboard was said to be "semi-professional" (according to the Brazilian manufacturer), with the addition of some Sinclair BASIC commands that did not exist in the ZX Spectrum's basic set (for user-defined charactersUDG), and better compatibility with the original ZX Spectrum (compared to the TK90X). Like the Spectrum, the machine had 48 kilobytes of RAM. Inside, the same processor: Z80A running at 3.58 MHz, a 16 KB ROM chip and some RAM chips (old dynamic rams 4116 and 4416). Microdigital did some reverse engineering to develop a chip with the functions of the original ULA from Sinclair/Ferranti. The modulator was tuned to VHF channel 3 and the TV system was PAL-M (60 Hz). The cassette interface ran at a faster speed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapourware
In the computer industry, vaporware (or vapourware) is a product, typically computer hardware or software, that is announced to the general public but is late, never actually manufactured, or officially canceled. Use of the word has broadened to include products such as automobiles. Vaporware is often announced months or years before its purported release, with few details about its development being released. Developers have been accused of intentionally promoting vaporware to keep customers from switching to competing products that offer more features. ''Network World'' magazine called vaporware an "epidemic" in 1989 and blamed the press for not investigating if developers' claims were true. Seven major companies issued a report in 1990 saying that they felt vaporware had hurt the industry's credibility. The United States accused several companies of announcing vaporware early enough to violate antitrust laws, but few have been found guilty. "Vaporware" was coined by a Micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRS-80 Color Computer
The RadioShack TRS-80 Color Computer, later marketed as the Tandy Color Computer, is a series of home computers developed and sold by Tandy Corporation. Despite sharing a name with the earlier TRS-80, the Color Computer is a completely different system and a radical departure in design based on the Motorola 6809, Motorola 6809E processor rather than the Zilog Z80 of earlier models. The Tandy Color Computer line, nicknamed CoCo, started in 1980 with what is now called the Color Computer 1. It was followed by the Color Computer 2 in 1983, then the Color Computer 3 in 1986. All three models maintain a high level of software and hardware compatibility, with few programs written for an older model being unable to run on the newer ones. The Color Computer 3 was discontinued in 1991. All Color Computer models shipped with Color BASIC, an implementation of Microsoft BASIC, in ROM. Variants of the OS-9 computer multitasking, multitasking operating system were available from third parties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK85
The TK85 was a ZX81 clone made by Microdigital Eletrônica, a computer company located in Brazil. It came with 16 or 48 KB RAM, and had a ZX Spectrum–style case, similar to a ''Timex Sinclair 1500''. Unlike the ZX81, the TK85 used standard logic components rather than a gate array ("ULA"), and during manufacture several of them were scraped so that competitors couldn't easily copy the circuit. The circuit board had space for a AY-3-8912 sound generator chip (compatible with the ''ZonX-81'' sound board), and although none came factory installed, it is possible to add the necessary circuits. The TK85 came with a copy of the 8K ZX81 floating point BASIC, and an additional 2K EPROM, mapped to addresses 8192-10240, containing machine code routines for use with tape files. These routines could save with HISAVE, load with HILOAD and verify with HIVERIFY in "Hi-Speed" (4200 bps); save and load, BASIC variables in 300 bps (standard ZX81 speed) using SAVE and DLOAD functions and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK83
The TK83 was a home computer produced by the Brazilian company Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda. and introduced in August 1982. By December 1984, it was no longer being advertised by Microdigital, being discontinued in 1985. The TK83 was a clone of the Sinclair ZX81, and can for all practical purposes, be considered a version of the TK82C with repagged memory and including the SLOW function which permitted the video be shown during processing. General information The TK83 had the Zilog Z80A processor running at 3.25 MHz, 2 KB RAM (expandable to 64 KB) and 8 KB of ROM that included the BASIC interpreter. The keyboard was made of layers of conductive (membrane) material and followed the Sinclair layout with 40 keys. Video output was sent via a RF modulator to a TV set tuned at VHF channel 3, and featured black characters on a white background. The maximum resolution was 64 x 44 pixels, based on semigraphic characters useful for games and basic images (see ZX81 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK82C
TK82C was a Sinclair ZX81 clone made by Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda., a computer company located in Brazil. General information The TK82C had the Zilog Z80A processor running at 3.25 MHz, 2 KB SRAM and 8 KB of EPROM with the BASIC interpreter. The C letter stands for "Científico", or "Scientific" in English. The keyboard was made of layers of conductive (membrane) material and followed the Sinclair layout. The video output was sent via a RF modulator to a TV set tuned at VHF channel 3, and featured black characters on a white background. The maximum resolution was 64 x 44 pixels, based on semigraphic characters useful for games and basic images (see ZX81 character set). The TK82C included the SLOW function, which permitted the video be shown during the processing (the prior version, TK82, a Sinclair ZX80 clone, ran only in fast mode, so the image was not shown during its processing). In reality, the SLOW function was done by an add-on board that was fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK82
TK82 was a Sinclair ZX80 clone made by Microdigital Eletrônica Ltda., a computer company located in Brazil. It was introduced along with the TK80 in 1981, during the "''I Feira Internacional de Informática".'' In the January 1982 issue of ''Micro Sistemas'' magazine, Tomas Roberto Kovari, ''Microdigital'''s engineer, stated that the machines were being sold with a photocopied manual, while a printed version was being developed. Kovari estimated a potential market for 10000 machines in Brazil, with expected buyers being novelty seekers, students and self employed professionals. The TK82 was replaced by the TK82C and TK83 Sinclair ZX81 clones. Microdigital later produced the TK90X and TK95, which were clones of the ZX Spectrum. General information The TK82 was introduced in 1981, had the Zilog Z80A processor running at 3.25 MHz, 2 KB RAM and a 4 KB ROM with the BASIC interpreter. The keyboard was made of layers of conductive (membrane) material and followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK80
The TK80 was a home computer produced by ''Microdigital Eletrônica''. A clone of the Sinclair ZX80, it was introduced along with the TK82 in 1981 during the "''I Feira Internacional de Informática".'' There were two versions, one with 1 KB RAM costing Cr$ 68,850 and another with 2 KB costing Cr$73,650. In the January 1982 issue of ''Micro Sistemas'' magazine, Tomas Roberto Kovari, ''Microdigital'''s engineer, stated that the machines were being sold with a photocopied manual, while a printed version was being developed. Kovari estimated a potential market for 10000 machines in Brazil, with expected buyers being novelty seekers, students and self employed professionals. According to some sources, the TK80 was never commercially produced, with only prototypes existing. Specifications Specifications were similar to the original machine: * CPU: Z80A @ 3.25 MHz * Memory: ROM: 4 KiB; RAM: 1 or 2 KiB * Keyboard: 40 keys membrane keyboard * Display: 32 × 22 text; 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |