|
Meridiungulata
South American native ungulates, commonly abbreviated as SANUs, are extinct ungulate-like mammals that were indigenous to South America from the Paleocene (from at least 63 million years ago) until the end of the Late Pleistocene (~12,000 years ago). They represented a dominant element of South America's Cenozoic terrestrial mammal fauna prior to the arrival of living ungulate groups in South America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange. They comprise five major groups conventionally ranked as orders— Astrapotheria, Litopterna, Notoungulata, Pyrotheria, and Xenungulata—as well as the primitive " condylarth" groups Didolodontidae and Kollpaniinae. It has been proposed that some or all of the members of this group form a clade, named Meridiungulata, though the relationships of South American ungulates remain largely unresolved. The two largest groups of South American ungulates, the notoungulates and the litopterns, were the only gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrapotheria
Astrapotheria is an extinct order of South American and Antarctic hoofed mammals that existed from the late Paleocene to the Middle Miocene, ."The uruguaytheriine Astrapotheriidae from the rich middle Miocene Honda Group of the upper Magdalena River valley in Colombia (...) are the youngest securely dated remains of that order in South America." Astrapotheres were large, rhinoceros-like animals and have been called one of the most bizarre orders of mammals with an enigmatic evolutionary history. The taxonomy of this order is not clear, but it may belong to Meridiungulata (along with Notoungulata, Litopterna, Pyrotheria and Xenungulata). In turn, Meridungulata is believed to belong to the extant superorder Laurasiatheria. Some scientists have regarded the astrapotheres (and sometimes the Meridiungulata as a whole) as members of the clade Atlantogenata. However, collagen and mitochondrial DNA sequence data analysed in 2015 places at least the notoungulates and litopterns firmly w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrotheria
Pyrotheria is an order (biology), order of extinct South American native ungulates, meridiungulate mammals. These elephant-like ungulates include the genus, genera ''Baguatherium'', ''Carolozittelia'', ''Colombitherium'', ''Griphodon'', ''Propyrotherium'', ''Proticia'', and ''Pyrotherium''. They had the appearance of large, digitigrade, tapir-like mammals with relatively short, slender limbs and five-toed feet with broad, flat phalanges. Their fossils are restricted to Paleocene through Oligocene deposits of Brazil, Peru and Argentina. Some experts place the clade Xenungulata (which contains several genera, including ''Carodnia'') within Pyrotheria, even when dentition, although bilophodont in both orders, is very different. For most scholars, the two orders remain separated. The dentition is complete with strong, procumbent, chisel-shaped incisors, strong sharp-pointed Canine tooth, canines, and low-crowned cheek teeth with bilophodont molars. The affinities of the Xenungulata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perissodactyla
Perissodactyla (, ), or odd-toed ungulates, is an order of ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three families: Equidae (horses, asses, and zebras), Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They typically have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three or one of the five original toes, though tapirs retain four toes on their front feet. The nonweight-bearing toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, artiodactyls (even-toed ungulates) bear most of their weight equally on four or two (an even number) of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that perissodactyls digest plant cellulose in their intestines, rather than in one or more stomach chambers as artiodactyls, with the exception of Suina, do. The order was considerably more diverse in the past, with notable extinct groups including the brontotheres, palaeotheres, chalicotheres, and the paracer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which land and freshwater fauna (animals), fauna migrated from North America to South America via Central America and vice versa, as the volcanic Isthmus of Panama rose up from the sea floor, forming a land bridge between the previously separated continents. Although earlier dispersals had occurred, probably over water, the migration accelerated dramatically about 2.7 million years (Ma (unit), Ma) ago during the Piacenzian age. It resulted from the joining of the Neotropical realm, Neotropic (roughly South American) and Nearctic realm, Nearctic (roughly North American) biogeographic realms definitively to form the Americas. The interchange is visible from observation of both biostratigraphy and nature (neontology). Its most dramatic effect is on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notoungulate
Notoungulata is an extinct order of ungulates that inhabited South America from the early Paleocene to the end of the Pleistocene, living from approximately 61 million to 11,000 years ago. Notoungulates were morphologically diverse, with forms resembling animals as disparate as rabbits and rhinoceroses. Notoungulata are the largest group of South American native ungulates, with over 150 genera in 14 families having been described, divided into two major subgroupings, Typotheria and Toxodontia. Notoungulates first diversified during the Eocene. Their diversity declined from the late Neogene onwards, with only the large toxodontids persisting until the end of the Pleistocene (with '' Mixotoxodon'' expanding into Central America and southern North America), perishing as part of the Late Pleistocene megafauna extinctions along with most other large mammals across the Americas. Collagen sequence analysis suggests that notoungulates are closely related to litopterns, another group of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenungulata
Xenungulata ("strange ungulates") is an order of extinct and primitive South American hoofed mammals that lived from the Late Paleocene to Early Eocene ( Itaboraian to Casamayoran in the SALMA classification). Fossils of the order are known from deposits in Brazil, Argentina, Peru, and Colombia. The best known member of this enigmatic order is the genus '' Carodnia'', a tapir-like and -sized animal with a gait similar to living African elephant African elephants are members of the genus ''Loxodonta'' comprising two living elephant species, the African bush elephant (''L. africana'') and the smaller African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''). Both are social herbivores with grey skin. ...s. Description Xenungulates are characterized by bilophodonty, bilophodont M1–2 and M1–2, similar to Pyrotheria, pyrotheres, and complex lophate third molars, similar to Uintatheriidae, uintatheres. Though other relationships, to arctocyonidae, arctocyonids for example, have been su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxodon
''Toxodon'' (meaning "bow tooth" in reference to the curvature of the teeth) is an extinct genus of large ungulate native to South America from the Pliocene to the end of the Late Pleistocene. ''Toxodon'' is a member of Notoungulata, an order of extinct South American native ungulates distinct from the two living ungulate orders that had been indigenous to the continent for over 60 million years since the early Cenozoic, prior to the arrival of living ungulates into South America around 2.5 million years ago during the Great American Interchange. ''Toxodon'' is a member of the family Toxodontidae, which includes medium to large sized herbivores. ''Toxodon'' was one of the largest members of Toxodontidae and Notoungulata, with ''Toxodon platensis'' having an estimated body mass of . Remains of ''Toxodon'' were first collected by Charles Darwin during the voyage of the Beagle in 1832-33, and later scientifically named by Richard Owen in 1837. Both Darwin and Owen were puzzled by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didolodontidae
Didolodontidae is a possibly paraphyletic family of "condylarth" mammals known from the Paleogene of South America, with most specimens known from Argentina. They were generally small-medium in body size, and had a bunodont dentition. A close relationship with litopterns has been suggested by some studies. They range in age from the early Paleocene (Selandian/Peligran) to late Eocene (Priabonian/Mustersan The Mustersan age is a period of geologic time (48.0–42.0 Mya (unit), Ma) within the Eocene epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically within the South American land mammal age (SALMA) classification. It follows the Casamayoran and precedes th ...). The attribution of '' Salladolodus deuterotheroides'' from the Late Oligocene of Bolivia to the family is doubtful. References Paleocene first appearances Eocene extinctions Prehistoric mammal families Condylarths Meridiungulata {{Paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined to be a polyphyletic and thereby invalid clade based on molecular data. As a result, true ungulates had since been reclassified to the newer clade Euungulata in 2001 within the clade Laurasiatheria while Paenungulata has been reclassified to a distant clade Afrotheria. Living ungulates are divided into two orders: Perissodactyla including Equidae, equines, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and Artiodactyla including Bos, cattle, antelope, Sus (genus), pigs, giraffes, camels, Ovis, sheep, deer, and Hippopotamidae, hippopotamuses, among others. Cetaceans such as Whale, whales, Dolphin, dolphins, and Porpoise, porpoises are also classified as artiodactyls, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condylarth
Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an Order (biology), order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates and is now largely considered to be a wastebasket taxon, having served as a dumping ground for classifying ungulates which had not been clearly established as part of either Perissodactyla or Artiodactyla, being composed thus of several unrelated lineages. Taxonomic history Condylarthra always was a problematic group. When first described by , Phenacodontidae was the type and only family therein. , however, raised Condylarthra to an order and included a wide range of diverse placentals with generalized dentitions and postcranial skeletons. More recent researchers (i.e. post-WW2) have been more restrictive; either including only a limited number of taxa, or proposing that the term should be abandoned altogether. Due to their primitive characteristics condylarths ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixotoxodon
''Mixotoxodon'' ("mixture '' Toxodon''") is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene epoch, from 1,800,000—12,000 years ago.''Mixotoxodon'' at .org Description 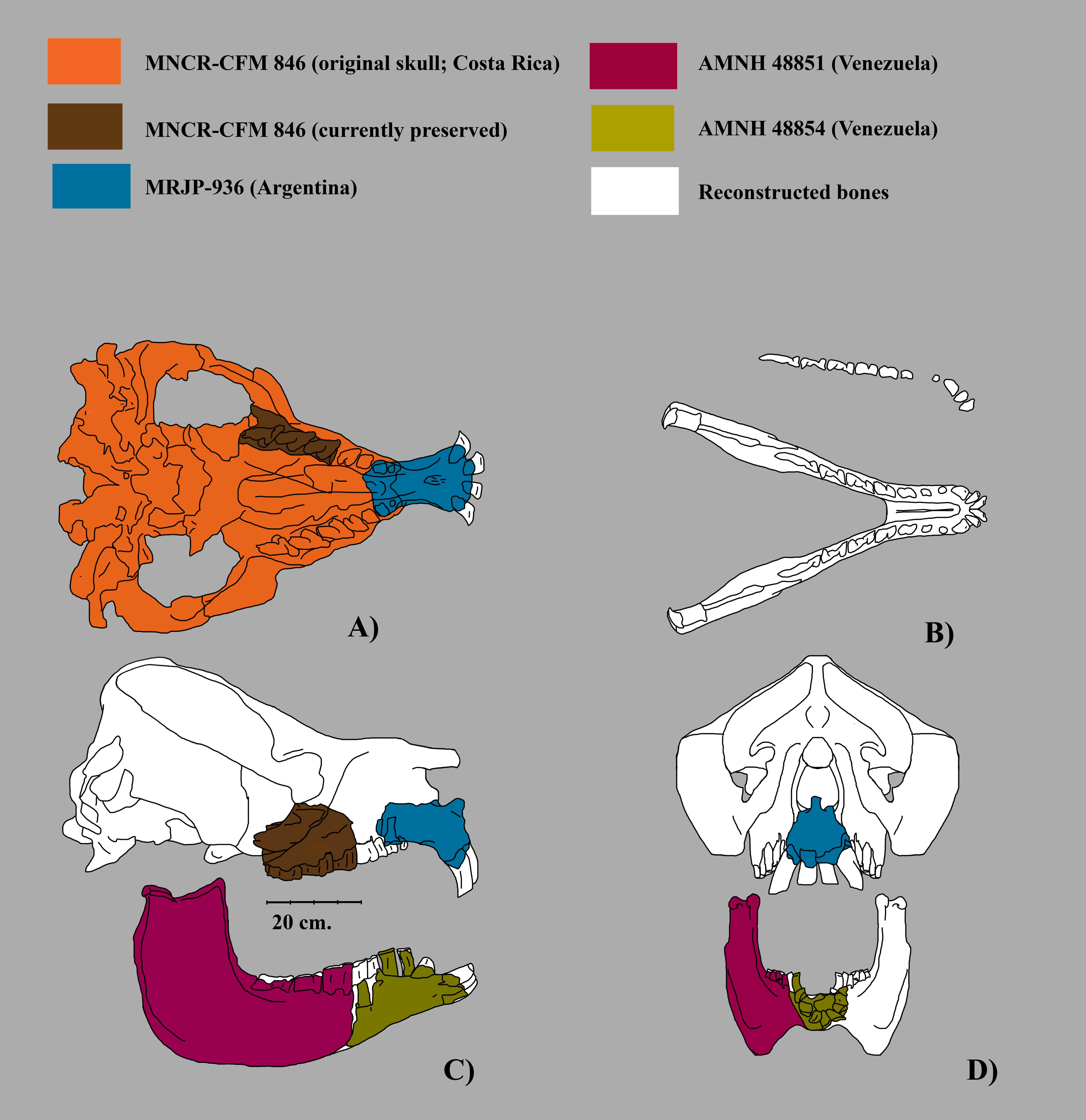
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




