|
Lepisosteidae
Gars are an ancient group of ray-finned fish in the Family (biology), family Lepisosteidae. They comprise seven living species of fish in two genera that inhabit Fresh water, fresh, Brackish water, brackish, and occasionally marine waters of eastern North America, Central America and Cuba in the Caribbean, though extinct members of the family were more widespread. They are the only surviving members of the Ginglymodi, a clade of fish which first appeared during the Triassic period, over 240 million years ago, and are one of only two surviving groups of holosteian fish, alongside the bowfins, which have a similar distribution. Gars have elongated bodies that are heavily armored with ganoid scales, and fronted by similarly elongated jaws filled with long, sharp teeth. Gars are sometimes referred to as "garpike", but are not closely related to pike (fish), pike, which are in the fish family Esocidae. All of the gars are relatively large fish, but the alligator gar (''Atractost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepisosteus
''Lepisosteus'' (from Greek ''lepis'' (), 'scale' and ''osteon'' (), 'bone') is a genus of gars in the family Gar, Lepisosteidae. It contains four extant species, found throughout eastern and central North America. It is one of two extant gar genera alongside ''Atractosteus.'' Distribution ''Lepisosteus'' is known to be a freshwater fish. However, they do have the ability to survive in high salinity, and low oxygen water after gulping air. ''Lepisosteus'' prefers to reside in Brackish water, brackish and shallow slow-moving waters, living usually in Shoaling and schooling, schools. The habitat range of this genus ranges on the Eastern coast from the Gulf of Mexico in Florida north to Quebec City, Quebec. Habitats can be found in the Missouri River Valley, Missouri River Basin and Mississippi River System, Mississippi River drainage area, westward in the Rio Grande, Rio Grande River basin of Southern Texas and Northern Mexico. There are also populations in the Great Lakes except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atractosteus
''Atractosteus'' (from Greek ''atraktos'' (ἀτρακτὀς), 'spindle' and ''osteon'' (ὀστέον), 'bone') is a genus of gars in the family Lepisosteidae, with three extant species. It is one of two surviving gar genera alongside ''Lepisosteus''. The three surviving species are all widely separated from one another, with ''A. spatula'' being found in the south-central United States, ''A. tropicus'' in southern Mexico and Central America, and ''A. tristoechus'' in Cuba. Although generally inhabiting fresh water, they are tolerant of marine conditions. Evolution The genus first appeared during the Santonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, having diverged from ''Lepisosteus'' earlier in the Cretaceous. It quickly achieved a widespread distribution throughout the rest of the Cretaceous, being known from North America, South America and Europe. ''Atractosteus'' survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, with one articulated foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
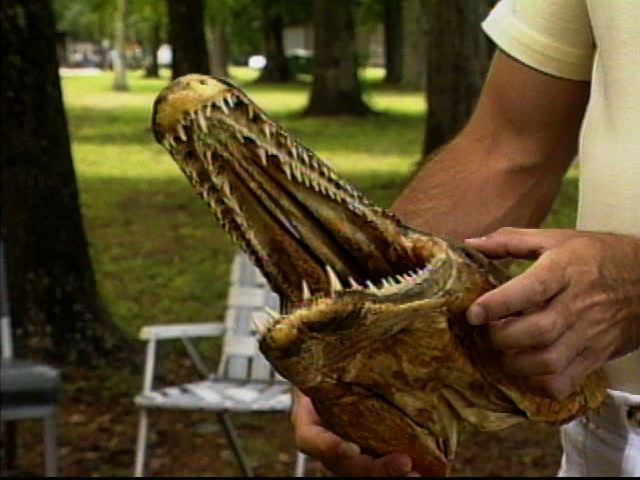
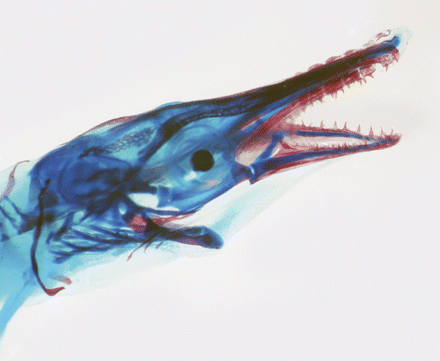
Alligator Gar
The alligator gar (''Atractosteus spatula'') is a euryhaline ray-finned fish in the clade Ginglymodi of the infraclass Holostei , being most closely related to the bowfins. It is the largest species in the gar family (biology), family (Lepisosteidae), and is among the largest freshwater fishes in North America. The fossil record traces its group's existence back to the Early Cretaceous over 100 million years ago. Gars are often referred to as "primitive fishes" or "living fossils", because they have retained some Morphological (biology), morphological characteristics of their early ancestors, such as a spiral valve intestine, which is also common to the digestive system of sharks, and the ability to breathe in both air and water. Their common name was derived from their resemblance to the American alligator, particularly their broad snouts and long, sharp teeth. It is suggested that an alligator gar can grow up to in length. The body of an alligator gar is torpedo-shaped, usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
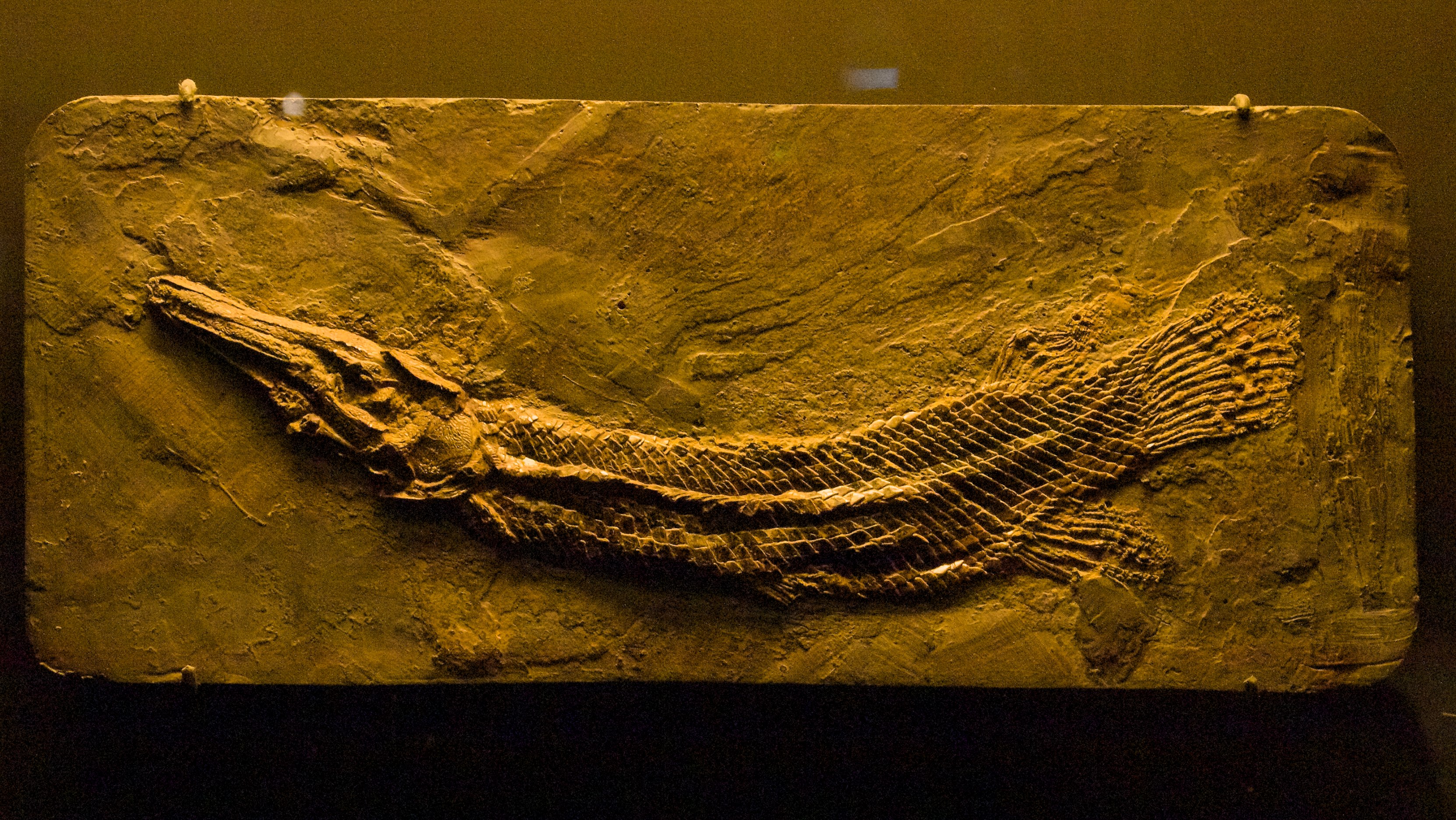
Oniichthys
''Oniichthys'' is an Extinction, extinct genus of gar in the family Lepisosteidae. It contains a single species, ''O. falipoui'', known from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) of Morocco. It is known from a few very well-preserved, near-complete specimens from the Kem Kem Group, Kem Kem Formation, where it coexisted with the famous ''Spinosaurus''. It closely resembles the modern genus ''Atractosteus'', and is generally placed as its Sister group, sister genus, a sister to ''Atractosteus'' and ''Lepisosteus'', or even as a species within ''Atractosteus'' as per Lance Grande, Grande (2010), although this latter view has been disputed based on differences in skull morphology. The genus name references the List of rulers of Ife, Ooni, divine Yoruba people, Yoruba kings, while the Binomial nomenclature, specific epithet honors Christian Falipou, who loaned one of the Type (biology), type specimens. References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q52158826, from2=Q52158831 Lepisosteidae Prehist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herreraichthys
''Herreraichthys'' is an Extinction, extinct genus of gar from the Late Cretaceous of Mexico. It contains a single species, ''H. coahuilaensis''. The genus name honors the famous Mexican scientist Alfonso L. Herrera. It is known from Santonian-aged sediments from the "Los Temporales" quarry in Coahuila. It is a long-snouted fish that appears to be more closely related to extant gar (''Atractosteus'' and ''Lepisosteus'') than to other fossil gar, and it is thus placed in the same tribe (Lepisosteini) as extant gar. Its occurrence in marine strata suggests that it may have been a fully marine species, similar to what is thought of ancestral gars and in contrast to extant gar, which are found in freshwater habitats. However, it is also possible that as with the modern alligator gar, it could temporarily survive in the sea. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q21347414 Lepisosteidae Prehistoric ray-finned fish genera Late Cretaceous fish of North America Late Cretaceous bony fish Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spotted Gar
The spotted gar (''Lepisosteus oculatus'') is a freshwater fish native to North America that has an abundance of dark spots on its head, fins, and dart-like body. Spotted gar have an elongated mouth with many needle-like teeth to catch other fish and crustaceans. It is one of the smallest of the seven species of gar found in North America, growing 2–3 ft (0.61–0.91 m) in length and weighing 4–6 lb (1.8–2.7 kg) typically. Gars have diamond-shaped, thick, enamel (ganoid) scales. The name ''Lepisosteus'' is Greek for "bony scale". Gars are almost never eaten in the central and northern United States. They have high levels of mercury and are considered a cancer risk. Distribution and habitat The spotted gar is native to North America and its current range is from southern Ontario to the west from the Devils River in Texas east to the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico and southeast to the lower Apalachicola River in Florida. The gar population is small in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masillosteus
''Masillosteus'' ("bony one from Messel") is an extinct genus of gar that inhabited western North America and Europe during the Eocene. It is known from two species, each from a famous freshwater lagerstätte: ''M. kelleri'' from the Messel pit in the Messel Formation of Germany, and ''M. janeae'' from Fossil Butte in the Green River Formation of Wyoming. They are known from only a few specimens from both localities, and may have not been permanent inhabitants of the fossil lakes where they were preserved. ''Masillosteus'' was an atypical gar with a short, broad snout and molariform teeth likely adapted to crushing crustaceans and other hard-shelled invertebrate prey. It shares the short, broad snout with the extinct gar '' Cuneatus'', which inhabited western North America during the same time period; both genera are classified in the tribe Cuneatini. Although fossils of both genera are known only from the Paleogene, it is assumed that both diverged from one another during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holostei
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by the single living genus, '' Amia'' with two species, the bowfins (''Amia calva'' and '' Amia ocellicauda''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Lepisosteidae), represented by seven living species in two genera ('' Atractosteus'', '' Lepisosteus''). The earliest members of the clade, which are putative " semionotiforms" such as '' Acentrophorus'' and '' Archaeolepidotus'', are known from the Middle to Late Permian and are among the earliest known neopterygians. Holostei was thought to be regarded as paraphyletic. However, a recent study provided evidence that the Holostei are the closest living relatives of the Teleostei, both within the Neopterygii. This was found from the morphology of the Holostei, for example presence of a paired vomer. Holosteans are closer to teleosts than are the chondrosteans, the other group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Needlefish
Needlefish (family Belonidae) or long toms are piscivorous fishes primarily associated with very shallow marine habitats or the surface of the open sea. Some genera include species found in marine, brackish, and freshwater environments (e.g., '' Strongylura''), while a few genera are confined to freshwater rivers and streams, including '' Belonion'', '' Potamorrhaphis'', and '' Xenentodon''. Needlefish closely resemble North American freshwater gars (family Lepisosteidae) in being elongated and having long, narrow jaws filled with sharp teeth, and some species of needlefishes are referred to as gars or garfish despite being only distantly related to the true gars. In fact, the name " garfish" was originally used for the needlefish '' Belone belone'' in Europe and only later applied to the North American fishes by European settlers during the 18th century. Description Needlefish are slender, ranging from in length. They have a single dorsal fin, placed far back on the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ginglymodi
Ginglymodi is a clade of ray-finned fish containing modern-day gars (Lepisosteidae) and their extinct relatives (including the family (biology), family Lepidotidae) in the Order (biology), order Lepisosteiformes, the extinct orders Semionotiformes and Kyphosichthyiformes, and various other extinct taxa. Ginglymodi is one of the two major subgroups of the infraclass Holostei, the other one being Halecomorphi, which contains the bowfin and eyespot bowfin and their fossil relatives. Fossil record The fossil record of ginglymodians goes back at least to the Anisian stage (geology), stage of the Triassic period (geology), period, over 240 million years ago. ''Eosemionotus'' is one of the earliest ginglymodians. ''Acentrophorus'', another taxon from the Middle and Late Permian, and ''Paracentrophorus'' from the Early Triassic epoch (geology), epoch, could be even earlier members of the group. Ginglymodi was biodiversity, diverse and widespread during the Mesozoic era (geology), era, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandemarinus
''Grandemarinus'' is an extinct genus of gar from the Late Cretaceous of Morocco. It contains a single species, ''G. gherisensis''. The genus name honors evolutionary biologist Lance Grande and references the species' apparent marine nature, while the specific epithet references Oued Gheris, a wadi near the type locality. It is known from three specimens, one of which is fully preserved, from the Turonian Akrabou Formation, one of several formations comprising the Kem Kem Group. The complete specimen was found in the house of a local collector, but had been sold to a private collector before it could be acquired to science. It was recovered later when it was found being sold on an internet forum. The Akrabou Formation preserves a largely pelagic ecosystem, indicating that ''Grandemarinus'' was an entirely marine species, in contrast to extant gar, which are found in mostly freshwater and brackish ecosystems, but similar to what is thought to have been the ancestral condition for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneatus
''Cuneatus'' is an extinct genus of gar that inhabited western North America during the early Paleogene. As the genus name suggests, they are distinguishable from modern gar by their cuneate (wedge-shaped) heads, with a significantly shortened snout. Three species are known: ''C. cuneatus'', ''C. maximus'', and ''C. wileyi''. Taxonomy They are thought to belong to the Cuneatini, a now-extinct tribe of short-snouted gar. The genus ''Masillosteus'' is also sometimes placed in this tribe, but other studies have found ''Cuneatus'' to be more closely related to extant gars than to ''Masillosteus''. The tribe is thought to have originated in the Cretaceous, despite being only known from Paleogene fossils. Species in ''Cuneatus'' are known to have coexisted with species belonging to both extant gar genera (''Atractosteus'' and ''Lepisosteus'') in known localities. The type species of the genus was described as "''Lepisosteus''" ''cuneatus'' by Edward Drinker Cope from the Green Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |