|
Lycian Language
The Lycian language ( )Bryce (1986) page 30. was the language of the ancient Lycians who occupied the Anatolian region known during the Iron Age as Lycia. Most texts date back to the fifth and fourth century BC. Two languages are known as Lycian: regular Lycian or Lycian A, and Lycian B or Milyan language, Milyan. Lycian became extinct around the beginning of the first century BC, replaced by the Ancient Greek language during the Hellenization of Anatolia. Lycian had its Lycian script, own alphabet, which was closely related to the Greek alphabet but included at least one character borrowed from Carian language, Carian as well as characters proper to the language. The words were often separated by two points. Area Lycia covered the region lying between the modern cities of Antalya and Fethiye in southern Turkey, especially the mountainous headland between Fethiye Bay and the Gulf of Antalya. The ''Lukka'', as they were referred to in ancient Egyptian sources, which mention t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycia
Lycia (; Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; , ; ) was a historical region in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is today the provinces of Antalya and Muğla in Turkey as well some inland parts of Burdur Province. The region was known to history from the Late Bronze Age records of ancient Egypt and the Hittite Empire. Lycia was populated by speakers of Luwic languages. Written records began to be inscribed in stone in the Lycian language after Lycia's involuntary incorporation into the Achaemenid Empire in the Iron Age. At that time (546 BC) the Luwian speakers were displaced as Lycia received an influx of Persian speakers. The many cities in Lycia were wealthy as shown by their elaborate architecture starting at least from the 5th century BC and extending to the Roman period. Lycia fought for the Persians in the Persian Wars, but on the defeat of the Achaemenid Empire by the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antalya
Antalya is the fifth-most populous city in Turkey and the capital of Antalya Province. Recognized as the "capital of tourism" in Turkey and a pivotal part of the Turkish Riviera, Antalya sits on Anatolia's southwest coast, flanked by the Taurus Mountains. The urban population of the city is 1,335,002 (Konyaalti, Kepez, Muratpasa), with a metropolitan population of 2,722,103.2011 Census Turkish Statistical Institute (Büyükşehir belediyeleri ve bağlı belediyelerin nüfusları) – 2011 The city was formerly known as Attalia and was founded in around 200 BC by King [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycian Alphabet
The Lycian alphabet was used to write the Lycian language of the Asia Minor region of Lycia. It was an extension of the Greek alphabet, with half a dozen additional letters for sounds not found in Greek. It was largely similar to the Lydian alphabet, Lydian and the Phrygian alphabets. The alphabet The Lycian alphabet contains letters for 29 sounds. Some sounds are represented by more than one symbol, which is considered one "letter". There are six vowel letters, one for each of the four oral vowels of Lycian, and separate letters for two of the four nasal vowels. Nine of the Lycian letters do not appear to derive from the Greek alphabet. Numbers Lycian uses the following number symbols: I (vertical stroke) = 1, < ("less than" sign) (or, rarely, ''L'' or C or V or Y) = 5, O (circle) = 10; a horizontal stroke — is one half; a symbol somewhat like our letter H may mean 100. The number 128½ would therefore be expressed as HOO [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antoine-Jean Saint-Martin
Antoine-Jean Saint-Martin (; 17 January 1791 – 17 July 1832) was a French academic, orientalist, and pioneer in the field of what would be known as Armenian Studies. Biography Antoine-Jean Saint-Martin was born in Paris on 17 January 1791, the son of a tradesman. Intending to enter commerce, he attended the Collège des Quatre-Nations. There he learned Arabic, Armenian, Persian, Syriac and Turkish, plus the basics of several other languages such as Zend and Georgian. By the age of 20 he had already acquired a solid theory and spoken fluency in Armenian and Arabic. On 2 September 1820 he was elected a member of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-lettres, part of the Institut de France. In April 1821 he probably was the "Saint Martin" who published the first decipherment of an inscription in the Lycian language. He later entered the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. In 1822 he was one of the founders of the Société Asiatique, and directed the publication of its journal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Testament
The New Testament (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus, as well as events relating to Christianity in the 1st century, first-century Christianity. The New Testament's background, the first division of the Christian Bible, is called the Old Testament, which is based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible; together they are regarded as Sacred Scripture by Christians. The New Testament is a collection of 27 Christianity, Christian texts written in Koine Greek by various authors, forming the second major division of the Christian Bible. It includes four Gospel, gospels, the Acts of the Apostles, epistles attributed to Paul the Apostle, Paul and other authors, and the Book of Revelation. The Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon developed gradually over the first few centuries of Christianity through a complex process of debate, rejection of Heresy, heretical texts, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is considered one of the most revered and influential authors in history. The ''Iliad'' centers on a quarrel between King Agamemnon and the warrior Achilles during the last year of the Trojan War. The ''Odyssey'' chronicles the ten-year journey of Odysseus, king of Homer's Ithaca, Ithaca, back to his home after the fall of Troy. The epics depict man's struggle, the ''Odyssey'' especially so, as Odysseus perseveres through the punishment of the gods. The poems are in Homeric Greek, also known as Epic Greek, a literary language that shows a mixture of features of the Ionic Greek, Ionic and Aeolic Greek, Aeolic dialects from different centuries; the predominant influence is Eastern Ionic. Most researchers believe that the poems w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artumpara
Artumpara, also Arttum̃para, Artembares (Persian name, *Rtambura, self-identified as "the Mede) was an Achaemenid Satrap of Lycia circa 400-370 BCE. He was involved in the Great Satraps' Revolt on the side of central Achaemenid authority in 366-360 BCE, helping to put down the rebel Datames. He is well known for his coinage. Artumpara is known to have competed for power with another man named Mithrapata.D. T. Potts, ''A Companion to the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East'' (2012), p. 912: "...c. 380–370 BC, two western Lycian dynasts named Arttumpara and Mithrapata claimed power simultaneously." It is thought he was defeated by Perikle. Coinage The portrait of Artumpara appears on his coinage, wearing the Achaemenid satrapal headdress. File:DYNASTS of LYCIA. Artumpara. Circa 400-370 BC.jpg, Coin of Artumpara, Satrap of Lycia Lycia (; Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; , ; ) was a historical region in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Payava
The Tomb of Payava is a Lycian tall rectangular free-standing barrel-vaulted stone sarcophagus, and one of the most famous tombs of Xanthos. It was built in the Achaemenid Persian Empire, for Payava, who was probably the ruler of Xanthos, Lycia (modern-day Kınık, Kaş, Turkey) at the time, in around 360 BC. The tomb was discovered in 1838 and brought to England in 1844 by the explorer Sir Charles Fellows. He described it as a 'Gothic-formed Horse Tomb'. According to Melanie Michailidis, though bearing a "Greek appearance", the Tomb of Payava, the Harpy Tomb and the Nereid Monument were built according to the main Zoroastrian criteria "by being composed of thick stone, raised on plinths off the ground, and having single windowless chambers". The tomb Payava, who is named in the inscriptions, is only known from this tomb. The tomb is a particularly fine example of a common Lycian style, carved from stone but accurately depicting a wooden structure. Three of the four t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamphylia
Pamphylia (; , ''Pamphylía'' ) was a region in the south of Anatolia, Asia Minor, between Lycia and Cilicia, extending from the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean to Mount Taurus (all in modern-day Antalya province, Turkey). It was bounded on the north by Pisidia and was therefore a country of small extent, having a coast-line of only about 120 km (75 miles) with a breadth of about 50 km (30 miles). Under the Roman administration the term Pamphylia was extended so as to include Pisidia and the whole tract up to the frontiers of Phrygia and Lycaonia, and in this wider sense it is employed by Ptolemy. Name The name ''Pamphylia'' comes from the Greek language, Greek Παμφυλία, itself from (''pamphylos''), literally "of mingled tribes or races", a compound of πᾶν (''pan''), neuter of πᾶς (''pas'') "all" + φυλή (''phylē''), "race, tribe". Herodotus derived its etymology from a Dorians, Dorian tribe, the Pamphyloi (Πάμφυλοι), who were said to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mersin
Mersin () is a large city and port on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast of Mediterranean Region, Turkey, southern Turkey. It is the provincial capital of the Mersin Province (formerly İçel). It is made up of four district governorates, each having its own municipality: Akdeniz, Mersin, Akdeniz, Mezitli, Toroslar and Yenişehir, Mersin, Yenişehir. Mersin lies on the western side of Çukurova, a geographical, economic and cultural region of Turkey. It is an important hub for Turkey's economy, with Port of Mersin, Turkey's largest seaport located here. The city hosted the 2013 Mediterranean Games. As urbanisation continues eastward, a larger metropolitan region combining Mersin with Tarsus, Mersin, Tarsus and Adana (the Adana-Mersin Metropolitan Area) is in the making with more than 3.3 million inhabitants. Çukurova International Airport (COV), 74 kilometres (46mi) from Mersin city center, is the nearest international airport. There are ferry services from Mersin to F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
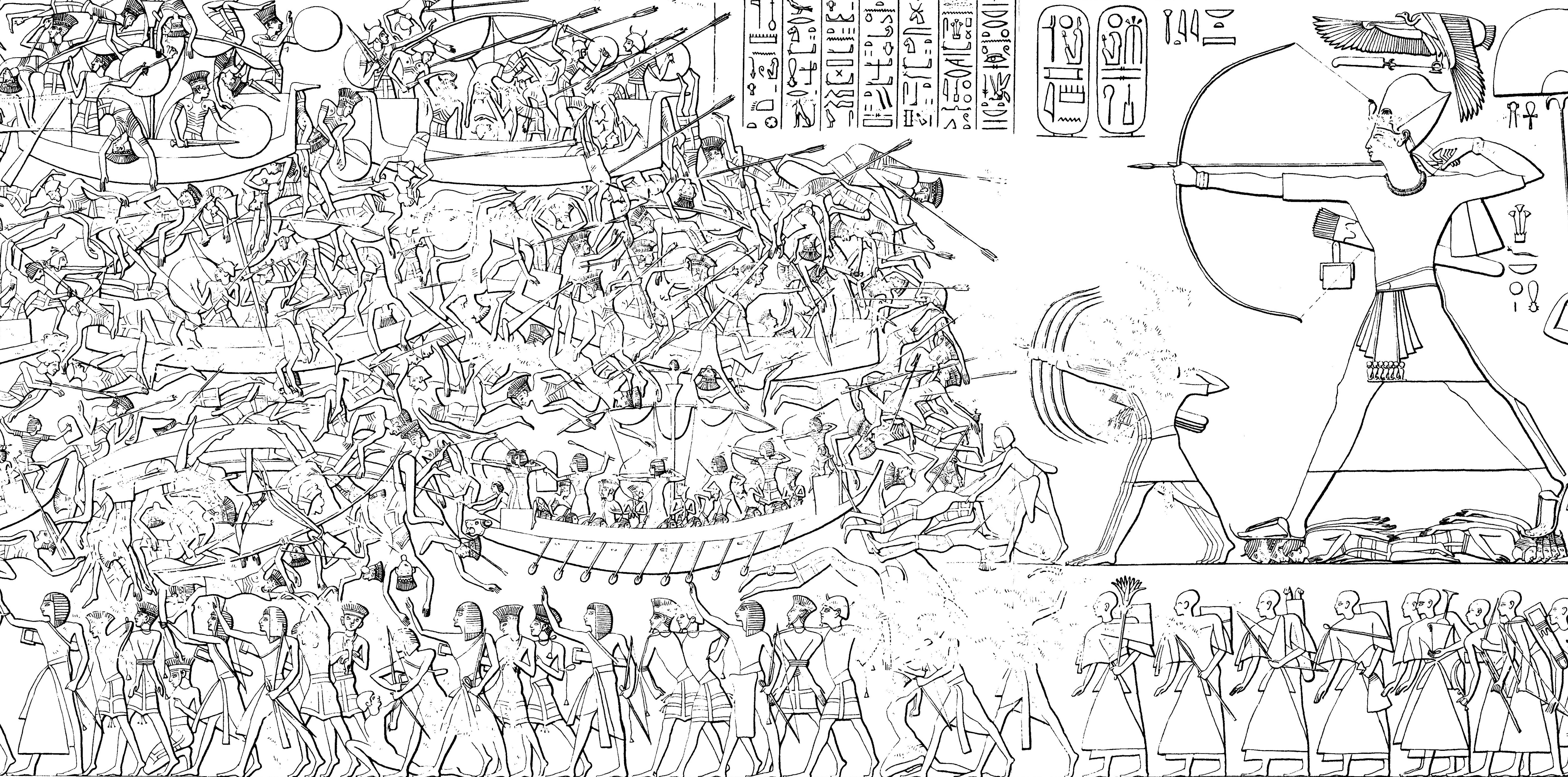
Sea Peoples
The Sea Peoples were a group of tribes hypothesized to have attacked Ancient Egypt, Egypt and other Eastern Mediterranean regions around 1200 BC during the Late Bronze Age. The hypothesis was proposed by the 19th-century Egyptology, Egyptologists Emmanuel de Rougé and Gaston Maspero, on the basis of primary sources such as the reliefs on the Mortuary Temple of Ramesses III at Medinet Habu (temple), Medinet Habu. Subsequent research developed the hypothesis further, attempting to link these sources to other Late Bronze Age evidence of migration, piracy, and destruction. While initial versions of the hypothesis regarded the Sea Peoples as a primary cause of the Late Bronze Age collapse, more recent versions generally regard them as a symptom of events which were already in motion before their purported attacks. The Sea Peoples included well-attested groups such as the Lukka, as well as others such as the Weshesh whose origins are unknown. Hypotheses regarding the origin of the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northern coast of Egypt, the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to Egypt–Israel barrier, the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to Egypt–Sudan border, the south, and Libya to Egypt–Libya border, the west; the Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital, list of cities and towns in Egypt, largest city, and leading cultural center, while Alexandria is the second-largest city and an important hub of industry and tourism. With over 109 million inhabitants, Egypt is the List of African countries by population, third-most populous country in Africa and List of countries and dependencies by population, 15th-most populated in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |