|
Medicinal Clay
The use of medicinal clay in folk medicine goes back to prehistoric times. Indigenous peoples around the world still use clay widely. Such uses include external application to the skin and geophagy. The first recorded use of medicinal clay goes back to ancient Mesopotamia. A wide variety of clays are used for medicinal purposes—primarily for external applications, such as the clay baths in health spas ( mud therapy). Among the clays most commonly used are kaolin and the smectite clays such as bentonite, montmorillonite, and Fuller's earth. However, their use is declining, and modern evidence-based medicine has ended the use of many types. History Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia The first recorded use of medicinal clay is on Mesopotamian clay tablets around 2500 BC. Also, ancient Egyptians used clay. The Pharaohs’ physicians used the material as anti-inflammatory agents and antiseptics. It was used as a preservative for making mummies and is also reported that Cleopatra us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luvos Heilerde
Heilerde-Gesellschaft Luvos Just GmbH & Co. KG is a German manufacturer of medicinal clay (''Heilerde'', "healing-earth")-based products for both internal and external application. Four different fineness grades of loess in both capsule and powder form are available from the company, as well as cosmetics products. The Luvos purified loess consists mainly of montmorillonite. History Luvos was established by alternative medicine practitioner Adolf Just in Blankenburg in 1918. Previously, Just had founded the ''Jungborn'' in 1895, a center for alternative healing, where he had extolled and popularized the healing properties of certain clays. The ''Jungborn'' was situated between Eckertal and Stapelburg in the Harz, an area which later became part of East Germany. Therefore, the Luvos company was relocated to Friedrichsdorf in the Taunus. The company is still family-owned today and run by Just's great-granddaughter Ariane Kaestner. In 2017 the company was fined €40,000 for fraudu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioscorides
Pedanius Dioscorides (, ; 40–90 AD), "the father of pharmacognosy", was a Greek physician, pharmacologist, botanist, and author of (in the original , , both meaning "On Materia medica, Medical Material") , a 5-volume Greek encyclopedic pharmacopeia on herbal medicine and related medicinal substances, that was widely read for more than 1,500 years. For almost two millennia Dioscorides was regarded as the most prominent writer on plants and plant drugs. Life A native of Anazarbus, Cilicia, Asia Minor, Dioscorides likely studied medicine nearby at the school in Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus, which had a pharmacological emphasis, and he dedicated his medical books to Laecanius Arius, a medical practitioner there. Though he writes he lived a "soldier's life" or "soldier-like life", his pharmacopeia refers almost solely to plants found in the Greek-speaking eastern Mediterranean, making it likely that he served in campaigns, or travelled in a civilian capacity, less widely as supposed. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaopectate
Kaopectate is an orally taken medication for the treatment of mild diarrhea. It is also sometimes used to treat indigestion, nausea, and stomach ulcers. The active ingredients have varied over time, and are different between the United States and Canada. The original active ingredients were kaolinite and pectin. In Canada and Switzerland, the active ingredient is now Attapulgite, while in the US, the active ingredient is now bismuth subsalicylate (the same as in Pepto-Bismol). Ingredients The active ingredient in Kaopectate has changed since its original creation. Originally, kaolinite was used as the adsorbent and pectin as the emollient. Attapulgite (a type of absorbent clay) replaced the kaolinite in the 1980s, but was banned by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in a ruling made in April 2003. As a consequence, since 2004, bismuth subsalicylate has been used as the active ingredient in U.S. marketed products. In Canada, McNeil Consumer Healthcare continues to market Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
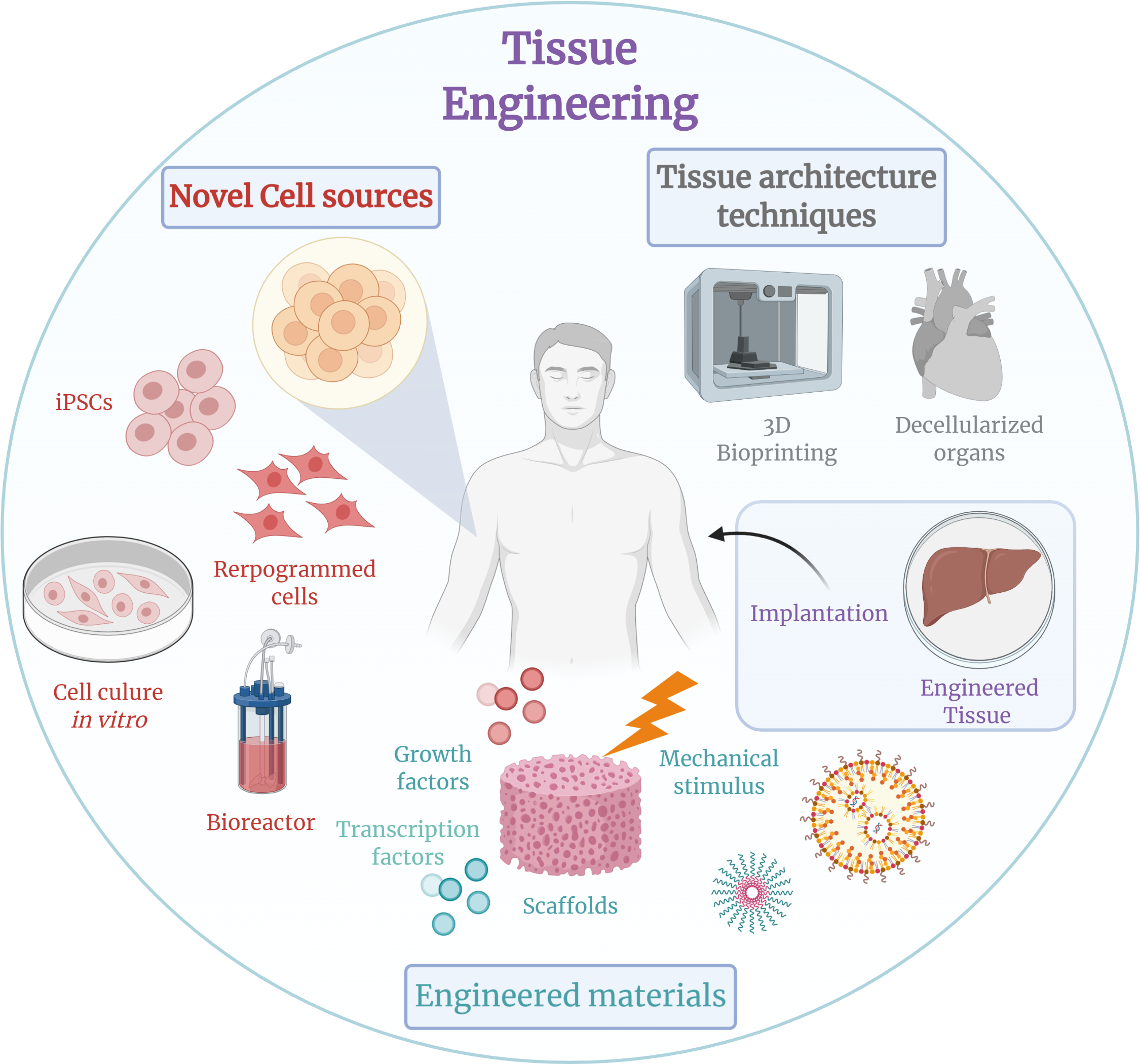
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose, but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance, it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice, the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. organs, bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most abundant element in the Earth's crust, being mainly deposited by meteorites in its metallic state. Extracting usable metal from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching , about 500 °C (900 °F) higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BC and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys – in some regions, only around 1200 BC. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In the modern world, iron alloys, such as steel, stainless steel, cast iron and special steels, are by far the most common industrial metals, due to their mechan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trace Element
__NOTOC__ A trace element is a chemical element of a minute quantity, a trace amount, especially used in referring to a micronutrient, but is also used to refer to minor elements in the composition of a rock, or other chemical substance. In nutrition, trace elements are classified into two groups: essential trace elements, and non-essential trace elements. Essential trace elements are needed for many physiological and biochemical processes in both plants and animals. Not only do trace elements play a role in biological processes but they also serve as catalysts to engage in redox – oxidation and reduction mechanisms. Trace elements of some heavy metals have a biological role as essential micronutrients. Types The two types of trace element in biochemistry are classed as essential or non-essential. Essential trace elements An essential trace element is a dietary element, a mineral that is only needed in minute quantities for the proper growth, development, and physiology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algonquians
The Algonquians are one of the most populous and widespread North American indigenous American groups, consisting of the peoples who speak Algonquian languages. They historically were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and in the interior regions along St. Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. Before contact with Europeans, most Algonquian settlements lived by hunting and fishing, with many of them supplementing their diet by cultivating corn, beans and squash (the " Three Sisters"). The Ojibwe cultivated wild rice. Colonial period At the time of European arrival in North America, Algonquian peoples resided in present-day Canada east of the Rocky Mountains, New England, New Jersey, southeastern New York, Delaware, and down the Atlantic Coast to the Upper South, and around the Great Lakes in present-day Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin. The precise homeland of the Algonquian peoples is not known. At the time of European contact, the hegemonic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Harriot
Thomas Harriot (; – 2 July 1621), also spelled Harriott, Hariot or Heriot, was an English astronomer, mathematician, ethnographer and translator to whom the theory of refraction is attributed. Thomas Harriot was also recognized for his contributions in navigational techniques, working closely with John White to create advanced maps for navigation. While Harriot worked extensively on numerous papers on the subjects of astronomy, mathematics and navigation, he remains obscure because he published little of it, namely only ''The Briefe and True Report of the New Found Land of Virginia'' (1588). This book includes descriptions of English settlements and financial issues in Virginia at the time. He is sometimes credited with the introduction of the potato to the British Isles. Harriot invented binary notation and arithmetic several decades before Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, but this remained unknown until the 1920s. He was also the first person to make a drawing of the Moon thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
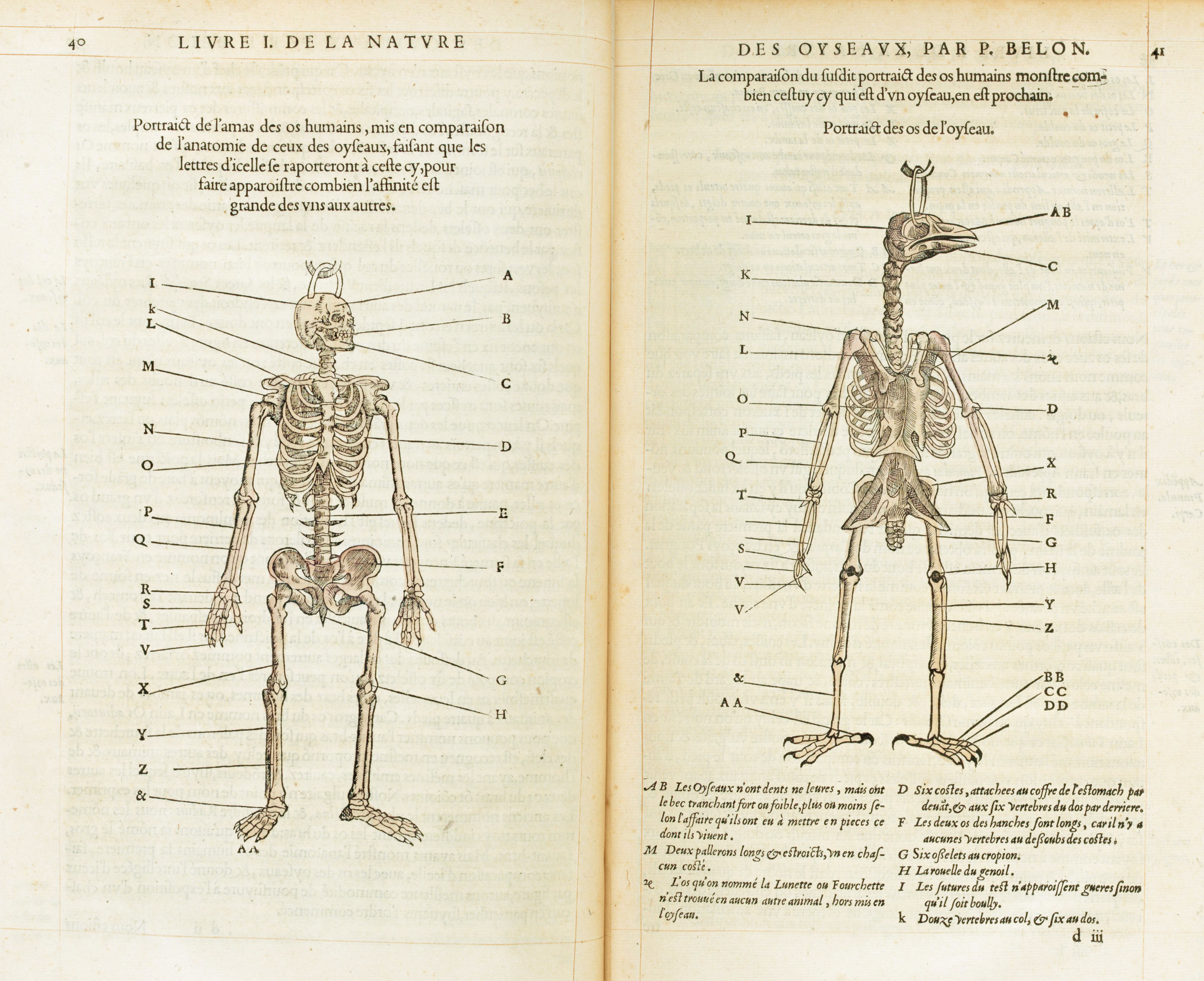
Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon (1517–1564) was a French traveller, natural history, naturalist, writer and diplomat. Like many others of the Renaissance period, he studied and wrote on a range of topics including ichthyology, ornithology, botany, comparative anatomy, architecture and Egyptology. He is sometimes known as Pierre Belon du Mans, or, in the Latin in which his works appeared, as Petrus Bellonius Cenomanus. The Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (known for Ivan Pavlov#Legacy, Pavlov's dogs) called him the "prophet of comparative anatomy". Life Belon was born in 1517 at the hamlet of Souletière near Cérans-Foulletourte in the Pays de la Loire. Nothing is known about his descent. Somewhere between 1532 and 1535 he started working as an apprentice to René des Prez, born in Foulletourte but by then an apothecary to the bishop of Clermont, Guillaume Duprat. Between 1535 and 1538 he entered the service of René du Bellay, bishop of Le Mans, who allowed him to study medicine at the University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armenian Bole
Armenian bole, also known as bolus armenus or bole armoniac, is an earthy clay, usually red, native to Armenia but also found in other places. The term Armenian was later referred to a specific quality of the clay. Originally used in medication, it has also been used as a pigment, as a poliment or base for gilding, and for other uses. It is red due to the presence of iron oxide; the clay also contains hydrous silicates of aluminum and possibly magnesium. Uses Historically, the term bolu or bolus was used only for medicinal earths and Armenian bole was used as an astringent, prescribed against diarrhea, dysentery, and bleeding. References to Armenian bole were made by Theophrastus, Pedanius Dioscorides, Dioscorides (c. 41–90 AD) and Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD). Externally, it was used in strengthening plasters, against dislocations of the joints. Physicians sometimes also called it ''Rubrica Synopica'', from the city of Sinop, Turkey, Synope, where it is supposed to be found. U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Al-Baitar
Diyāʾ al-Dīn Abū Muḥammad ʿAbd Allāh ibn Aḥmad al-Mālaqī, commonly known as Ibn al-Bayṭār () (1197–1248 AD) was an Al-Andalus, Andalusian Arabs, Arab physician, botanist, pharmacist and scientist. His main contribution was to systematically record the additions made by Medicine in medieval Islam, Islamic physicians in the Middle Ages, which added between 300 and 400 types of medicine to the one thousand previously known since antiquity. He was a student of Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati. Life Ibn al-Baitar was born in the city of Málaga in al-Andalus (Muslim Spain) at the end of the twelfth century, hence his ''Nisba (onomastics), nisba'' "al-Mālaqī". His name "Ibn al-Baitar" is Arabic for "son of the veterinarian", which was his father's profession. Ibn al-Bayṭār learned botany from the Málagan botanist Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati, Abū al-ʿAbbās al-Nabātī with whom he started collecting plants in and around Spain. In 1219, Ibn al-Bayṭār left Málaga, travellin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( – 22 June 1037), commonly known in the West as Avicenna ( ), was a preeminent philosopher and physician of the Muslim world, flourishing during the Islamic Golden Age, serving in the courts of various Iranian peoples, Iranian rulers. He is often described as the father of early modern medicine. His philosophy was of the Peripatetic school derived from Aristotelianism. His most famous works are ''The Book of Healing'', a philosophical and scientific encyclopedia, and ''The Canon of Medicine'', a medical encyclopedia which became a standard medical text at many medieval European University, universities and remained in use as late as 1650. Besides philosophy and medicine, Avicenna's corpus includes writings on Astronomy in medieval Islam, astronomy, Alchemy and chemistry in medieval Islam, alchemy, Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, geography and geology, Psychology in medieval Islam, psychology, Islamic theology, Logic in Islamic philosophy, logic, Mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |