|
Melody
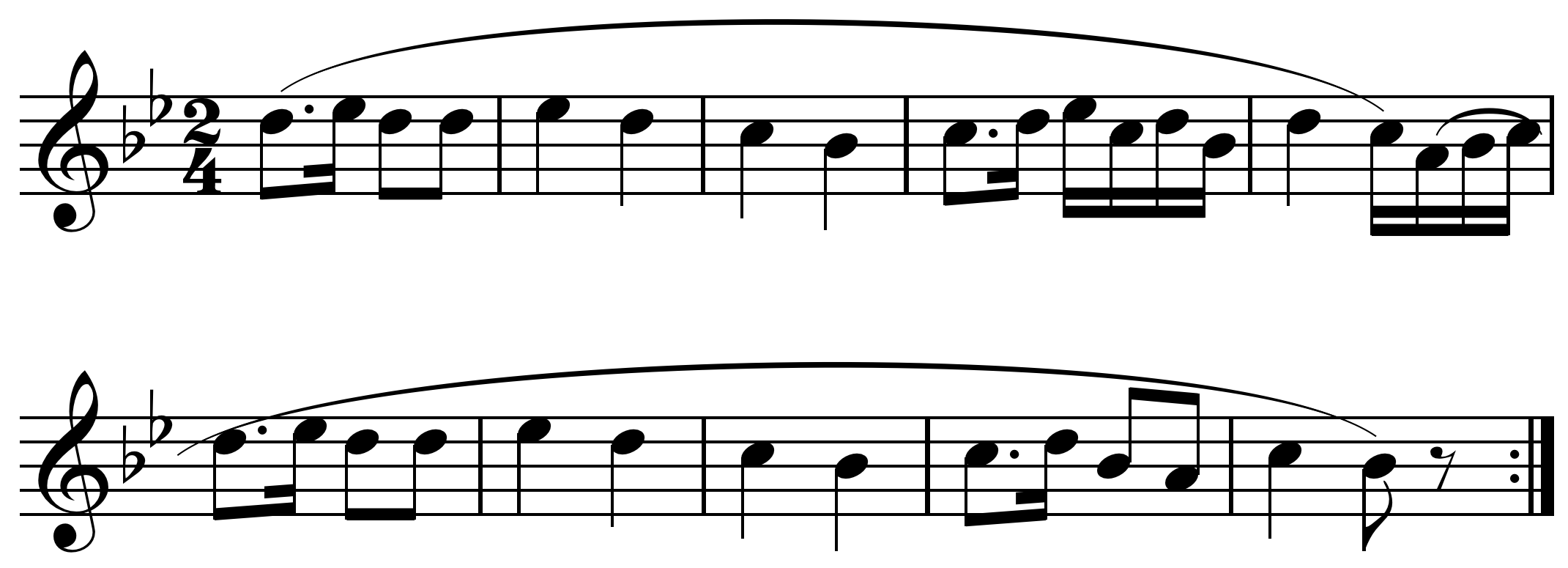
A melody (), also tune, voice, or line, is a linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of Pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term can include other musical elements such as Timbre, tonal color. It is the foreground to the background accompaniment. A line or Part (music), part need not be a foreground melody. Melodies often consist of one or more musical Phrase (music), phrases or Motif (music), motifs, and are usually repeated throughout a Musical composition, composition in various forms. Melodies may also be described by their melodic motion or the pitches or the interval (music), intervals between pitches (predominantly steps and skips, conjunct or disjunct or with further restrictions), pitch range, tension (music), tension and release, continuity and coherence, cadence (music), cadence, and shape. Function and elements Johann Philipp Kirnberger arg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steps And Skips
In music, a step, or conjunct motion,Bonds, Mark Evan (2006). ''A History of Music in Western Culture'', p.123. 2nd ed. . is the difference in pitch (music), pitch between two consecutive Musical note, notes of a musical scale. In other words, it is the interval (music), interval between two consecutive Degree (music), scale degrees. Any larger interval is called a skip (also called a leap), or disjunct motion. In the diatonic scale, a step is either a minor second (sometimes also called ''half step'') or a major second (sometimes also called ''whole step''), with all intervals of a minor third or larger being skips. For example, C to D (major second) is a step, whereas C to E (major third) is a skip. More generally, a step is a smaller or narrower interval in a musical line, and a skip is a wider or larger interval with the categorization of intervals into steps and skips is determined by the Musical tuning, tuning system and the pitch space used. Melodic motion in which the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Part (music)
A part in music refers to a component of a musical composition. Because there are multiple ways to separate these components, there are several contradictory senses in which the word "part" is used: * any individual melody (or voice), whether vocal or instrumental, that can be abstracted as continuous and independent from other notes being performed simultaneously in polyphony. Within the music played by a single pianist, one can often identify outer parts (the top and bottom parts) or an inner part (those in between). On the other hand, within a choir, "outer parts" and "inner parts" would refer to music performed by different singers. (See ) * the musical instructions for any individual instrument or voice (often given as a handwritten, printed, or digitized document) of sheet music (as opposed to the full score which shows all parts of the ensemble in the same document). A musician's part usually does not contain instructions for the other players in the ensemble, only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
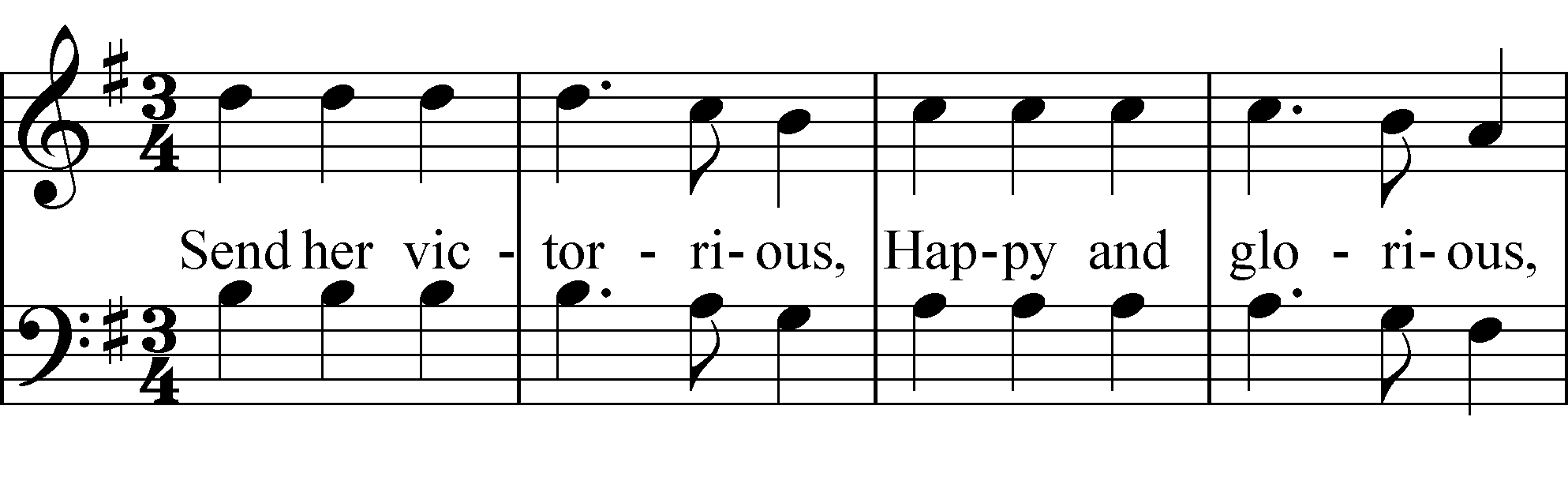
Melodic Pattern
In music and jazz improvisation, a melodic pattern (or motive) is a cell or germ serving as the basis for repetition (music), repetitive pattern. It is a figure that can be used with any scale (music), scale. It is used primarily for solo (music), solos because, when practiced enough, it can be extremely useful when musical improvisation, improvising. "Sequence" refers to the repetition of a part at a higher or lower pitch, and melodic sequence is differentiated from sequence (music), harmonic sequence. One example of melodic motive and sequence are the pitches of the first line, "Send her victorious," repeated, a step lower, in the second line, "Happy and glorious," from "God Save the Queen". "A melodic pattern is just what the name implies: a melody with some sort of fixed pattern to it." "The strong subject (music), theme or motif (music), motive is stated. It is repeated more or less exactly, but at a different pitch level."Haerle, Dan (1993). ''Jazz Improvisation for Keyyb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (music)
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord. In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. Intervals between successive notes of a scale are also known as scale steps. The smallest of these intervals is a semitone. Intervals smaller than a semitone are called microtones. They can be formed using the notes of various kinds of non-diatonic scales. Some of the very smallest ones are called commas, and describe small discrepancies, observed in some tuning systems, between enharmonically equivalent notes such as C and D. Intervals can be arbitrarily small, and even imperceptible to the human ear. In physical terms, an interval is the ratio between two sonic fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (music)
In music, texture is how the tempo and the melodic and harmonic materials are combined in a musical composition, determining the overall quality of the sound in a piece. The texture is often described in regard to the density, or thickness, and range, or width, between lowest and highest pitches, in relative terms as well as more specifically distinguished according to the number of voices, or parts, and the relationship between these voices (see Common types below). For example, a thick texture contains many 'layers' of instruments. One of these layers could be a string section or another brass. The thickness also is changed by the amount and the richness of the instruments playing the piece. The thickness varies from light to thick. A piece's texture may be changed by the number and character of parts playing at once, the timbre of the instruments or voices playing these parts and the harmony, tempo, and rhythms used. The types categorized by number and relationship of parts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or frequency of anything from microseconds to several seconds (as with the riff in a rock music song); to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years. The Oxford English Dictionary defines rhythm as ''"The measured flow of words or phrases in verse, forming various patterns of sound as determined by the relation of long and short or stressed and unstressed syllables in a metrical foot or line; an instance of this"''. Rhythm is related to and distinguished from pulse, meter, and beats: In the performance arts, rhythm is the timing of events on a human scale; of musical sounds and silences that occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motif (music)
In music, a motif () or motive is a short musical idea, a Salience (neuroscience), salient recurring Figure (music), figure, musical fragment or succession of notes that has some special importance in or is characteristic of a musical composition, composition. The motif is the smallest structural unit possessing theme (music), thematic identity. History The defines a motif as a "melodic, rhythmic, or harmonic cell (music), cell", whereas the 1958 maintains that it may contain one or more cells, though it remains the smallest analyzable element or phrase within a subject (music), subject. It is commonly regarded as the shortest subdivision of a Theme (music), theme or Phrase (music), phrase that still maintains its identity as a musical idea. "The smallest structural unit possessing thematic identity". The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians, Grove and Éditions Larousse, Larousse also agree that the motif may have harmonic, melodic and/or rhythmic aspects, Grove a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Paus
Marcus Nicolay Paus (; born 14 October 1979) is a Norwegian composer and one of the most performed contemporary Scandinavian composers. As a classical contemporary composer he is noted as a representative of a reorientation toward tradition, tonality and melody, and his works have been lauded by critics in Norway and abroad. His work includes chamber music, Choir, choral works, solo works, concerts, orchestral works, operas, symphony, symphonies and church music, as well as works for theatre, film and television. Paus is regarded as "one of the most celebrated classical composers of Norway" and "the leading Norwegian composer of his generation." Paus has said he considers himself to be a "musical dramatist" or storyteller. Although often tonal and melodically driven, Paus's music employs a wide range of both traditional and modernist techniques, and several of Paus's works have been influenced by folk music and non-Western classical music. Paus has referred to himself as a "melody, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadence (music)
In Classical music, Western musical theory, a cadence () is the end of a Phrase (music), phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution (music), resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (1999). ''The Harvard Concise Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', pp. 105-106. . A harmonic cadence is a chord progression, progression of two or more chord (music), chords that conclusion (music), concludes a phrase, section (music), section, or composition (music), piece of music. A rhythmic cadence is a characteristic rhythmic pattern that indicates the end of a phrase. A cadence can be labeled "weak" or "strong" depending on the impression of finality it gives. While cadences are usually classified by specific chord or melodic progressions, the use of such progressions does not necessarily constitute a cadence—there must be a sense of closure, as at the end of a phrase. Harmonic rhythm plays an important part in de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tension (music)
In music, tension is the anticipation music creates in a listener's mind for relaxation or release. For example, tension may be produced through reiteration, increase in dynamic level, gradual motion to a higher or lower pitch, or (partial) syncopations between consonance and dissonance. Experiments in music perception have explored perceived tension in music and perceived emotional intensity. The balance between tension and repose are explored in musical analysis—determined by contrasts that are, "...of great interest to the style analyst," and can be analyzed in several, even conflicting layers—as different musical elements such as harmony may create different levels of tension than rhythm and melody. Heavy metal and rock musicians adapted tension-building techniques originally developed by classical composers. Van Halen has been noted for incorporating harmonic tension and release in the guitar solo Eruption:"Van Halen continually sets up implied harmonic goals, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melodic Motion
Melodic motion is the quality of movement of a melody, including nearness or farness of successive pitches or notes in a melody. This may be described as conjunct or disjunct, stepwise, skipwise or no movement, respectively. See also contrapuntal motion. In a conjunct melodic motion, the melodic phrase moves in a stepwise fashion; that is the subsequent notes move up or down a semitone or tone, but no greater. In a disjunct melodic motion, the melodic phrase leaps upwards or downwards; this movement is greater than a whole tone. In popular Western music, a melodic leap of disjunct motion is often present in the chorus of a song, to distinguish it from the verses and captivate the audience. In traditional culture music Ethnomusicologist Bruno Nettl describes various types of melodic movement or contour to categorise a song's melody. There are three general categories, ''ascending'', ''descending'', and ''undulating'': *''Ascending'': Upwards melodic movement (only found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase (music)
In music theory, a phrase () is a unit of Meter (music), musical meter that has a complete musical sense of its own, built from figure (music), figures, motif (music), motifs, and Cell (music), cells, and combining to form Melody, melodies, period (music), periods and larger Section (music), sections. Terms such as ''sentence'' and ''verse'' have been adopted into the vocabulary of music from linguistic syntax. Though the analogy between the musical and the phrase, linguistic phrase is often made, still the term "is one of the most ambiguous in music....there is no consistency in applying these terms nor can there be...only with melodies of a very simple type, especially those of some dances, can the terms be used with some consistency." John D. White defines a phrase as "the smallest musical unit that conveys a more or less complete musical thought. Phrases vary in length and are terminated at a point of full or partial repose, which is called a ''cadence''." Edward T. Cone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |