|
Lycium
''Lycium'' is a genus of flowering plants in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. The genus has a disjunct distribution around the globe, with species occurring on most continents in temperate and subtropical regions. South America has the most species, followed by North America and southern Africa. There are several scattered across Europe and Asia, and one is native to Australia.Fukuda, T., et al. (2001)Phylogeny and biogeography of the genus ''Lycium'' (Solanaceae): Inferences from chloroplast DNA sequences. ''Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution'' 19(2), 246-58. Common English names for plants of this genus include box-thorn,''Lycium''. The Jepson eFlora 2013. , and desert-thorn. |
Goji
Goji, goji berry, or wolfberry () is the sweet fruit of either ''Lycium barbarum'' or ''Lycium chinense'', two closely related species of boxthorn in the nightshade family, Solanaceae. ''L. barbarum'' and ''L. chinense'' fruits are similar but can be distinguished by differences in taste and sugar content. Goji berries are primarily cultivated in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region and Xinjiang in China, where the unique climate and soil conditions contribute to their vibrant color and nutrient-rich profile. Both of these species are native to East Asia, and have been long used in traditional East Asian cuisine. In the United States, varieties of the genus, ''Lycium'', are given the common names, ''desert-thorn'' and ''Berlandier's wolfberry'' for the species, ''Lycium berlandieri''. The fruit has also been an ingredient in East Asian traditional medicine, namely traditional Chinese, Japanese, and Korean medicine since at least the 3rd century AD.Nobuo Kaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycium Ferocissimum
''Lycium ferocissimum'', the African boxthorn or boxthorn, is a shrub in the nightshade family (Solanaceae) indigenous to South Africa. Distribution The species is native to the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces in South Africa, where it tends to occur in sands along the southern coast. It has also been recorded in the Free State, but these may represent introductions. It has been widely introduced in South Africa and elsewhere in Africa, as far north as Morocco.Venter, A.M. (2000). Taxonomy of the Genus ''Lycium'' L. (Solanaceae) in Africa. Thesis (Ph.D. (Botany and Genetics))--University of the Free State. https://scholar.ufs.ac.za/handle/11660/1960?show=full It has been recorded in Sardinia, Italy. This shrub is found in other Mediterranean countries such as Tunisia and Spain. There is one record in France from 2020. It has become naturalised in Australia and New Zealand. It is listed in Australia's Weed of National Significance list and is a declared noxious weed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solanaceae
Solanaceae (), commonly known as the nightshades, is a family of flowering plants in the order Solanales. It contains approximately 2,700 species, several of which are used as agricultural crops, medicinal plants, and ornamental plants. Many members of the family have high alkaloid contents, making some highly toxic, but many—such as tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and peppers—are commonly used in food. Originating in South America, Solanaceae now inhabits every continent on Earth except Antarctica. After the K—Pg extinction event they rapidly diversified and have adapted to live in deserts, tundras, rainforests, plains, and highlands, and taken on wide range of forms including trees, vines, shrubs, and epiphytes. Nearly 80% of all nightshades are included in the subfamily Solanoideae, most of which are members of the type genus ''Solanum''. Most taxonomists recognize six other subfamilies: Cestroideae, Goetzeoideae, Nicotianoideae, Petunioideae, Schizanthoideae, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple Plant stem, stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botany, botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some define a shrub as less than and a tree as over 6 m. Others use as the cutoff point for classification. Many trees do not reach this mature height because of hostile, less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble shrub-sized plants. Others in such species have the potential to grow taller in ideal conditions. For longevity, most shrubs are classified between Perennial plant, perennials and trees. Some only last about five years in good conditions. Others, usually larger and more woody, live beyond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function. If substances have medicinal properties, they are considered pharmaceuticals. The field encompasses drug composition and properties, functions, sources, synthesis and drug design, molecular and cellular mechanisms, organ/systems mechanisms, signal transduction/cellular communication, molecular diagnostics, interactions, chemical biology, therapy, and medical applications and antipathogenic capabilities. The two main areas of pharmacology are pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Pharmacodynamics studies the effects of a drug on biological systems, and pharmacokinetics studies the effects of biological systems on a drug. In broad terms, pharmacod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
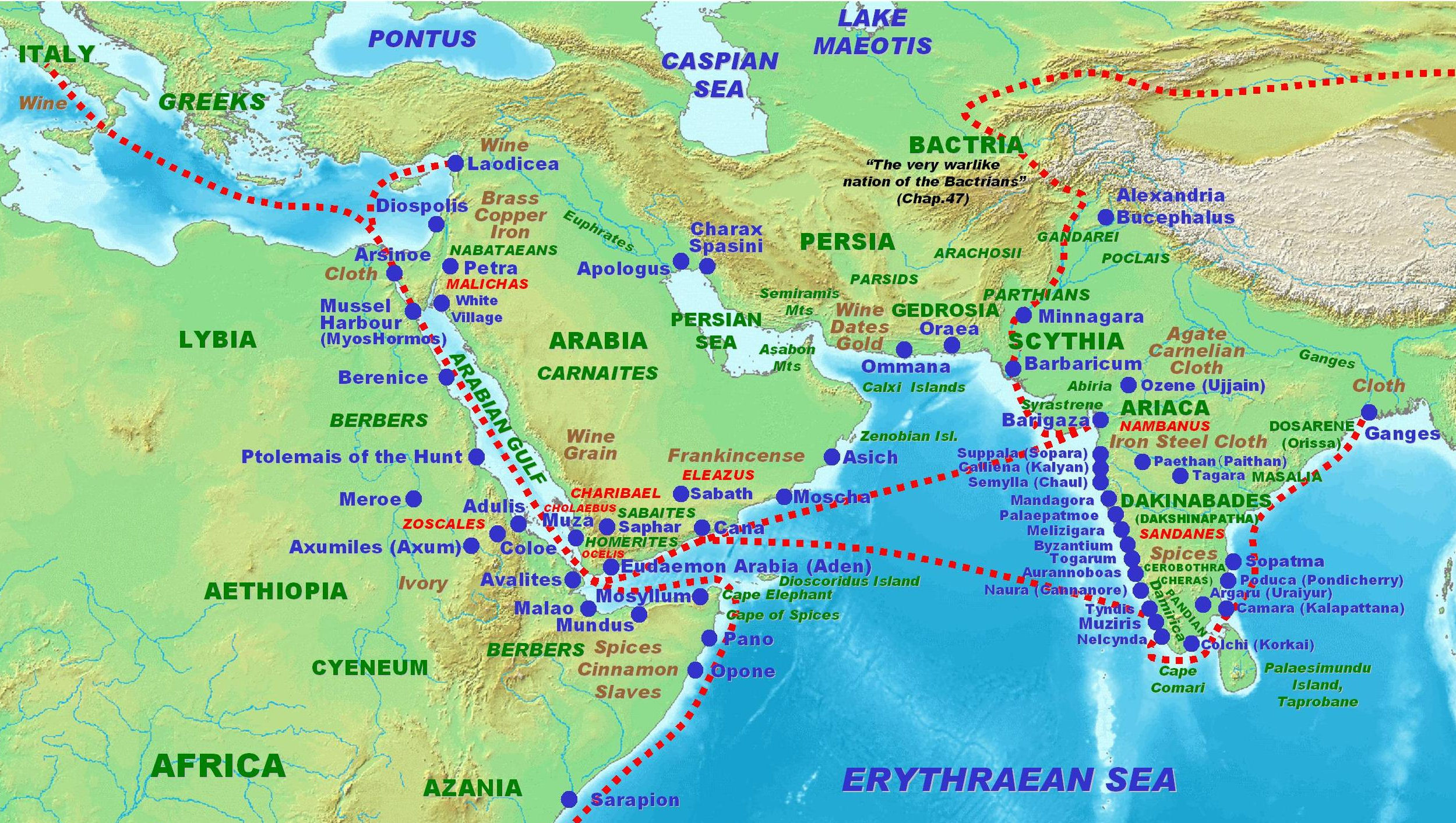
Barbarikon
Barbarikon () was the name of a sea port near the modern-day city of Karachi, Sindh, Pakistan, important in the ancient era of the Indian subcontinent in Indian Ocean trade. The port is considered one of the premiere ports regarding the interaction between ancient India with the Middle East and Mediterranean world. It comes from the Greek word of the term (also in Latin, ''barbaricum''), designating areas outside the Greco-Roman world. It may have been a translation from Sumerian word Meluhha for the Sindh from which the Sanskrit word for barbarian, Mleccha derives. Barbarikon is mentioned briefly in the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea: :"This river Indus.html" ;"title="he Indus">he Indushas seven mouths, very shallow and marshy, so that they are not navigable, except the one in the middle; at which by the shore, is the market-town, Barbaricum. Before it there lies a small island, and inland behind it is the metropolis of Scythia, Minnagara; it is subject to Parthian princes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariaca
Ariaca () was a region of Western India beyond Barigaza, mentioned in ancient geographical sources, usually associated with the Western Satraps. According to the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea, Ariaca was part of the kingdom of ''Nambanus'', thought to be the Western Satrap ruler Nahapana: Ptolemy Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ... further describes Ariaca as being composed of the cities of Suppara ( Sopara), Dunga, Symilla emporium ( Chaul), Balepatna, Hippocura (the seat of the palace of a king, whom Ptolemy calls Baleocarus), ending before the city of Mandagora.Ptolemy, Geographia, Book 7 Notes {{reflist Ancient Indian geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Trade With India
Indo-Roman trade relations (see also the spice trade and incense road) was trade between the Indian subcontinent and the Roman Empire in Europe and the Mediterranean Sea. Trade through the overland caravan routes via Asia Minor and the Middle East, though at a relative trickle compared to later times, preceded the southern trade route via the Red Sea, which started around the beginning of the Common Era (CE), following the reign of Augustus and his conquest of Egypt in 30 BCE. The southern route so helped enhance trade between the ancient Roman Empire and the Indian subcontinent, that Roman politicians and historians are on record decrying the loss of silver and gold to buy silk to pamper Roman wives, and the southern route grew to eclipse and then totally supplant the overland trade route. Roman and Greek traders frequented the ancient Tamil country, present day Southern India and Sri Lanka, securing trade with the seafaring Tamil states of the Pandyan, Chola and Cher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In modern times, the term ''Far East'' has widely fallen out of use and been substituted by Asia–Pacific, while the terms Middle East and Near East, although now pertaining to different territories, are still commonly used today. The term first came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 15th century, particularly the British people, British, denoting the Far East as the "farthest" of the three "Easts", beyond the Near East and the Middle East. Likewise, during the Qing dynasty of the 19th and early 20th centuries, the term "Far West (Taixi), Tàixī ()" – i.e., anything further west than the Arab world – was used to refer to the Western countries. Since the mid-20th century, the term has mostly gone out of use for the region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbalism
Herbal medicine (also called herbalism, phytomedicine or phytotherapy) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. Scientific evidence for the effectiveness of many herbal treatments remains limited, prompting ongoing regulatory evaluation and research into their safety and efficacy. Standards for purity or dosage are generally not provided. The scope of herbal medicine sometimes includes fungi, fungal and bee products, as well as Dietary mineral, minerals, Exoskeleton, shells and certain animal parts. Paraherbalism is the Pseudoscience, pseudoscientific use of plant or animal extracts as medicine, relying on unproven beliefs about the safety and effectiveness of minimally processed natural substances. Herbal medicine has been used since at least the Paleolithic era, with written records from ancient Sumer, Egypt, Greece, China, and India documenting its development and application over millennia. Modern herbal medici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioecy
Dioecy ( ; ; adj. dioecious, ) is a characteristic of certain species that have distinct unisexual individuals, each producing either male or female gametes, either directly (in animals) or indirectly (in seed plants). Dioecious reproduction is biparental reproduction. Dioecy has costs, since only the female part of the population directly produces offspring. It is one method for excluding self-fertilization and promoting allogamy (outcrossing), and thus tends to reduce the expression of recessive deleterious mutations present in a population. Plants have several other methods of preventing self-fertilization including, for example, dichogamy, herkogamy, and self-incompatibility. In zoology In zoology, dioecy means that an animal is either male or female, in which case the synonym gonochory is more often used. Most animal species are gonochoric, almost all vertebrate species are gonochoric, and all bird and mammal species are gonochoric. Dioecy may also describe colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Reproductive Morphology
Plant reproductive morphology is the study of the physical form and structure (the morphology) of those parts of plants directly or indirectly concerned with sexual reproduction. Among all living organisms, flowers, which are the reproductive structures of angiosperms, are the most varied physically and show a correspondingly great diversity in methods of reproduction. Plants that are not flowering plants ( green algae, mosses, liverworts, hornworts, ferns and gymnosperms such as conifers) also have complex interplays between morphological adaptation and environmental factors in their sexual reproduction. The breeding system, or how the sperm from one plant fertilizes the ovum of another, depends on the reproductive morphology, and is the single most important determinant of the genetic structure of nonclonal plant populations. Christian Konrad Sprengel (1793) studied the reproduction of flowering plants and for the first time it was understood that the pollination proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |